Summary
Healthcare is a broad term encompassing the diagnosis, treatment, and prevention of disease, as well as the maintenance of health. It is an essential component of any society, providing individuals with the tools and resources to live healthy, productive lives.
- There are many issues related to Healthcare that Congress is looking to address with legislation. In the ‘About’ section of this post is an overview of the issues and potential solutions, party positions, and web links. Other sections have information on relevant committees, chairs, & caucuses; departments & agencies; and the judiciary, nonpartisan & partisan organizations, and a wikipedia entry.
- To participate in ongoing forums, ask the post’s curators questions, and make suggestions, scroll to the ‘Discuss’ section at the bottom of each post or select the “comment” icon.
The Healthcare category has related posts and three posts on issues of particular focus: Infectious Diseases, Addictions, and Health Promotion.
CNBC – 28/02/2022 (11:19)
Health-care spending is consistently rising around the world, but the United States is the worst performer when it comes to controlling costs. A lack of universal coverage in the U.S. and a fragmented and heavily commercialized system leads to rising costs and excessive spending. Watch the video to learn more about why health-care costs are rising in the U.S. more than anywhere else and how that can be stopped.
OnAir Post: Healthcare
News
Latest
PBS NewsHour – January 1, 2024 (07:00)
As recently as the early 80s, about three of every four doctors in the U.S. worked for themselves, owning small clinics. Today, some 75 percent of physicians are employees of hospital systems or large corporate entities. Some worry the trend is leading to diminished quality of care and is one reason doctors at a large Midwestern health provider decided to unionize. Fred de Sam Lazaro reports.
Spotlight
PBS NewsHour – January 1, 2024 (07:00)
As recently as the early 80s, about three of every four doctors in the U.S. worked for themselves, owning small clinics. Today, some 75 percent of physicians are employees of hospital systems or large corporate entities. Some worry the trend is leading to diminished quality of care and is one reason doctors at a large Midwestern health provider decided to unionize. Fred de Sam Lazaro reports.
Videos
PBS NewsHour – January 1, 2024 (07:00)
As recently as the early 80s, about three of every four doctors in the U.S. worked for themselves, owning small clinics. Today, some 75 percent of physicians are employees of hospital systems or large corporate entities. Some worry the trend is leading to diminished quality of care and is one reason doctors at a large Midwestern health provider decided to unionize. Fred de Sam Lazaro reports.
About
Issues & Potential Legislative Solutions
1. Rising Healthcare Costs
- Issue: Escalating costs of prescription drugs, hospital stays, and other medical services.
- Solution: Implement price transparency measures, negotiate drug prices with pharmaceutical companies, and expand affordable healthcare options.
2. Access to Healthcare
- Issue: Unequal access to quality healthcare, especially for low-income and rural populations.
- Solution: Expand Medicaid eligibility, provide subsidies for private health insurance, and increase funding for community health centers.
3. Prescription Drug Costs
- Issue: High prices of prescription drugs, especially for essential medications.
- Solution: Implement price controls, allow Medicare to negotiate drug prices, and encourage generic drug development.
4. Chronic Disease Management
- Issue: Rising prevalence of chronic diseases like diabetes, heart disease, and obesity.
- Solution: Promote preventive care, invest in public health programs, and incentivize healthy lifestyle choices.
5. Mental Health Services
- Issue: Lack of access to mental health services, especially in rural areas.
- Solution: Increase funding for mental health programs, expand telehealth services, and reduce stigma associated with mental health conditions.
6. Aging Population
- Issue: Increasing healthcare costs associated with an aging population.
- Solution: Implement long-term care insurance, expand home-based care options, and promote healthy aging.
7. Healthcare Workforce Shortage
- Issue: Lack of healthcare professionals, particularly in rural areas and specialized fields.
- Solution: Increase funding for medical education, offer loan forgiveness programs, and promote immigration of healthcare workers.
8. Healthcare Disparities
- Issue: Racial and ethnic disparities in healthcare outcomes.
- Solution: Address social determinants of health, implement culturally competent care, and invest in community health programs.
9. Healthcare Fraud
- Issue: Healthcare fraud and abuse, leading to higher costs and reduced access to care.
- Solution: Strengthen enforcement of anti-fraud laws, invest in fraud detection technology, and promote transparency in healthcare billing.
10. Technology in Healthcare
- Issue: Balancing the benefits and risks of technology in healthcare, such as electronic health records and telemedicine.
- Solution: Develop standardized interoperability standards, invest in cybersecurity, and ensure equitable access to technology.
Party positions
Republican Party platform: In 2020, the Republican Party decided not to write a platform for that presidential election cycle, instead simply expressing its support for Donald Trump’s agenda.
- Go here to see a PDF on 2016 Republican Platform.
- Go to this Wikipedia entry to read “Political positions of Donald Trump”.
Democratic Party platform:
- Go here to read the Democratic Party’s plaform on the DNC’s website especially the section on Protecting Americans and recovering from the COVID-19 pandemic”
- Go to this Wikipedia entry to read the”Political positions of the Democratic Party”
Republican Party
- Support free-market healthcare: Republicans generally favor reducing government involvement in healthcare and allowing the private sector to compete more freely. They believe this will lead to lower costs and more innovation.
- Oppose government-run healthcare: Republicans are opposed to government-run healthcare programs, such as Medicare for All, which they argue would stifle competition and lead to higher costs and lower quality of care.
- Support patient choice: Republicans believe that patients should have more choice and control over their healthcare decisions. They support measures such as allowing people to purchase health insurance across state lines and expanding the use of health savings accounts.
- Promote personal responsibility: Republicans believe that individuals are responsible for their own health and should not rely on government programs to provide them with healthcare. They support measures such as requiring people to work or have health insurance in order to receive government assistance.
Democratic Party
- Support universal healthcare: Democrats generally favor expanding access to healthcare and providing affordable coverage to all Americans. They support programs such as Medicare for All, which would create a single-payer healthcare system that covers all Americans.
- Regulate the healthcare industry: Democrats believe that the healthcare industry should be regulated to protect consumers and ensure that everyone has access to quality, affordable care. They support measures such as price controls on prescription drugs and expanding Medicaid coverage.
- Invest in public health: Democrats believe that the government should invest in public health programs to improve the health of all Americans. They support programs such as expanding access to mental health services and promoting healthy eating and exercise.
- Address social determinants of health: Democrats believe that addressing social factors that affect health, such as poverty, housing insecurity, and lack of education, is essential to improving the health of all Americans. They support programs such as expanding access to affordable housing and early childhood education.
Other Parties
- Libertarian Party: The Libertarian Party supports a free-market healthcare system with minimal government involvement. They believe that individuals should be free to choose their own healthcare plans and providers, and that the government should not interfere with the doctor-patient relationship.
- Green Party: The Green Party supports a single-payer healthcare system that provides affordable coverage to all Americans. They believe that healthcare is a right, not a privilege, and that everyone should have access to quality care regardless of their ability to pay.
- Constitution Party: The Constitution Party supports a free-market healthcare system with limited government involvement. They believe that the government should not be involved in healthcare at all, and that individuals should be free to choose their own healthcare plans and providers.
Websites
Government Agencies
- Centers for Medicare & Medicaid Services (CMS): https://www.cms.gov/
- National Institutes of Health (NIH): https://www.nih.gov/
- U.S. Department of Health and Human Services (HHS): https://www.hhs.gov/
- Food and Drug Administration (FDA): https://www.fda.gov/
Healthcare Organizations
- American Medical Association (AMA): https://www.ama-assn.org/
- American Hospital Association (AHA): https://www.aha.org/
- American Health Insurance Plans (AHIP): https://www.ahip.org/
- Kaiser Family Foundation (KFF): https://www.kff.org/
Healthcare News and Information
- HealthDay: https://healthday.com/
- Healthline: https://www.healthline.com/
- Medical News Today: https://www.medicalnewstoday.com/
- Stat: https://www.statnews.com/
Healthcare Policy and Research
- Kaiser Family Foundation Health Tracking Poll: https://www.kff.org/health-tracking-poll/
- Commonwealth Fund: https://www.commonwealthfund.org/
- RAND Corporation: https://www.rand.org/health/
- Urban Institute: https://www.urban.org/research/topics/health-policy
Patient Advocacy and Support
- National Patient Advocate Foundation: https://www.patient-advocate.org/
- Patient Rights Advocate: https://www.patientadvocate.org/
- Healthcare Alliance for Patient Safety: https://www.patientsafetyalliance.org/
- CancerCare: https://www.cancercare.org/
Other Healthcare Resources
- HealthCare.gov (for health insurance information): https://www.healthcare.gov/
- Medicare.gov (for seniors and people with disabilities): https://www.medicare.gov/
- Medicaid.gov (for low-income individuals and families): https://www.medicaid.gov/
- National Library of Medicine (NLM) (for health information and research): https://www.nlm.nih.gov/
Departments & Agencies
Departments
Source: Google Search + Gemini + onAir curation
Federal Departments:
- Department of Health and Human Services (HHS)
- Oversees a wide range of health programs, including Medicare, Medicaid, and public health initiatives
- Centers for Medicare & Medicaid Services (CMS)
- Part of HHS, administers Medicare and Medicaid programs
- Food and Drug Administration (FDA)
- Regulates food, drugs, medical devices, and cosmetics
- National Institutes of Health (NIH)
- Conducts and supports medical research
Other Agencies and Departments:
- Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC)
- Part of HHS, focuses on disease prevention and control
- Health Resources and Services Administration (HRSA)
- Part of HHS, provides healthcare services to underserved populations
- Substance Abuse and Mental Health Services Administration (SAMHSA)
- Part of HHS, addresses substance abuse and mental health issues
- Social Security Administration (SSA)
- Provides income and disability benefits to seniors, disabled individuals, and their dependents
- Department of Veterans Affairs (VA)
- Provides healthcare and other services to veterans
- Department of Defense (DoD)
- Provides healthcare services to active-duty military members and their families
- Congress
- Enacts legislation related to healthcare and appropriates funding for healthcare programs
Agencies
Source: Google Search + Gemini + onAir curation
Federal Agencies
- Centers for Medicare & Medicaid Services (CMS): Regulates Medicare and Medicaid programs, ensures healthcare quality, and promotes healthcare innovation.
- Food and Drug Administration (FDA): Regulates drugs, medical devices, and biological products to ensure safety and effectiveness.
- National Institutes of Health (NIH): Conducts medical research and provides funding to support biomedical research.
- Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC): Protects the public’s health through disease prevention and control measures.
- Agency for Healthcare Research and Quality (AHRQ): Conducts research on healthcare quality and patient safety, and disseminates findings to healthcare providers and consumers.
Independent Agencies
- Medicare Payment Advisory Commission (MedPAC): Advises Congress on Medicare payment policies and provides recommendations to improve program sustainability.
- Patient-Centered Outcomes Research Institute (PCORI): Funds and conducts research on patient-centered outcomes and comparative effectiveness of healthcare interventions.
Departmental Agencies
- Health Resources and Services Administration (HRSA): Provides grants and technical assistance to support healthcare providers serving underserved populations and communities.
- National Cancer Institute (NCI): Coordinates the nation’s cancer research efforts and provides support to cancer patients and survivors.
- Substance Abuse and Mental Health Services Administration (SAMHSA): Provides funding and support for substance use disorder and mental health treatment programs.
Committees & Caucuses
Committees
Source: Google Search + Gemini + onAir curation
House of Representatives
- Energy and Commerce Committee, Subcommittee on Health
- Appropriations Committee, Subcommittee on Labor, Health and Human Services, Education, and Related Agencies
- Ways and Means Committee, Subcommittee on Health
- Education and Labor Committee, Subcommittee on Health, Employment, Labor, and Pensions
Senate
- Health, Education, Labor, and Pensions (HELP) Committee
- Appropriations Committee, Subcommittee on Labor, Health and Human Services, Education, and Related Agencies
- Finance Committee, Subcommittee on Health Care
- Judiciary Committee, Subcommittee on Antitrust, Competition Policy and Consumer Rights (for issues related to healthcare competition and pricing)
Joint Committees
- Joint Economic Committee, Subcommittee on Fiscal and Intergovernmental Policy (for examining macroeconomic and budget issues related to healthcare)
- Joint Select Committee on Deficit Reduction (for addressing healthcare costs as part of deficit reduction efforts)
Other Notable Committees
- House Rules Committee (for setting rules for consideration of healthcare legislation)
- Senate Majority Leader’s Office (for coordinating healthcare policy and scheduling legislation)
- House Minority Leader’s Office (for providing input and opposition to healthcare policies)
Caucuses
Source: Google Search + Gemini + onAir curation
Congressional Caucuses on US Healthcare Issues:
1. Congressional Caucus on Black Health
- Focus: Addressing health disparities faced by African Americans
2. Congressional Caucus on Cancer
- Focus: Fighting cancer through research, education, and advocacy
3. Congressional Caucus on Childhood Cancer
- Focus: Improving outcomes for children with cancer
4. Congressional Diabetes Caucus
- Focus: Supporting those living with diabetes and preventing its development
5. Congressional Glaucoma Caucus
- Focus: Raising awareness and promoting prevention of glaucoma
6. Congressional HIV/AIDS Caucus
- Focus: Combating the HIV/AIDS epidemic both domestically and globally
7. Congressional Kidney Caucus
- Focus: Advocating for policies that protect and improve the lives of those affected by kidney disease
8. Congressional Mental Health Caucus
- Focus: Ensuring accessible and affordable mental health care for all
9. Congressional Rural Health Caucus
- Focus: Improving access to healthcare for rural communities
10. Congressional Sickle Cell Caucus
- Focus: Addressing the needs and concerns of those affected by sickle cell disease
11. Congressional Task Force on Alzheimer’s Disease
- Focus: Advancing research, care, and support for Alzheimer’s disease
12. Congressional Vaccination Caucus
- Focus: Promoting vaccination as a public health priority
13. House Democratic Health Forum
- Focus: Advancing healthcare policies that prioritize equity, affordability, and accessibility
14. Senate Democrats’ Health Care Task Force
- Focus: Developing and advocating for healthcare legislation that aligns with Democratic values
15. Senate Republican Health Caucus
- Focus: Promoting conservative healthcare policies that emphasize market competition and patient choice
More Information
Judiciary
Source: Google Search + Bard AI + onAir curation
Judiciary and Healthcare: A Complex Interplay
The judiciary plays a pivotal role in shaping healthcare policy and practice. Through its rulings, the judiciary can significantly influence the accessibility, affordability, and quality of healthcare services.
Key Areas of Influence:
- Healthcare Law Interpretation: The judiciary interprets laws related to healthcare, such as the Affordable Care Act (ACA), Medicaid, and Medicare. These interpretations can determine the scope and applicability of these laws, affecting millions of people.
- Constitutional Rights: The judiciary often addresses constitutional challenges related to healthcare, such as the right to abortion, the right to access medical treatments, and the right to privacy in medical records.
- Medical Malpractice: The judiciary adjudicates medical malpractice cases, which can have a significant impact on healthcare providers, insurers, and patients. These cases can lead to changes in medical practices and standards of care.
- Healthcare Reform: The judiciary can play a role in shaping healthcare reform efforts by ruling on the constitutionality of new laws or regulations. For example, the Supreme Court’s ruling on the ACA upheld the law’s individual mandate and Medicaid expansion provisions.
- Drug and Medical Device Regulation: The judiciary can influence the regulation of drugs and medical devices by reviewing decisions made by regulatory agencies, such as the FDA.
Challenges and Considerations:
- Political Influence: The judiciary can be influenced by political factors, which can sometimes lead to decisions that are not based solely on legal principles.
- Lack of Medical Expertise: While judges are trained in law, they may not have the medical expertise necessary to fully understand complex healthcare issues. This can sometimes lead to decisions that are not in the best interests of patients.
- Cost and Accessibility: Judicial decisions can have a significant impact on the cost and accessibility of healthcare. For example, rulings that increase the liability of healthcare providers can lead to higher insurance premiums and reduced access to care.
In conclusion, the judiciary plays a vital role in shaping healthcare policy and practice. Its decisions can have far-reaching consequences for individuals, healthcare providers, and the healthcare system as a whole. Understanding the relationship between the judiciary and healthcare is essential for policymakers, healthcare professionals, and the public.
Nonpartisan Organizations
Source: Google Search + Gemini + onAir curation
Nonprofit Organizations:
- Kaiser Family Foundation (KFF): Conducts health policy analysis and surveys on topics such as health insurance, healthcare costs, and healthcare access.
- Commonwealth Fund: A health policy research foundation that focuses on improving healthcare quality and equity.
- RAND Corporation: A nonpartisan research organization that provides analysis and policy recommendations on a wide range of healthcare issues, including healthcare access, quality, and costs.
- National Committee for Quality Assurance (NCQA): A nonpartisan organization that sets standards for healthcare quality and accredits healthcare organizations.
- Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC): A federal agency that provides information and guidance on public health issues, including healthcare.
Think Tanks:
- Brookings Institution: A nonpartisan think tank that conducts research on a variety of healthcare topics, including healthcare policy, health economics, and healthcare technology.
- Urban Institute: A nonpartisan think tank that focuses on economic and social policy, including healthcare.
- Center for American Progress (CAP): A progressive think tank that advocates for healthcare policies that improve access, affordability, and quality.
- American Enterprise Institute (AEI): A conservative think tank that advocates for free-market solutions to healthcare challenges.
- Manhattan Institute for Policy Research: A conservative think tank that conducts research on healthcare policy and advocates for market-based reforms.
Partisan Organizations
Source: Google Search + Gemini + onAir curation
Democratic-Leaning Organizations:
- Families USA: Advocates for affordable and accessible healthcare for all Americans.
- Center for American Progress: A think tank that promotes progressive policies, including healthcare reform.
- National Health Law Program: Provides legal aid and advocates for policies that improve health equity.
- Kaiser Family Foundation: A nonpartisan organization that produces research and analysis on healthcare issues, often with a focus on health insurance.
Republican-Leaning Organizations:
- American Health Care Association / National Center for Assisted Living: Represents nursing homes and assisted living facilities, advocating for policies that support the industry.
- American Medical Association: The largest physician organization in the US, advocates for policies that promote physician autonomy and patient care.
- American Hospital Association: Represents hospitals and health systems, advocating for policies that support the hospital industry.
- PhRMA (Pharmaceutical Research and Manufacturers of America): Represents pharmaceutical companies and advocates for policies that support innovation and intellectual property protection.
“Healthcare in the US” (Wiki)
(Top)
1
History
2
Statistics
3
Providers
4
Spending
5
Regulation and oversight
6
Overall system effectiveness
7
System efficiency and equity
8
Prescription drug issues
9
Healthcare reform debate
10
Health insurance coverage for immigrants
11
See also
12
References
13
Further reading
14
External links
- What links here
- Related changes
- Upload file
- Permanent link
- Page information
- Cite this page
- Get shortened URL
- Download QR code
- Download as PDF
- Printable version
- Wikimedia Commons
- Wikiquote
- Wikidata item
| This article is part of a series on |
| Healthcare reform in the United States |
|---|
Legislation
|
Third-party payment models |
| |

