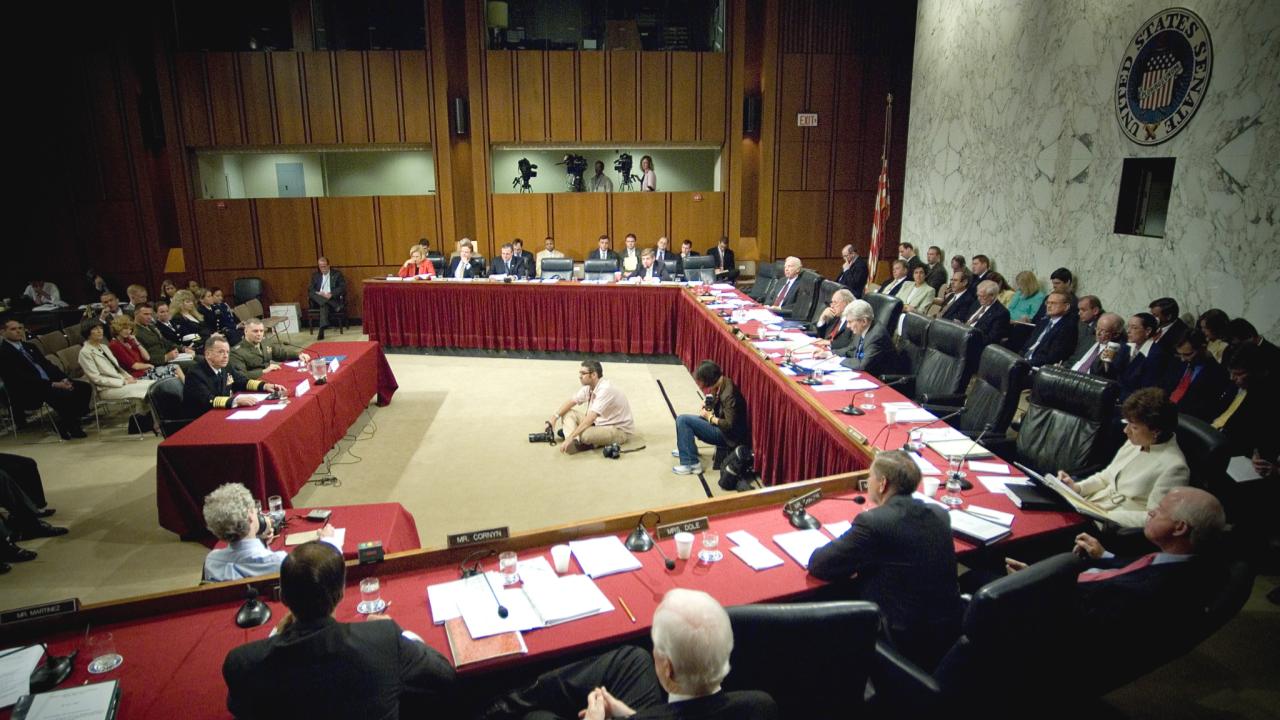
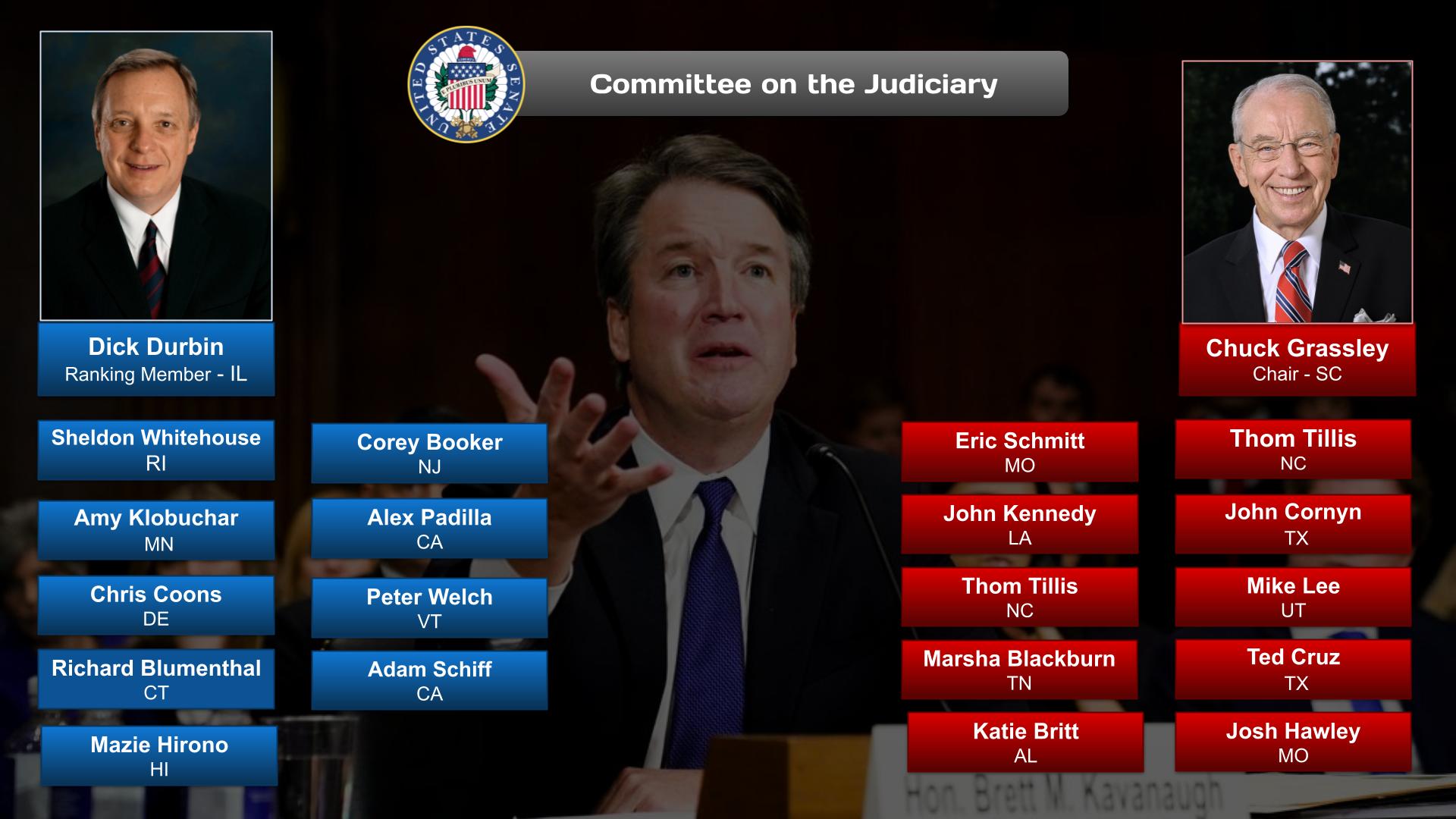
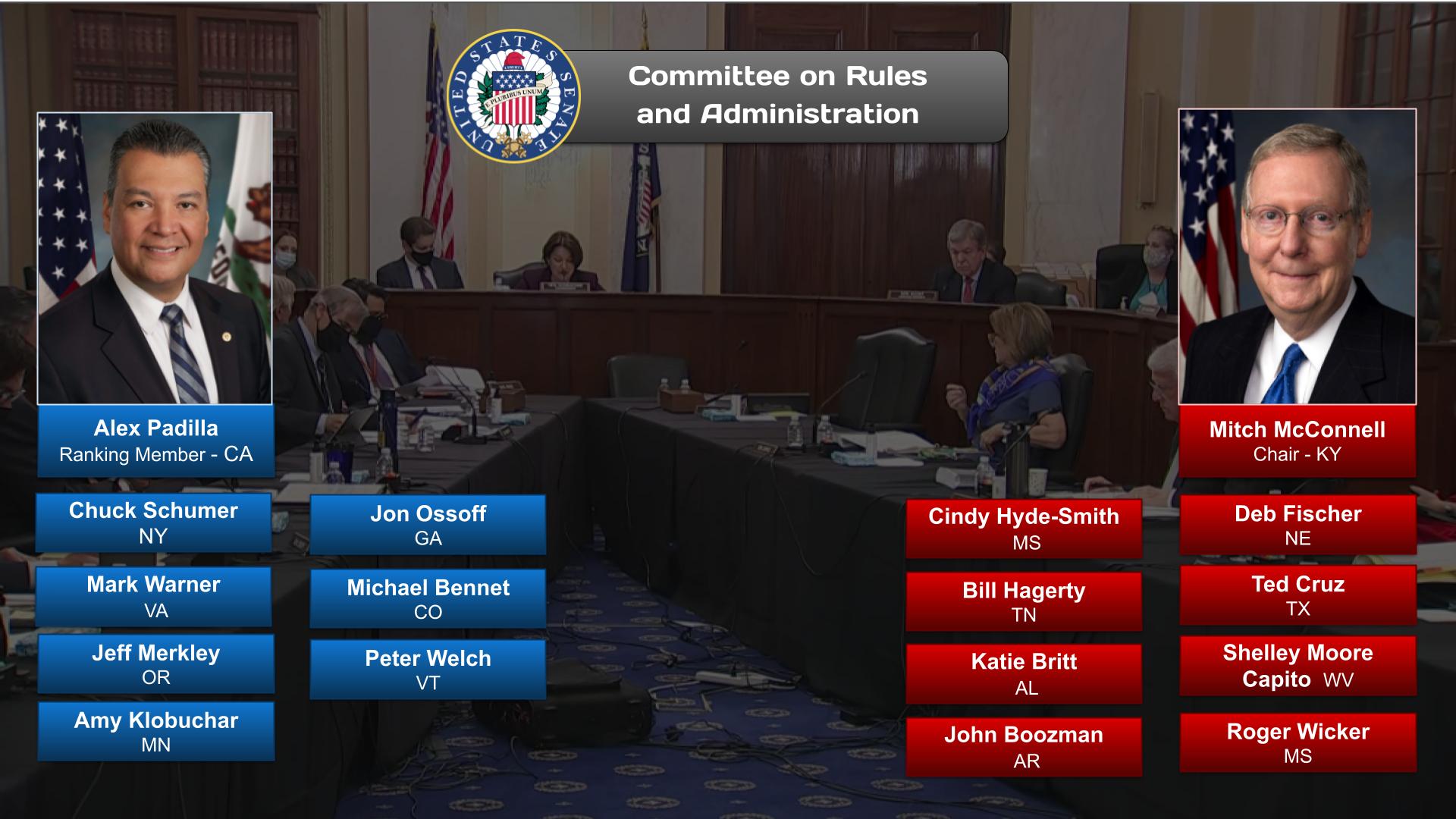
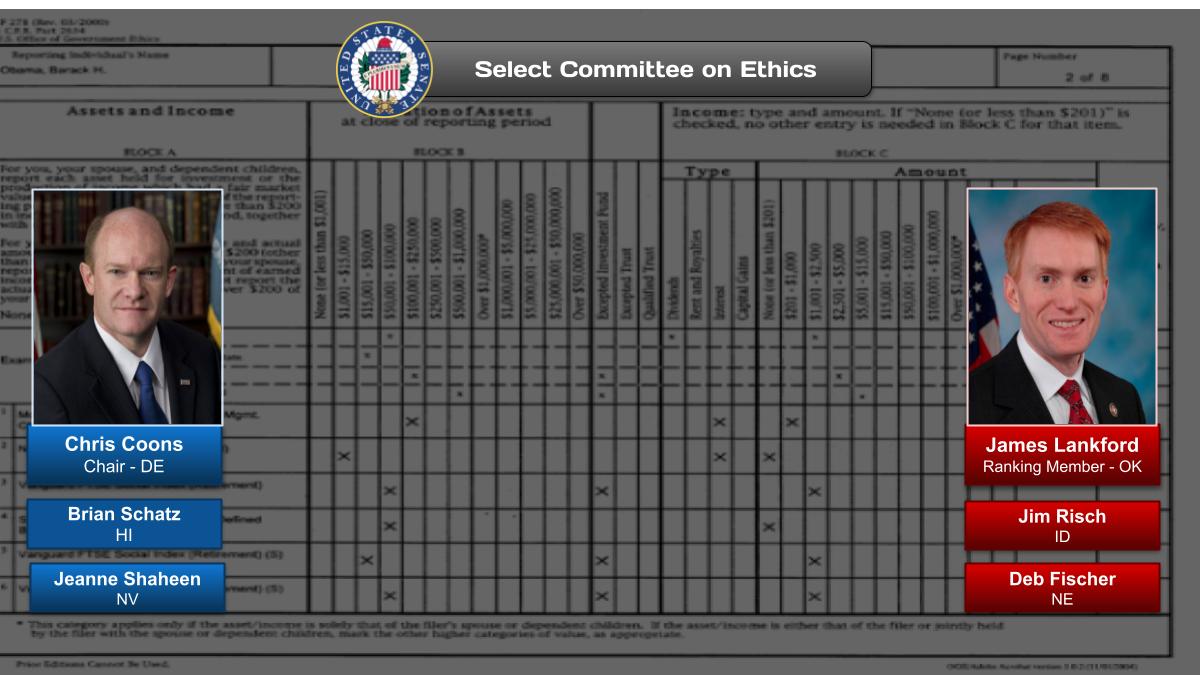
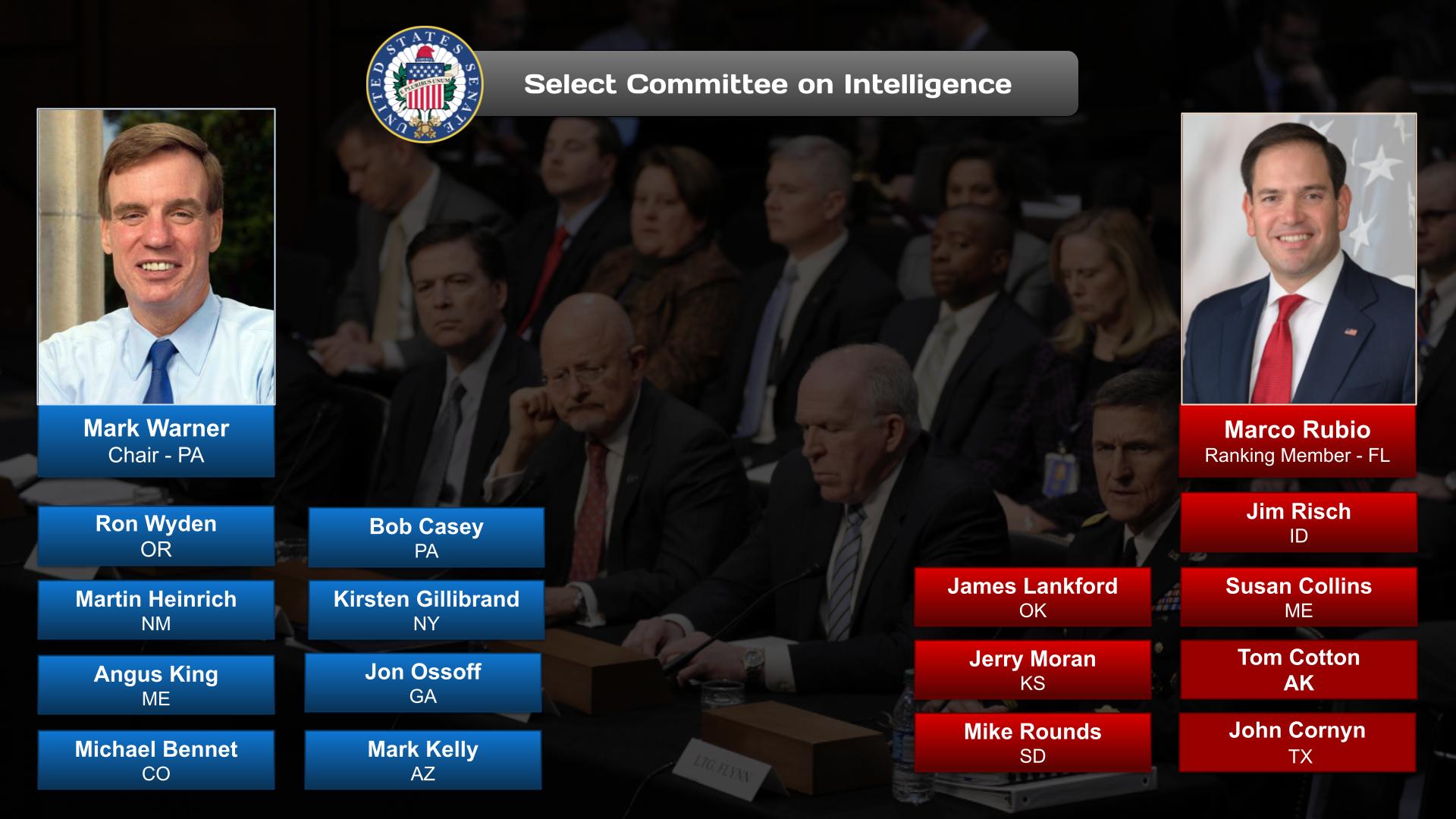
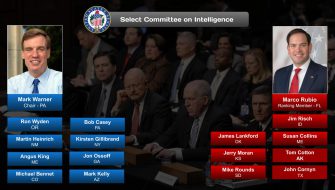
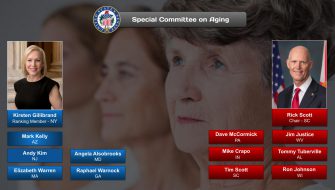
Today the Senate operates with 21 committees (16 standing and 5 select). These select committees, however, are permanent in nature and are treated as standing committees under Senate rules.
Committees are essential to the effective operation of the Senate. Through investigations and hearings, committees gather information on national and international problems within their jurisdiction in order to draft, consider, and recommend legislation to the full membership of the Senate. Only a small percentage of bills considered by committees reach the Senate floor. They evaluate presidential nominees for executive and judicial posts and provide oversight of federal government operations.
The Senate is currently home to 24 committees: there are 16 standing committees, four special or select committees, and four joint committees. Standing committees are permanent bodies with specific responsibilities and jurisdictions that are defined in the Senate’s rules. Although some committees are almost as old as the Senate itself, the Senate periodically updates the names and jurisdictions of standing committees to address the issues of an evolving nation. The four special or select committees were initially created by a Senate resolution for specific purposes and are now regarded as permanent. The Senate has authorized other select investigating committees throughout its history that have expired after submitting a final report. The four joint committees, made up of senators and representatives, provide administrative coordination between the House and Senate and conduct studies for the benefit of both houses.