Healthcare in the United States is largely provided by private sector healthcare facilities, and paid for by a combination of public programs, private insurance, and out-of-pocket payments. The U.S. is the only developed country without a system of universal healthcare, and a significant proportion of its population lacks health insurance.[2][3][4][5] The United States spends more on healthcare than any other country, both in absolute terms and as a percentage of GDP;[2] however, this expenditure does not necessarily translate into better overall health outcomes compared to other developed nations. In 2022, the United States spent approximately 17.8% of its Gross Domestic Product (GDP) on healthcare, significantly higher than the average of 11.5% among other high-income countries.[6][7] Coverage varies widely across the population, with certain groups, such as the elderly, disabled and low-income individuals receiving more comprehensive care through government programs such as Medicaid and Medicare.
The U.S. healthcare system has been the subject of significant political debate and reform efforts, particularly in the areas of healthcare costs, insurance coverage, and the quality of care. Legislation such as the Affordable Care Act of 2010 has sought to address some of these issues, though challenges remain. Uninsured rates have fluctuated over time, and disparities in access to care exist based on factors such as income, race, and geographical location.[8][9][10][11] The private insurance model predominates, and employer-sponsored insurance is a common way for individuals to obtain coverage.[2][12][13]
The complex nature of the system, as well as its high costs, has led to ongoing discussions about the future of healthcare in the United States. At the same time, the United States is a global leader in medical innovation, measured either in terms of revenue or the number of new drugs and medical devices introduced.[14][15] The Foundation for Research on Equal Opportunity concluded that the United States dominates science and technology, which “was on full display during the COVID-19 pandemic, as the U.S. government [delivered] coronavirus vaccines far faster than anyone had ever done before”, but lags behind in fiscal sustainability, with “[government] spending … growing at an unsustainable rate”.[16]
In the early 20th century, advances in medical technology and a focus on public health contributed to a shift in healthcare.[17] The American Medical Association (AMA) worked to standardize medical education, and the introduction of employer-sponsored insurance plans marked the beginning of the modern health insurance system.[18] More people were starting to get involved in healthcare like state actors, other professionals/practitioners, patients and clients, the judiciary, and business interests and employers.[19] They had interest in medical regulations of professionals to ensure that services were provided by trained and educated people to minimize harm.[20] The post–World War II era saw a significant expansion in healthcare where more opportunities were offered to increase accessibility of services. The passage of the Hill–Burton Act in 1946 provided federal funding for hospital construction, and Medicare and Medicaid were established in 1965 to provide healthcare coverage to the elderly and low-income populations, respectively.[21][22]

The healthcare system in the United States can be traced back to the Colonial Era.[23] Community-oriented care was typical, with families and neighbors providing assistance to the sick.[24][25] During the 19th century, the practice of medicine began to professionalize, following the “Anglo-American model” where these new medical professionals were empowered by the state to govern their own affairs, leading to various collaborations to acquire status and win legislation granting them the power to self-regulate.[19] The establishment of medical schools and professional organizations led to standardized training and certification processes for doctors.[26] Despite this progress, healthcare services remained disparate, particularly between urban and rural areas. The concept of hospitals as institutions for the sick began to take root, leading to the foundation of many public and private hospitals.[27][page needed]

The latter part of the 20th century saw continued evolution in healthcare policy, technology, and delivery. Following the Stabilization Act of 1942, employers, unable to provide higher salaries to attract or retain employees, began to offer insurance plans, including healthcare packages, as a benefit in kind, thereby beginning the practice of employer-sponsored health insurance, a practice that is cemented into the work culture of today.[28] The Health Maintenance Organization Act of 1973 encouraged the development of managed care, while advances in medical technology revolutionized treatment. In the 21st century, the Affordable Care Act (ACA) was passed in 2010, extending healthcare coverage to millions of uninsured Americans and implementing reforms aimed at improving quality and reducing costs.[29]
Hospitalizations

According to a statistical brief by the Healthcare Cost and Utilization Project (HCUP), there were 35.7 million hospitalizations in 2016,[30] a significant decrease from the 38.6 million in 2011.[31] For every 1,000 in the population, there was an average of 104.2 stays and each stay averaged $11,700 (equivalent to $15,329 in 2024[32]),[30] an increase from the $10,400 (equivalent to $14,244 in 2024[32]) cost per stay in 2012.[33] Approximately 7.6% of the population had overnight stays in 2017,[34] each stay lasting an average of 4.6 days.[30]
A study by the National Institutes of Health reported that the lifetime per capita expenditure at birth, using the year 2000 dollars, showed a large difference between the healthcare costs of females ($361,192, equivalent to $659,498 in 2024[32]) and males ($268,679, equivalent to $490,579 in 2024[32]). A large portion of this cost difference is in the shorter lifespan of men, but, even after adjustment for age (assuming men live as long as women), there still is a 20% difference in lifetime healthcare expenditures.[35]
Health insurance and accessibility
Unlike most developed nations, the US health system does not provide healthcare to the country’s entire population.[36] In 1977, the United States was said to be the only industrialized country not to have some form of national health insurance or direct healthcare provision to citizens through a nationalized healthcare system.[37] A 1978 study argued that “Today every government in the world-including Red China with its squadrons of semi-trained “barefoot doctors”-realizes it has a responsibility to keep its citizens in good physical and mental health. Unlike the U.S., nations like Scandinavia, the U.K., Ireland, Japan and others have opted for a universal health care system in which the state pays everyone’s medical bills.”[38] Instead, most citizens are covered by a combination of private insurance and various federal and state programs.[39] As of 2017, health insurance was most commonly acquired through a group plan tied to an employer, covering 150 million people.[40] Other major sources include Medicaid, covering 70 million, Medicare, 50 million, and health insurance marketplaces created by the ACA covering around 17 million.[40] In 2017, a study found that 73% of plans on ACA marketplaces had narrow networks, limiting access and choice in providers.[40]
Healthcare coverage is provided through a combination of private health insurance and public health coverage (e.g., Medicare, Medicaid). In 2013, 64% of health spending was paid for by the government,[41][42] and funded via programs such as Medicare, Medicaid, the Children’s Health Insurance Program, Tricare, and the Veterans Health Administration. People aged under 65 acquire insurance via their or a family member’s employer, by purchasing health insurance on their own, getting government and/or other assistance based on income or another condition, or are uninsured. Health insurance for public sector employees is primarily provided by the government in its role as employer.[43] Managed care, where payers use various techniques intended to improve quality and limit cost, has become ubiquitous.

Measures of accessibility and affordability tracked by national health surveys include: percent of population with insurance, having a usual source of medical care, visiting the dentist yearly, rates of preventable hospitalizations, reported difficulty seeing a specialist, delaying care due to cost, and rates of health insurance coverage.[44] In 2004, an OECD report noted that “all OECD countries [except Mexico, Turkey, and the US] had achieved universal or near-universal (at least 98.4% insured) coverage of their populations by 1990″.[45] The 2004 IOM report also observed that “lack of health insurance causes roughly 18,000 unnecessary deaths every year in the US”.[36] A 2009 study done at Harvard Medical School with Cambridge Health Alliance by cofounders of Physicians for a National Health Program, a pro-single payer lobbying group, showed that nearly 45,000 annual deaths are associated with a lack of patient health insurance. The study also found that uninsured, working Americans have an approximately 40% higher mortality risk compared to privately insured working Americans.[46]
The Gallup organization tracks the percent of adult Americans who are uninsured for healthcare, beginning in 2008. The rate of uninsured peaked at 18.0% in 2013 prior to the ACA mandate, fell to 10.9% in the third quarter of 2016, and stood at 13.7% in the fourth quarter of 2018.[47] “The 2.8-percentage-point increase since that low represents a net increase of about seven million adults without health insurance.”[47]
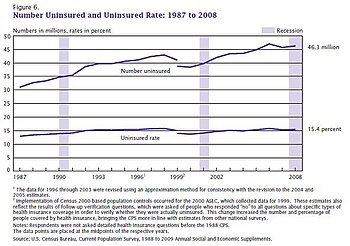
The US Census Bureau reported that 28.5 million people (8.8%) did not have health insurance in 2017,[48] down from 49.9 million (16.3%) in 2010.[49][50] Between 2004 and 2013, a trend of high rates of underinsurance and wage stagnation contributed to a healthcare consumption decline for low-income Americans.[51] This trend was reversed after the implementation of the major provisions of the ACA in 2014.[52]

As of 2017, the possibility that the ACA may be repealed or replaced has intensified interest in the questions of whether and how health insurance coverage affects health and mortality.[54] An estimated 13 million people gained coverage through Medicaid expansion, and 76 million people gained eligibility for free preventative services.[55] Several studies have indicated that there is an association with expansion of the ACA and factors associated with better health outcomes such as having a regular source of care and the ability to afford care.[54] A 2016 study concluded that an approximately 60% increased ability to afford care can be attributed to Medicaid expansion provisions enacted by the Patient Protection and Affordable Care Act.[56] Additionally, an analysis of changes in mortality post Medicaid expansion suggests that Medicaid saves lives at a relatively more cost effective rate of a societal cost of $327,000 to $867,000 (equivalent to $428,428 to $1.14 million in 2024[32]) per life saved compared to other public policies which cost an average of $7.6 million (equivalent to $9.96 million in 2024[32]) per life.[57]
A 2009 study in five states found that medical debt contributed to 46.2% of all personal bankruptcies, and 62.1% of bankruptcy filers claimed high medical expenses in 2007.[58] Since then, health costs and the numbers of uninsured and underinsured have increased.[59] A 2013 study found that about 25% of all senior citizens declare bankruptcy due to medical expenses.[60]
In practice, the uninsured are often treated, but the cost is covered through taxes and other fees which shift the cost.[61] Forgone medical care due to extensive cost sharing may ultimately increase costs due to downstream medical issues; this dynamic may play a part in US’s international ranking as having the highest healthcare expenditures despite significant patient cost-sharing.[52]
Those who are insured may be underinsured such that they cannot afford adequate medical care. A 2003 study estimated that 16 million US adults were underinsured, disproportionately affecting those with lower incomes—73% of the underinsured in the study population had annual incomes below 200% of the federal poverty level.[62] Lack of insurance or higher cost sharing (user fees for the patient with insurance) create barriers to accessing healthcare: use of care declines with increasing patient cost-sharing obligation.[52] Before the ACA passed in 2014, 39% of below-average income Americans reported forgoing seeing a doctor for a medical issue (whereas 7% of low-income Canadians and 1% of low-income British citizens reported the same).[63]
Health in the US in global context