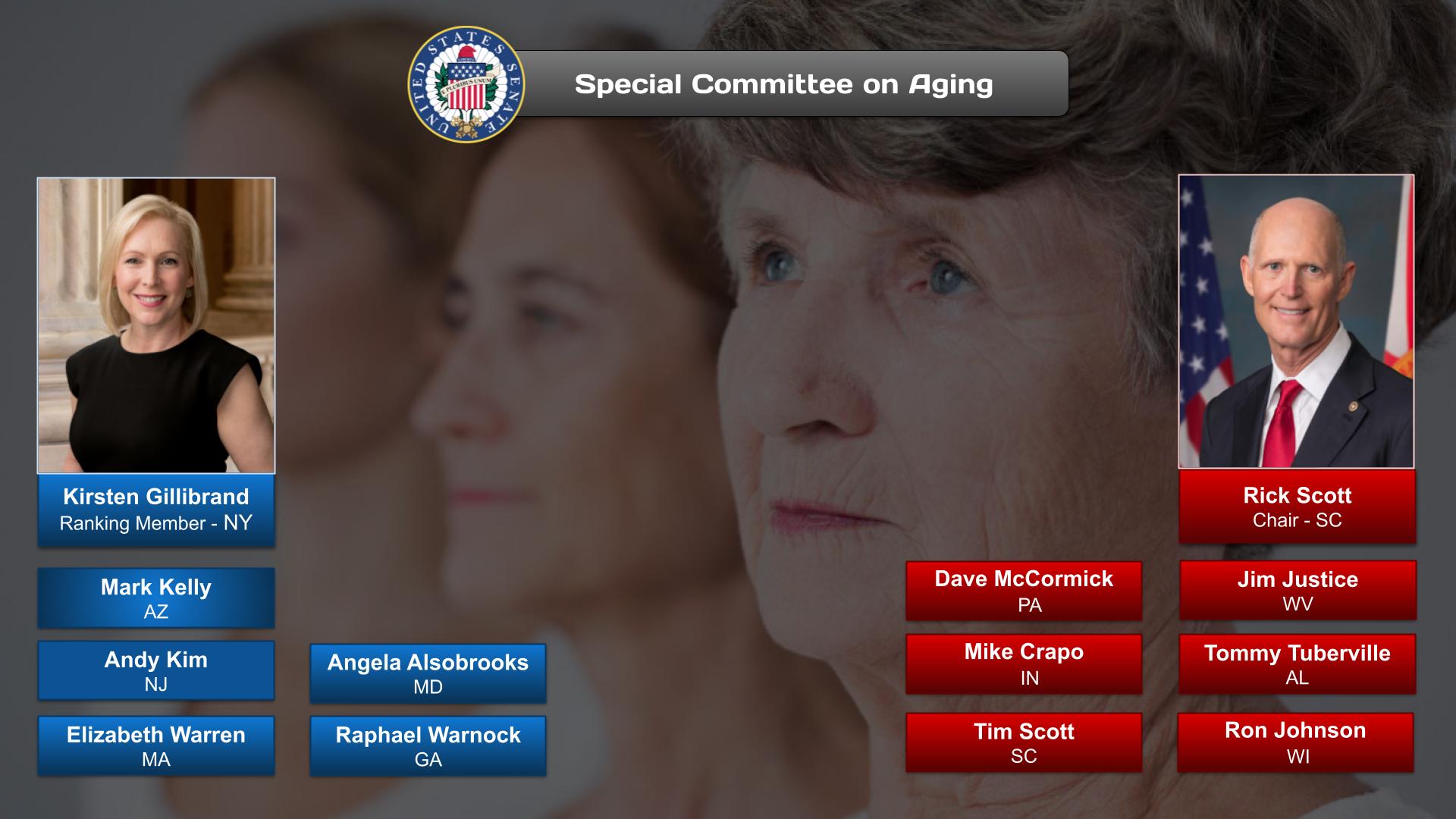
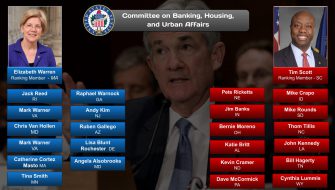
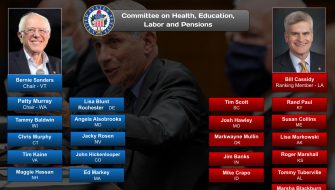
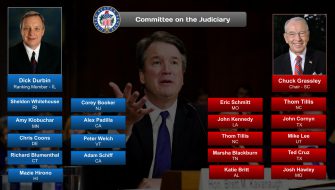
For a complete list of Senate committees and their current membership, click here.