The US life expectancy in 2010 was 78.6 years at birth, up from 75.2 years in 1990; this ranks 42nd among 224 nations, and 22nd out of the 35 OECD countries, down from 20th in 1990.[66][67] In 2021, US life expectancy fell to 76.4 years, the shortest in roughly two decades. Drivers for this drop in life expectancy include accidents, drug overdoses, heart and liver disease, suicides and the COVID-19 pandemic.[68]
In 2019, the under-five child mortality rate was 6.5 deaths per 1000 live births, placing the US 33rd of 37 OECD countries.[69]
While not as high in 2015 (14)[70] as in 2013 (18.5), maternal deaths related to childbirth have shown recent increases; in 1987, the mortality ratio was 7.2 per 100,000.[71] As of 2015, the US rate is double the maternal mortality rate in Belgium or Canada, and more than triple the rate in Finland as well as several other Western European countries.[70] In 2019, Black maternal health advocate and Parents writer Christine Michel Carter interviewed Vice President Kamala Harris. As a senator, in 2019 Harris reintroduced the Maternal Care Access and Reducing Emergencies (CARE) Act which aimed to address the maternal mortality disparity faced by women of color by training providers on recognizing implicit racial bias and its impact on care. Harris stated:
We need to speak the uncomfortable truth that women—and especially Black women—are too often not listened to or taken seriously by the health care system, and therefore they are denied the dignity that they deserve. And we need to speak this truth because today, the United States is 1 of only 13 countries in the world where the rate of maternal mortality is worse than it was 25 years ago. That risk is even higher for Black women, who are three to four times more likely than white women to die from pregnancy-related causes. These numbers are simply outrageous.

Life expectancy at birth for a child born in the US in 2015 is 81.2 (females) or 76.3 (males) years.[72] According to the WHO, life expectancy in the US is 31st in the world (out of 183 countries) as of 2015.[73] The US’s average life expectancy (both sexes) is just over 79.[73] Japan ranks first with an average life expectancy of nearly 84 years. The US ranks lower (36th) when considering health-adjusted life expectancy (HALE) at just over 69 years.[73] Another source, the Central Intelligence Agency, indicates life expectancy at birth in the US is 79.8, ranking it 42nd in the world. Monaco is first on this list of 224, with an average life expectancy of 89.5.[66]
A 2013 National Research Council study stated that, when considered as one of 17 high-income countries, the US was at or near the top in infant mortality, heart and lung disease, sexually transmitted infections, adolescent pregnancies, injuries, homicides, and rates of disability. Together, such issues place the US at the bottom of the list for life expectancy in high-income countries.[74] Females born in the US in 2015 have a life expectancy of 81.6 years, and males 76.9 years; more than three years less and as much as over five years less than people born in Switzerland (85.3 F, 81.3 M) or Japan (86.8 F, 80.5 M) in 2015.[72]
Causes of mortality in the US

The top three causes of death among both sexes and all ages in the US have consistently remained cardiovascular diseases (ranked 1st), neoplasms (2nd) and neurological disorders (3rd), since the 1990s.[75] In 2015, the total number of deaths by heart disease was 633,842, by cancer it was 595,930, and from chronic lower respiratory disease it was 155,041.[76] In 2015, 267.18 deaths per 100,000 people were caused by cardiovascular diseases, 204.63 by neoplasms and 100.66 by neurological disorders.[75] Diarrhea, lower respiratory, and other common infections were ranked sixth overall, but had the highest rate of infectious disease mortality in the US at 31.65 deaths per 100,000 people.[75] There is evidence, however, that a large proportion of health outcomes and early mortality can be attributed to factors other than communicable or non-communicable disease. As a 2013 National Research Council study concluded, more than half the men who die before the age of 50 die due to murder (19%), traffic accidents (18%), and other accidents (16%). For women, the percentages are different: 53% of women who die before the age of 50 die due to disease, whereas 38% die due to accidents, homicide, and suicide.[77] Diseases of despair (drug overdoses, alcoholic liver disease, and suicide), which started increasing in the early 1990s, kill roughly 158,000 Americans a year as of 2018.[78] Suicides reached record levels in the United States in 2022, with nearly 49,500 suicide deaths. Since 2011, around 540,000 people in the U.S. have died by suicide.[79][80] Cumulative poverty of ten years or more is the fourth leading risk factor for mortality in the United States annually.[81][82][83][84]

Since 2020, the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) reports that the life expectancy for the US population was 77.0 years, a decrease of 1.8 years from 2019.[85] Life expectancy fell again in 2021 to 76.4 years, which has been attributed to COVID-19 and rising death rates from suicide, drug overdoses and liver disease.[86] As of 2023, U.S. life expectancy has increased slightly following the COVID-19 pandemic, but still trails behind peer and rival countries including Canada, China and Germany.[87] Death certificate data from the CDC reveals that mortality rates among children and adolescents increased by 11% for the years 2019 and 2020 and a further 8% for 2020 and 2021, with injuries being a driving factor, along with homicide, suicide, drug overdoses and motor vehicle accidents impacting those aged 10 to 19.[88][89] In 2024 a study reported obesity-related deaths have surged in the United States in recent years, particularly among men, according to new data published in The American Journal of Cardiology.[90] The study noted that while the age-adjusted mortality rate has increased due to obesity, deaths related to cardiovascular disease, including ischemic heart disease and heart failure, have actually decreased.[91]
Healthcare providers in the US encompass individual healthcare personnel, healthcare facilities, and medical products.
Facilities

In the US, ownership of the healthcare system is now mainly in private hands, though federal, state, county, and city governments also own certain facilities.
As of 2018, there were 5,534 registered hospitals in the US. There were 4,840 community hospitals, which are defined as nonfederal, short-term general, or specialty hospitals.[93] The nonprofit hospitals share of total hospital capacity has remained relatively stable (about 70%) for decades.[94] There are also privately owned for-profit hospitals as well as government hospitals in some locations, mainly owned by county and city governments. The Hill–Burton Act was passed in 1946, which provided federal funding for hospitals in exchange for treating poor patients.[95] The largest hospital system in 2016 by revenue was HCA Healthcare;[96] in 2019, Dignity Health and Catholic Health Initiatives merged into CommonSpirit Health to create the largest by revenue, spanning 21 states.[97]
Integrated delivery systems, where the provider and the insurer share the risk in an attempt to provide value-based healthcare, have grown in popularity.[98] Regional areas have separate healthcare markets, and in some markets competition is limited as the demand from the local population cannot support multiple hospitals.[99][100]
About two-thirds of doctors practice in small offices with less than seven physicians, with over 80% owned by physicians; these sometimes join groups such as independent practice associations to increase bargaining power.[101]

There is no nationwide system of government-owned medical facilities open to the general public but there are local government-owned medical facilities open to the general public. The US Department of Defense operates field hospitals as well as permanent hospitals via the Military Health System to provide military-funded care to active military personnel.[102]
The federal Veterans Health Administration operates VA hospitals open only to veterans, though veterans who seek medical care for conditions they did not receive while serving in the military are charged for services. The Indian Health Service (IHS) operates facilities open only to Native Americans from recognized tribes. These facilities, plus tribal facilities and privately contracted services funded by IHS to increase system capacity and capabilities, provide medical care to tribespeople beyond what can be paid for by any private insurance or other government programs.

Hospitals provide some outpatient care in their emergency rooms and specialty clinics, but primarily exist to provide inpatient care. Hospital emergency departments and urgent care centers are sources of sporadic problem-focused care. Surgicenters are examples of specialty clinics. Hospice services for the terminally ill who are expected to live six months or less are most commonly subsidized by charities and government. Prenatal, family planning, and dysplasia clinics are government-funded obstetric and gynecologic specialty clinics respectively, and are usually staffed by nurse practitioners. Because of the robust skills credited to nurse practitioners (NPs) they are able to address disparities in the U.S. Healthcare System. Government-funded healthcare facilities especially have a large reliance on these NPs due to the amount of services they are required to provide.[103] Services, particularly urgent-care services, may also be delivered remotely via telemedicine by providers such as Teladoc.
Besides government and private healthcare facilities, there are also 355 registered free clinics in the US that provide limited medical services. They are considered to be part of the social safety net for those who lack health insurance. Their services may range from more acute care (i.e., STIs, injuries, respiratory diseases) to long term care (i.e. dentistry, counseling).[104] Another component of the healthcare safety net would be federally funded community health centers.
Other healthcare facilities include long-term housing facilities which, as of 2019, there were 15,600 nursing homes across the US, with a large portion of that number being for-profit (69.3%)[105]
In 2022, 19 hospitals filed for bankruptcy, closed, or announced plans to close.[106]
Physicians (M.D. and D.O.)

Physicians in the US include those trained by the US medical education system, and those that are international medical graduates who have progressed through the necessary steps to acquire a medical license to practice in a state.[citation needed] This includes going through the three steps of the US Medical Licensing Examination (USMLE). The first step of the USMLE tests whether medical students both understand and are capable of applying the basic scientific foundations to medicine after the second year of medical school. The topics include: anatomy, biochemistry, microbiology, pathology, pharmacology, physiology, behavioral sciences, nutrition, genetics, and aging. The second step is designed to test whether medical students can apply their medical skills and knowledge to actual clinical practice during students’ fourth year of medical school. The third step is done after the first year of residency. It tests whether students can apply medical knowledge to the unsupervised practice of medicine.[107][unreliable source?]
The American College of Physicians, uses the term “physician” to describe all medical practitioners holding a professional medical degree. In the US, the vast majority of physicians have a Doctor of Medicine (M.D.) degree.[108] Those with Doctor of Osteopathic Medicine (D.O.) degrees get similar training and go through the same MLE steps as MD’s and so are also allowed to use the title “physician”.
Medical products, research, and development
As in most other countries, the manufacture and production of pharmaceuticals and medical devices is carried out by private companies. The research and development of medical devices and pharmaceuticals is supported by both public and private sources of funding. In 2003, research and development expenditures were approximately $95 billion (equivalent to $151 billion in 2023[109]) with $40 billion (equivalent to $63.5 billion in 2023[109]) coming from public sources and $55 billion (equivalent to $87.3 billion in 2023[109]) coming from private sources.[110][111] These investments into medical research have made the US the leader in medical innovation, measured either in terms of revenue or the number of new drugs and devices introduced.[14][15] In 2016, the research and development spending by pharmaceutical companies in the US was estimated to be around $59 billion (equivalent to $73.5 billion in 2023[109]).[112] In 2006, the US accounted for three quarters of the world’s biotechnology revenues and 82% of world R&D spending in biotechnology.[14][15] According to multiple international pharmaceutical trade groups, the high cost of patented drugs in the US has encouraged substantial reinvestment in such research and development.[14][15][113] Though, the ACA will force industry to sell medicine at a cheaper price.[114] Due to this, it is possible budget cuts will be made on research and development of human health and medicine in the US.[114]
In 2022, the United States had 10,265 drugs in the works, more than twice as many as China and the European Union, and four times as many as the United Kingdom.[115]