Source: Senate website
Summary
Today the Senate operates with 21 committees (16 standing and 5 select). These select committees, however, are permanent in nature and are treated as standing committees under Senate rules.
Committees are essential to the effective operation of the Senate. Through investigations and hearings, committees gather information on national and international problems within their jurisdiction in order to draft, consider, and recommend legislation to the full membership of the Senate. Only a small percentage of bills considered by committees reach the Senate floor. They evaluate presidential nominees for executive and judicial posts and provide oversight of federal government operations.
The Senate is currently home to 24 committees: there are 16 standing committees, four special or select committees, and four joint committees. Standing committees are permanent bodies with specific responsibilities and jurisdictions that are defined in the Senate’s rules. Although some committees are almost as old as the Senate itself, the Senate periodically updates the names and jurisdictions of standing committees to address the issues of an evolving nation. The four special or select committees were initially created by a Senate resolution for specific purposes and are now regarded as permanent. The Senate has authorized other select investigating committees throughout its history that have expired after submitting a final report. The four joint committees, made up of senators and representatives, provide administrative coordination between the House and Senate and conduct studies for the benefit of both houses.
For a complete list of Senate committees and their current membership, click here.
Source: Senate website
About
See also: List of current United States Senate committees.
The first Senate committee was established April 7, 1789, to draw up Senate rules of procedure. In those early days, the Senate operated with temporary select committees, which were responsive to the entire Senate, with the full Senate selecting their jurisdiction and membership. This system provided a great deal of flexibility, as if one committee proved unresponsive, another could be established in its place. The Senate could also forgo committee referral for actions on legislation or presidential nominations. These early committees generally consisted of three members for routine business and five members for more important issues. The largest committee established during the 1st Congress had eleven members, and was created to determine salaries of the president and vice president. Also in the first session, the entire membership of the Senate was divided into two large committees, with half the senators on the committee to prepare legislation establishing the federal judiciary and the other half on the committee to define the punishment of crimes against the United States.
This system proved ineffective, so in 1816 the Senate adopted a formal system of 11 standing committees with five members each. Three of those committees, the Finance, Foreign Relations and the Judiciary Committees exist largely unchanged today, while the duties of the others have evolved into successor committees. With the advent of this new system, committees are able to handle long-term studies and investigations, in addition to regular legislative duties. According to the Senate Historical Office, “the significance of the change from temporary to permanent committees was perhaps little realized at the time.” With the growing responsibilities of the Senate, the committees gradually grew to be the key policy-making bodies of the Senate, instead of merely technical aids to the chamber.
Governor La Follette of Wisconsin addressing the Chautauqua assembly in Decatur, Illinois in 1905.
By 1906, the Senate maintained 66 standing and select committees—eight more committees than members of the majority party. The large number of committees and the manner of assigning their chairmanships suggests that many of them existed solely to provide office space in those days before the Senate acquired its first permanent office building, the Russell Senate Office Building. There were so many committees that freshman Senator Robert La Follette of Wisconsin was assigned chairmanship of the Committee to Investigate the Condition of the Potomac River Front at Washington. According to La Follette, he “had immediate visions of cleaning up the whole Potomac River front. Then [he] found that in all its history, the committee had never had a bill referred to it for consideration, and had never held a meeting.” In 1920, the Congressional Directory listed nearly 80 committees, including the Committee on the Disposition of Useless Papers in the Executive Departments. By May 27, 1920, the Russell Senate Office Building had opened, and with all Senate members assigned private office space, the Senate quietly abolished 42 committees.
Web Links