Healthcare provider employment in the US
A major impending demographic shift in the US will require the healthcare system to provide more care, as the older population is predicted to increase medical expenses by 5% or more in North America[116] due to the “baby boomers” reaching retirement age.[117] The overall spending on healthcare has increased since the late 1990s, and not just due to general price raises as the rate of spending is growing faster than the rate of inflation.[118] Moreover, the expenditure on health services for people over 45 years old is 8.3 times the maximum of that of those under 45 years old.[119]
Alternative medicine
Other methods of medical treatment are being practiced more frequently than before.[when?] This field is labeled Complementary and Alternative Medicine (CAM) and are defined as therapies generally not taught in medical school nor available in hospitals. They include herbs, massages, energy healing, homeopathy, faith healing, and, more recently popularized, cryotherapy, cupping, and Transcranial Magnetic Stimulation or TMS.[120] Providers of these CAM treatments are sometimes legally considered healthcare providers in the US.[121] Common reasons for seeking these alternative approaches included improving their well-being, engaging in a transformational experience, gaining more control over their own health, or finding a better way to relieve symptoms caused by chronic disease. They aim to treat not just physical illness but fix its underlying nutritional, social, emotional, and spiritual causes. In a 2008 survey, it was found that 37% of hospitals in the US offer at least one form of CAM treatment, the main reason being patient demand (84% of hospitals).[122] Costs for CAM treatments average $33.9 (equivalent to $51.41 in 2024[32]) with two-thirds being out-of-pocket, according to a 2007 statistical analysis.[123] Moreover, CAM treatments covered 11.2% of total out-of-pocket payments on healthcare.[123] During 2002 to 2008, spending on CAM was on the rise, but usage has since plateaued to about 40% of adults in the US[124]
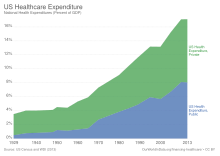
The US spends more as a percentage of GDP than similar countries, and this can be explained either through higher prices for services themselves, higher costs to administer the system, or more utilization of these services, or to a combination of these elements.[127] Healthcare costs rising far faster than inflation have been a major driver for healthcare reform in the US. As of 2016, the US spent $3.3 trillion (equivalent to $4.11 trillion in 2023;[109] 17.9% of GDP), or $10,438 (equivalent to $13,676 in 2024[32]) per person; major categories included 32% on hospital care, 20% on physician and clinical services, and 10% on prescription drugs.[128] In comparison, the United Kingdom spent $3,749 (equivalent to $4,912 in 2024[32]) per person.[129]
In 2018, an analysis concluded that prices and administrative costs were largely the cause of the high costs, including prices for labor, pharmaceuticals, and diagnostics.[130][131] The combination of high prices and high volume can cause particular expense; in the US, high-margin high-volume procedures include angioplasties, C-sections, knee replacements, and CT and MRI scans; CT and MRI scans also showed higher utilization in the US.[132]
Aggregate US hospital costs were $387.3 billion in 2011—a 63% increase since 1997 (inflation adjusted). Costs per stay increased 47% since 1997, averaging $10,000 in 2011 (equivalent to $13,978 in 2024[32]).[133] As of 2008, public spending accounts for between 45% and 56% of US healthcare spending.[134] Surgical, injury, and maternal and neonatal health hospital visit costs increased by more than 2% each year from 2003–2011. Further, while average hospital discharges remained stable, hospital costs rose from $9,100 in 2003 (equivalent to $15,555 in 2024[32]) to $10,600 in 2011 (equivalent to $14,816 in 2024[32]) and were projected to be $11,000 by 2013 (equivalent to $14,848 in 2024[32]).[135]
According to the WHO, total healthcare spending in the US was 18% of its GDP in 2011, the greatest amount in the world.[136] The Health and Human Services Department expects that the health share of GDP will continue its historical upward trend, reaching 19% of GDP by 2017.[137][138] Of each dollar spent on healthcare in the US, 31% goes to hospital care, 21% goes to physician/clinical services, 10% to pharmaceuticals, 4% to dental, 6% to nursing homes and 3% to home healthcare, 3% for other retail products, 3% for government public health activities, 7% to administrative costs, 7% to investment, and 6% to other professional services (physical therapists, optometrists, etc.).[139]
In 2017, a study estimated that nearly half of hospital-associated care resulted from emergency department visits.[140] As of 2017, data from 2009–2011 showed that end-of-life care in the last year of life accounted for about 8.5%, and the last three years of life about 16.7%.[141]
As of 2013, administration of healthcare constituted 30% of US healthcare costs.[142]
Free-market advocates claim that the healthcare system is “dysfunctional” because the system of third-party payments from insurers removes the patient as a major participant in the financial and medical choices that affect costs. The Cato Institute claims that because government intervention has expanded insurance availability through programs such as Medicare and Medicaid, this has exacerbated the problem.[143] According to a study paid for by America’s Health Insurance Plans (a Washington lobbyist for the health insurance industry) and carried out by PriceWaterhouseCoopers, increased utilization is the primary driver of rising healthcare costs in the US.[144] The study cites numerous causes of increased utilization, including rising consumer demand, new treatments, more intensive diagnostic testing, lifestyle factors, the movement to broader-access plans, and higher-priced technologies.[144] The study also mentions cost-shifting from government programs to private payers. Low reimbursement rates for Medicare and Medicaid have increased cost-shifting pressures on hospitals and doctors, who charge higher rates for the same services to private payers, which eventually affects health insurance rates.[145]
In March 2010, Massachusetts released a report on the cost drivers which it called “unique in the nation”.[146] The report noted that providers and insurers negotiate privately, and therefore the prices can vary between providers and insurers for the same services, and it found that the variation in prices did not vary based on quality of care but rather on market leverage; the report also found that price increases rather than increased utilization explained the spending increases in the past several years.[146]
Economists Eric Helland and Alex Tabarrok speculate that the increase in costs of healthcare in the US are largely a result of the Baumol effect. Since healthcare is relatively labor intensive, and productivity in the service sector has lagged that in the goods-producing sector, the costs of those services will rise relative to goods.[147]
An analysis by the US Congressional Budget Office (CBO) suggests allowing Medicare to cover weight loss drugs would raise federal spending by approximately $35 billion between 2026 and 2034.[148] Federal costs would rise from $1.6 billion in 2026 to $7.1 billion by 2034. However, the CBO projected that savings from improved health outcomes would be modest compared to the direct costs of the medications, totaling less than $50 million in 2026 and growing to $1 billion by 2034. Expanding coverage for weight loss drugs from Eli Lilly and Novo Nordisk would make an additional 12.5 million people eligible by 2026. Currently, around 52 million older or disabled Americans receive prescription drug coverage through Medicare, which does not include drugs specifically for weight loss.
Involved organizations and institutions
Healthcare is subject to extensive regulation at both the federal and the state level, much of which “arose haphazardly”.[149] Under this system, the federal government cedes primary responsibility to the states under the McCarran–Ferguson Act. Essential regulation includes the licensure of healthcare providers at the state level and the testing and approval of pharmaceuticals and medical devices by the Food and Drug Administration (FDA), and laboratory testing. These regulations are designed to protect consumers from ineffective or fraudulent healthcare. Additionally, states regulate the health insurance market and they often have laws which require that health insurance companies cover certain procedures,[150] although state mandates generally do not apply to the self-funded healthcare plans offered by large employers, which exempt from state laws under preemption clause of the Employee Retirement Income Security Act.
In 2010, the ACA was signed by President Barack Obama and includes various new regulations, with one of the most notable being a health insurance mandate which requires all citizens to purchase health insurance. While not regulation per se, the federal government also has a major influence on the healthcare market through its payments to providers under Medicare and Medicaid, which in some cases are used as a reference point in the negotiations between medical providers and insurance companies.[149]
At the federal level, the U.S. Department of Health and Human Services (HHS) oversees various federal agencies involved in healthcare, except for the Drug Enforcement Administration (DEA), which has final authority over the FDA in matters related to controlled substance regulations. The health agencies under the HHS umbrella are part of the U.S. Public Health Service. These include the FDA, responsible for certifying the safety of food and the effectiveness of drugs and medical products; the CDC, tasked with preventing disease, premature death, and disability; the Agency for Healthcare Research and Quality, which improves the quality, safety, efficiency, and effectiveness of healthcare; the Agency for Toxic Substances and Disease Registry, which manages hazardous substance spills; and the National Institutes of Health, which conducts groundbreaking medical research.
State governments maintain their own health departments, and local governments (counties and municipalities) often have health departments that are branches of the state health department. State boards may have executive and police authority to enforce state health laws, with all members required to be healthcare professionals in some states. These board members may be appointed by the governor or elected by the state committee, while local board members may be elected by the mayor’s council. The McCarran–Ferguson Act, which delegates regulation to the states, does not directly regulate insurance or mandate state regulation of insurance. Federal laws that do not explicitly regulate the “business of insurance” do not preempt state insurance laws or regulations. The act also stipulates that federal antitrust laws will not apply to the “business of insurance” as long as the state regulates it, though they will apply in cases of boycott, coercion, and intimidation. Conversely, most other federal laws will not apply to insurance regardless of state regulation.
Self-policing by healthcare providers plays a significant role in oversight. Many healthcare organizations voluntarily submit to inspection and certification by the Joint Commission on Accreditation of Healthcare Organizations (JCAHO). Providers also undergo rigorous testing to obtain board certification, attesting to their expertise. A report issued by Public Citizen in April 2008 found that, for the third consecutive year, the number of serious disciplinary actions against physicians by state medical boards declined from 2006 to 2007, prompting calls for increased oversight of these boards.
Additionally, the concept of final expense insurance is essential within the healthcare context. This type of insurance helps cover the costs associated with end-of-life expenses, providing financial peace of mind to individuals and their families. Final expense insurance ensures that healthcare-related costs, such as medical bills and funeral expenses, do not become a burden during an already challenging time.[151]
The federal Centers for Medicare and Medicaid Services (CMS) publishes an online searchable database of performance data on nursing homes.[152]
In 2004, libertarian think tank Cato Institute published a study which concluded that regulation provides benefits in the amount of $170 billion but costs the public up to $340 billion.[153] The study concluded that the majority of the cost differential arises from medical malpractice, FDA regulations, and facilities regulations.[153]
“Certificates of need” for hospitals
In 1978, the federal government required that all states implement Certificate of Need (CON) programs for cardiac care, meaning that hospitals had to apply and receive certificates prior to implementing the program; the intent was to reduce cost by reducing duplicate investments in facilities.[154] It has been observed that these certificates could be used to increase costs through weakened competition.[149] Many states removed the CON programs after the federal requirement expired in 1986, but some states still have these programs.[154] Empirical research looking at the costs in areas where these programs have been discontinued have not found a clear effect on costs, and the CON programs could decrease costs because of reduced facility construction or increase costs due to reduced competition.[154]
Licensing of providers
The American Medical Association (AMA) has lobbied the government to highly limit physician education since 1910, currently at 100,000 doctors per year,[155] which has led to a shortage of doctors.[156]
An even bigger problem may be that the doctors are paid for procedures instead of results.[157][158]
The AMA has also aggressively lobbied for many restrictions that require doctors to carry out operations that might be carried out by cheaper workforce. For example, in 1995, 36 states banned or restricted midwifery even though it delivers equally safe care to that by doctors.[155] The regulation lobbied by the AMA has decreased the amount and quality of healthcare, according to the consensus of economists: the restrictions do not add to quality, they decrease the supply of care.[155] Moreover, psychologists, nurses and pharmacists are not allowed to prescribe medicines.[clarification needed] Previously nurses were not even allowed to vaccinate the patients without direct supervision by doctors.
Thirty-six states require that healthcare workers undergo criminal background checks.[159]
Emergency Medical Treatment and Active Labor Act (EMTALA)
EMTALA, enacted by the federal government in 1986, requires that hospital emergency departments treat emergency conditions of all patients regardless of their ability to pay and is considered a critical element in the “safety net” for the uninsured, but established no direct payment mechanism for such care. Indirect payments and reimbursements through federal and state government programs have never fully compensated public and private hospitals for the full cost of care mandated by EMTALA. More than half of all emergency care in the US now goes uncompensated.[160] According to some analyses, EMTALA is an unfunded mandate that has contributed to financial pressures on hospitals in the last 20 years, causing them to consolidate and close facilities, and contributing to emergency room overcrowding. According to the Institute of Medicine, between 1993 and 2003, emergency room visits in the US grew by 26%, while in the same period, the number of emergency departments declined by 425.[161]
Mentally ill patients present a unique challenge for emergency departments and hospitals. In accordance with EMTALA, mentally ill patients who enter emergency rooms are evaluated for emergency medical conditions. Once mentally ill patients are medically stable, regional mental health agencies are contacted to evaluate them. Patients are evaluated as to whether they are a danger to themselves or others. Those meeting this criterion are admitted to a mental health facility to be further evaluated by a psychiatrist. Typically, mentally ill patients can be held for up to 72 hours, after which a court order is required.
Quality assurance
Healthcare quality assurance consists of the “activities and programs intended to assure or improve the quality of care in either a defined medical setting or a program. The concept includes the assessment or evaluation of the quality of care; identification of problems or shortcomings in the delivery of care; designing activities to overcome these deficiencies; and follow-up monitoring to ensure effectiveness of corrective steps.”[162] Private companies such as Grand Rounds also release quality information and offer services to employers and plans to map quality within their networks.[163]
One innovation in encouraging quality of healthcare is the public reporting of the performance of hospitals, health professionals or providers, and healthcare organizations. However, there is “no consistent evidence that the public release of performance data changes consumer behaviour or improves care”.[164]
A 2019 issue brief by the Commonwealth Fund concluded that “people in the United States experience the worst health outcomes overall of any high-income nation” and that “Americans are more likely to die younger, and from avoidable causes, than residents of peer countries.” A subsequent analysis in 2022 showed a worsening of these trends, though it acknowledged that the tumultuous impact of the COVID-19 pandemic and lockdowns on healthcare in the United States was challenging to disentangle from the longer term trajectory of the system.[165]
Measures of effectiveness
The US healthcare delivery system unevenly provides medical care of varying quality to its population.[166] In a highly effective healthcare system, individuals would receive reliable care that meets their needs and is based on the best scientific knowledge available. In order to monitor and evaluate system effectiveness, researchers and policy makers track system measures and trends over time. The HHS populates a publicly available dashboard called the Health System Measurement Project, to ensure a robust monitoring system. The dashboard captures the access, quality and cost of care; overall population health; and health system dynamics (e.g., workforce, innovation, health information technology). Included measures align with other system performance measuring activities including the HHS Strategic Plan,[167] the Government Performance and Results Act, Healthy People 2020, and the National Strategies for Quality and Prevention.[168][169]
Waiting times
Waiting times in US healthcare are usually short, but are not usually 0 for non-urgent care at least. Also, a minority of US patients wait longer than is perceived. In a 2010 Commonwealth Fund survey, most Americans self-reported waiting less than four weeks for their most recent specialist appointment and less than one month for elective surgery. However, about 30% of patients reported waiting longer than one month for elective surgery, and about 20% longer than four weeks for their most recent specialist appointment.[170] These percentages were smaller than in France, the UK, New Zealand, and Canada, but not better than Germany and Switzerland (although waits shorter than four weeks/one month may not be equally long across these three countries). The number of respondents may not be enough to be fully representative. In a study in 1994 comparing Ontario to three regions of the US, self-reported mean wait times to see an orthopedic surgeon were two weeks in those parts of the US, and four weeks in Canada. Mean waits for the knee or hip surgery were self-reported as three weeks in those parts of the US and eight weeks in Ontario.[171]
However, current waits in both countries’ regions may have changed since then (certainly in Canada waiting times went up later).[172] More recently, at one Michigan hospital, the waiting time for the elective surgical operation open carpel tunnel release was an average of 27 days, most ranging from 17 to 37 days (an average of almost four weeks, ranging from about 2.4 weeks to 5.3 weeks). This appears to be short compared with Canada’s waiting time but may compare less favorably to countries like Germany, the Netherlands (where the goal was five weeks), and Switzerland.
It is unclear how many of the patients waiting longer have to. Some may be by choice, because they wish to go to a well-known specialist or clinic that many people wish to attend, and are willing to wait to do so. Waiting times may also vary by region. One experiment reported that uninsured patients experienced longer waits;[citation needed] patients with poor insurance coverage probably face a disproportionate number of long waits.
US healthcare tends to rely on rationing by exclusion (uninsured and underinsured), out-of-pocket costs for the insured, fixed payments per case to hospitals (resulting in very short stays), and contracts that manage demand instead.[citation needed]
Population health: quality, prevention, vulnerable populations
The health of the population is also viewed as a measure of the overall effectiveness of the healthcare system. The extent to which the population lives longer healthier lives signals an effective system.
- While life expectancy is one measure, the HHS uses a composite health measure that estimates not only the average length of life but also the part of life expectancy that is expected to be “in good or better health, as well as free of activity limitations”. Between 1997 and 2010, the number of expected high quality life years increased from 61.1 to 63.2 years for newborns.[174]
- The underutilization of preventative measures, rates of preventable illness and prevalence of chronic disease suggest that the US healthcare system does not sufficiently promote wellness.[168] Over the past decade rates of teen pregnancy and low birth rates have come down significantly, but not disappeared.[175] Rates of obesity, heart disease (high blood pressure, controlled high cholesterol), and type 2 diabetes are areas of major concern. While chronic disease and multiple comorbidities became increasingly common among a population of elderly Americans who were living longer, the public health system has also found itself fending off a rise of chronically ill younger generation. According to the US Surgeon General “The prevalence of obesity in the US more than doubled (from 15% to 34%) among adults and more than tripled (from 5% to 17%) among children and adolescents from 1980 to 2008.”[176]
- A concern for the health system is that the health gains do not accrue equally to the entire population. In the US, disparities in healthcare and health outcomes are widespread.[177] Minorities are more likely to develop serious illnesses (e.g., type 2 diabetes, heart disease and colon cancer) and less likely to have access to quality healthcare, including preventative services.[178] Efforts are underway to close the gap and to provide a more equitable system of care.
Innovation: workforce, healthcare IT, R&D
Finally, the US tracks investment in the healthcare system in terms of a skilled healthcare workforce, meaningful use of healthcare IT, and R&D output. This aspect of the healthcare system performance dashboard is important to consider when evaluating cost of care in the US. That is because in much of the policy debate around the high cost of US healthcare, proponents of highly specialized and cutting-edge technologies point to innovation as a marker of an effective healthcare system.[179]
Compared to other countries



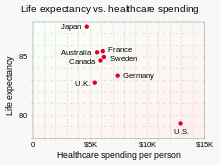
A 2014 study by the private US foundation Commonwealth Fund found that although the US healthcare system is the most expensive in the world, it ranks last on most dimensions of performance when compared with Australia, Canada, France, Germany, the Netherlands, New Zealand, Norway, Sweden, Switzerland, and the UK. The study found that the US failed to achieve better outcomes than other countries, and is last or near last in terms of access, efficiency, and equity. Study data came from international surveys of patients and primary care physicians, as well as information on healthcare outcomes from Commonwealth Fund, the WHO, and the OECD.[181][182]
As of 2017, the US stands 43rd in the world with a life expectancy of 80.00 years[66] In 2007, the CIA World Factbook ranked the US 180th worst (out of 221)—meaning 42nd best—in the world for infant mortality rate (5.01/1,000 live births).[183] Americans also undergo cancer screenings at significantly higher rates than people in other developed countries, and access MRI and CT scans at the highest rate of any OECD nation.[184]
A study found that between 1997 and 2003, preventable deaths declined more slowly in the US than in 18 other industrialized nations.[185] A 2008 study found that 101,000 people a year die in the US that would not if the healthcare system were as effective as that of France, Japan, or Australia.[186] A 2020 study by the economists Anne Case and Angus Deaton argues that the US “spends huge sums of money for some of the worst health outcomes in the Western world”.[187]
The OECD found that the US ranked poorly in terms of years of potential life lost (YPLL), a statistical measure of years of life lost under the age of 70 that were amenable to being saved by healthcare. Among OECD nations for which data are available, the US ranked third last for the healthcare of women (after Mexico and Hungary) and fifth last for men (Slovakia and Poland also ranked worse).
Recent studies find growing gaps in life expectancy based on income and geography. In 2008, a government-sponsored study found that life expectancy declined from 1983 to 1999 for women in 180 counties, and for men in 11 counties, with most of the life expectancy declines occurring in the Deep South, Appalachia, along the Mississippi River, in the Southern Plains, and in Texas. The difference is as high as three years for men, six years for women. The gap is growing between rich and poor and by educational level, but narrowing between men and women and by race.[188] Another study found that the mortality gap between the well-educated and the poorly educated widened significantly between 1993 and 2001 for adults ages 25 through 64; the authors speculated that risk factors such as smoking, obesity and high blood pressure may lie behind these disparities.[189] In 2011 the US National Research Council forecasted that deaths attributed to smoking, on the decline in the US, will drop dramatically, improving life expectancy; it also suggested that one-fifth to one-third of the life expectancy difference can be attributed to obesity which is the worst in the world and has been increasing.[190] In an analysis of breast cancer, colorectal cancer, and prostate cancer diagnosed during 1990–1994 in 31 countries, the US had the highest five-year relative survival rate for breast cancer and prostate cancer, although survival was systematically and substantially lower in Black US men and women.[191]
The debate about US healthcare concerns questions of access, efficiency, and quality purchased by the high sums spent. The WHO in 2000 ranked the US healthcare system first in responsiveness, but 37th in overall performance and 72nd by overall level of health (among 191 member nations included in the study).[192][193] The WHO study has been criticized by the free market advocate David Gratzer because “fairness in financial contribution” was used as an assessment factor, marking down countries with high per-capita private or fee-paying health treatment.[194] The WHO study has been criticized, in an article published in Health Affairs, for its failure to include the satisfaction ratings of the general public.[195] The study found that there was little correlation between the WHO rankings for health systems and the stated satisfaction of citizens using those systems.[195] Countries such as Italy and Spain, which were given the highest ratings by WHO were ranked poorly by their citizens while other countries, such as Denmark and Finland, were given low scores by WHO but had the highest percentages of citizens reporting satisfaction with their healthcare systems.[195] WHO staff, however, say that the WHO analysis does reflect system “responsiveness” and argue that this is a superior measure to consumer satisfaction, which is influenced by expectations.[196] Furthermore, the relationship between patient satisfaction and healthcare utilization, expenditures, clinically meaningful measures, and the evaluation of outcomes is complex, not well defined, and only beginning to be explored.[197][198]
A report released in April 2008 by the Foundation for Child Development, which studied the period from 1994 through 2006, found mixed results for the health of children in the US Mortality rates for children ages 1 through 4 dropped by a third, and the percentage of children with elevated blood lead levels dropped by 84%. The percentage of mothers who smoked during pregnancy also declined. On the other hand, both obesity and the percentage of low-birth weight babies increased. The authors note that the increase in babies born with low birth weights can be attributed to women delaying childbearing and the increased use of fertility drugs.[199][200]
In a sample of 13 developed countries, the US was third in its population weighted usage of medication in 14 classes in both 2009 and 2013. The drugs studied were selected on the basis that the conditions treated had high incidence, prevalence and/or mortality, caused significant long-term morbidity and incurred high levels of expenditure and significant developments in prevention or treatment had been made in the last 10 years. The study noted considerable difficulties in cross border comparison of medication use.[201]
A critic of the US healthcare system, British philanthropist Stan Brock, whose charity Remote Area Medical has served over half a million uninsured Americans, stated, “You could be blindfolded and stick a pin on a map of America and you will find people in need.”[202] The charity has over 700 clinics and 80,000 volunteer doctors and nurses around the US Simon Usborne of The Independent writes that in the UK “General practitioners are amazed to hear that poor Americans should need to rely on a charity that was originally conceived to treat people in the developing world.”[202]

Variations in the efficiency of healthcare delivery can cause variations in outcomes. The Dartmouth Atlas Project, for instance, reported that, for over 20 years, marked variations in how medical resources are distributed and used in the US were accompanied by marked variations in outcomes.[205] The willingness of physicians to work in an area varies with the income of the area and the amenities it offers, a situation aggravated by a general shortage of doctors in the US, particularly those who offer primary care. The ACA is anticipated to produce an additional demand for services which the existing stable of primary care doctors will be unable to fill, particularly in economically depressed areas. Training additional physicians would require some years.[206]
Lean manufacturing techniques such as value stream mapping can help identify and subsequently mitigate waste associated with costs of healthcare.[citation needed] Other product engineering tools such as FMEA and Fish Bone Diagrams have been used to improve efficiencies in healthcare delivery.[207]
Since 2004 the Commonwealth Fund has produced reports comparing healthcare systems in high income countries using survey and administrative data from the OECD and WHO which is analyzed under five themes: access to care, the care process, administrative efficiency, equity and healthcare outcomes. The US has been assessed as worst healthcare system overall among 11 high-income countries in every report, even though it spends the highest proportion of its gross domestic product on healthcare. In 2021 Norway, the Netherlands and Australia were the top-performing countries. The US spent 16.8% of GDP on healthcare in 2019; the next highest country on the list was Switzerland, at 11.3% of GDP. The lowest was New Zealand, which spent roughly 9% of its GDP on healthcare in 2019. It “consistently demonstrated the largest disparities between income groups” across indicators, apart from those related to preventive services and the safety of care.[208]
Efficiency
Preventable deaths
In 2010, coronary artery disease, lung cancer, stroke, chronic obstructive pulmonary diseases, and traffic accidents caused the most years of life lost in the US. Low back pain, depression, musculoskeletal disorders, neck pain, and anxiety caused the most years lost to disability. The most deleterious risk factors were poor diet, tobacco smoking, obesity, high blood pressure, high blood sugar, physical inactivity, and alcohol use. Alzheimer’s disease, drug abuse, kidney disease and cancer, and falls caused the most additional years of life lost over their age-adjusted 1990 per-capita rates.[67]
Between 1990 and 2010, among the 34 countries in the OECD, the US dropped from 18th to 27th in age-standardized death rate. The US dropped from 23rd to 28th for age-standardized years of life lost. It dropped from 20th to 27th in life expectancy at birth. It dropped from 14th to 26th for healthy life expectancy.[67]
According to a 2009 study conducted at Harvard Medical School by cofounders of Physicians for a National Health Program, a pro-single payer lobbying group, and published by the American Journal of Public Health, lack of health coverage is associated with nearly 45,000 excess preventable deaths annually.[209][210] Since then, as the number of uninsured has risen from about 46 million in 2009 to 49 million in 2012, the number of preventable deaths due to lack of insurance has grown to about 48,000 per year.[211] The group’s methodology has been criticized by economist John C. Goodman for not looking at cause of death or tracking insurance status changes over time, including the time of death.[212]
A 2009 study by former Clinton policy adviser Richard Kronick published in the journal Health Services Research found no increased mortality from being uninsured after certain risk factors were controlled for.[213]
Value for money
A study of international healthcare spending levels published in the health policy journal Health Affairs in the year 2000 found that the US spends substantially more on healthcare than any other country in the OECD (OECD), and that the use of healthcare services in the US is below the OECD median by most measures. The authors of the study conclude that the prices paid for healthcare services are much higher in the US than elsewhere.[214] While the 19 next most wealthy countries by GDP all pay less than half what the US does for healthcare, they have all gained about six years of life expectancy more than the US since 1970.[65]
Affordability
In 2023, American gold medal-winning gymnast Mary Lou Retton, critically ill with pneumonia, did not have health insurance, and, like many thousands of Americans who could not afford coverage, turned to crowdfunding to raise money for her medical expenses.[215][216]
Delays in seeking care and increased use of emergency care
Uninsured Americans are less likely to have regular healthcare and use preventive services. They are more likely to delay seeking care, resulting in more medical crises, which are more expensive than ongoing treatment for such conditions as diabetes and high blood pressure. A 2007 study published in JAMA concluded that uninsured people were less likely than the insured to receive any medical care after an accidental injury or the onset of a new chronic condition. The uninsured with an injury were also twice as likely as those with insurance to have received none of the recommended follow-up care, and a similar pattern held for those with a new chronic condition.[217] Uninsured patients are twice as likely to visit hospital emergency rooms as those with insurance; burdening a system meant for true emergencies with less-urgent care needs.[218]
In 2008 researchers with the American Cancer Society found that individuals who lacked private insurance (including those covered by Medicaid) were more likely to be diagnosed with late-stage cancer than those who had such insurance.[219]
Variations in provider practices
The treatment given to a patient can vary significantly depending on which healthcare providers they use. Research suggests that some cost-effective treatments are not used as often as they should be, while overutilization occurs with other healthcare services. Unnecessary treatments increase costs and can cause patients unnecessary anxiety.[220] The use of prescription drugs varies significantly by geographic region.[221] The overuse of medical benefits is known as moral hazard—individuals who are insured are then more inclined to consume healthcare. The way the healthcare system tries to eliminate this problem is through cost sharing tactics like copays and deductibles. If patients face more of the economic burden they will then only consume healthcare when they perceive it to be necessary. According to the RAND health insurance experiment, individuals with higher coinsurance rates consumed less healthcare than those with lower rates. The experiment concluded that with less consumption of care there was generally no loss in societal welfare but, for the poorer and sicker groups of people there were definitely negative effects. These patients were forced to forgo necessary preventative care measures in order to save money leading to late diagnosis of easily treated diseases and more expensive procedures later. With less preventative care, the patient is hurt financially with an increase in expensive visits to the ER. The healthcare costs in the US will also rise with these procedures as well. More expensive procedures lead to greater costs.[222][223]
One study has found significant geographic variations in Medicare spending for patients in the last two years of life. These spending levels are associated with the amount of hospital capacity available in each area. Higher spending did not result in patients living longer.[224][225]
Care coordination
Primary care doctors are often the point of entry for most patients needing care, but in the fragmented healthcare system of the US, many patients and their providers experience problems with care coordination. For example, a Harris Interactive survey of California physicians found that:
- Four of every ten physicians report that their patients have had problems with coordination of their care in the last 12 months.
- More than 60% of doctors report that their patients “sometimes” or “often” experience long wait times for diagnostic tests.
- Some 20% of doctors report having their patients repeat tests because of an inability to locate the results during a scheduled visit.[226]
According to an article in The New York Times, the relationship between doctors and patients is deteriorating.[227] A study from Johns Hopkins University found that roughly one in four patients believe their doctors have exposed them to unnecessary risks, and anecdotal evidence such as self-help books and web postings suggest increasing patient frustration. Possible factors behind the deteriorating doctor/patient relationship include the current system for training physicians and differences in how doctors and patients view the practice of medicine. Doctors may focus on diagnosis and treatment, while patients may be more interested in wellness and being listened to by their doctors.[227]
Many primary care physicians no longer see their patients while they are in the hospital; instead, hospitalists are used.[228] The use of hospitalists is sometimes mandated by health insurance companies as a cost-saving measure which is resented by some primary care physicians.[229]
Administrative costs
As of 2017, there were 907 health insurance companies in the US,[230] although the top 10 account for about 53% of revenue and the top 100 account for 95% of revenue.[231]: 70 The number of insurers contributes to administrative overhead in excess of that in nationalized, single-payer systems, such as that in Canada, where administrative overhead was estimated to be about half of the US.[232]
Insurance industry group America’s Health Insurance Plans estimates that administrative costs have averaged approximately 12% of premiums over the last 40 years, with costs shifting away from adjudicating claims and towards medical management, nurse help lines, and negotiating discounted fees with healthcare providers.[233]
A 2003 study published by the Blue Cross and Blue Shield Association (BCBSA) also found that health insurer administrative costs were approximately 11% to 12% of premiums, with Blue Cross and Blue Shield plans reporting slightly lower administrative costs, on average, than commercial insurers.[234] For the period 1998 through 2003, average insurer administrative costs declined from 13% to 12% of premiums. The largest increases in administrative costs were in customer service and information technology, and the largest decreases were in provider services and contracting and in general administration.[235] The McKinsey Global Institute estimated that excess spending on “health administration and insurance” accounted for as much as 21% of the estimated total excess spending ($477 billion in 2003).[236]
According to a report published by the CBO in 2008, administrative costs for private insurance represent approximately 12% of premiums. Variations in administrative costs between private plans are largely attributable to economies of scale. Coverage for large employers has the lowest administrative costs. The percentage of premium attributable to administration increases for smaller firms, and is highest for individually purchased coverage.[237] A 2009 study published by BCBSA found that the average administrative expense cost for all commercial health insurance products was represented 9.2% of premiums in 2008.[238] Administrative costs were 11.1% of premiums for small group products and 16.4% in the individual market.[238]
One study of the billing and insurance-related (BIR) costs borne not only by insurers but also by physicians and hospitals found that BIR among insurers, physicians, and hospitals in California represented 20–22% of privately insured spending in California acute care settings.[239]
Long-term living facilities
As of 2014, according to a report published[240] the higher the skill of the RN the lower the cost of a financial burden on the facilities. With a growing elderly population, the number of patients in these long term facilities needing more care creates a jump in financial costs. Based on research done in 2010,[241] annual out of pocket costs jumped 7.5% while the cost for Medicare grew 6.7% annually due to the increases. While Medicare pays for some of the care that the elderly populations receive, 40% of the patients staying in these facilities pay out of pocket.[242]
Third-party payment problem and consumer-driven insurance
Most Americans pay for medical services largely through insurance, and this can distort the incentives of consumers since the consumer pays only a portion of the ultimate cost directly.[149] The lack of price information on medical services can also distort incentives.[149] The insurance which pays on behalf of insureds negotiate with medical providers, sometimes using government-established prices such as Medicaid billing rates as a reference point.[149] This reasoning has led for calls to reform the insurance system to create a consumer-driven healthcare system whereby consumers pay more out-of-pocket.[243] In 2003, the Medicare Prescription Drug, Improvement, and Modernization Act was passed, which encourages consumers to have a high-deductible health plan and a health savings account. In October 2019, the state of Colorado proposed running public healthcare option through private insurers, which are to bear the brunt of the costs. Premiums under the public option are touted to be 9% to 18% cheaper by 2022.[244][needs update]
Equity

Mental health
In 2020, 52.9 million adults were affected by mental illness, nearly one in five adults in the country. 44.7 million adults were affected in 2016.[246] In 2006, mental disorders were ranked one of the top five most costly medical conditions, with expenditures of $57.5 billion (equivalent to $83.6 billion in 2023[109]).[247] A lack of mental health coverage for Americans bears significant ramifications to the US economy and social system. A report by the US Surgeon General found that mental illnesses are the second leading cause of disability in the nation and affect 20% of all Americans.[248] It is estimated that less than half of all people with mental illnesses receive treatment (or specifically, an ongoing, much needed, and managed care; where medication alone, cannot easily remove mental conditions) due to factors such as stigma and lack of access to care,[249] including a shortage of mental health professionals.[250] Treatment rates are understood to vary between different conditions; as an example, only 16% of adults with schizophrenia and 25% with bipolar disorder were estimated to be untreated with appropriate medication in 2007.[251] Some entities try to expand access to mental health services by providing access on a sliding-scale or reduced fee structure. Networks such as Open Path Collective are composed of professionals who offer their services to people who cannot otherwise find affordable treatment through insurance.[252]
The Paul Wellstone Mental Health and Addiction Equity Act of 2008 mandates that group health plans provide mental health and substance-related disorder benefits that are at least equivalent to benefits offered for medical and surgical procedures. The legislation renews and expands provisions of the Mental Health Parity Act of 1996. The law requires financial equity for annual and lifetime mental health benefits, and compels parity in treatment limits and expands all equity provisions to addiction services. Insurance companies and third-party disability administrators (most notably, Sedgwick CMS) used loopholes and, though providing financial equity, they often worked around the law by applying unequal copayments or setting limits on the number of days spent in inpatient or outpatient treatment facilities.[253][254]
Oral health
In the US, dental care is largely not recognized as healthcare, even though individuals visit a dentist more often than a general practitioner,[255] and thus the field and its practices developed independently. In modern policy and practice, oral health is thus considered distinct from primary health, and dental insurance is separate from health insurance. Disparities in oral healthcare accessibility mean that many populations, including those without insurance, the low-income, uninsured, racial minorities, immigrants, and rural populations, have a higher probability of poor oral health at every age. While changes have been made to address these disparities for children, the oral health disparity in adults of all previously listed populations has remained consistent or worsened.[256]
The magnitude of this health issue is surprising even in New York state, where the Medicaid program includes dental coverage and is one of the most impressive insurance programs in the nation. Seven out of ten older adults (aged ≥ 65) have periodontal disease, and one in four adults (aged > 65) has no teeth.[257] This raises concern about the New York State Department of Health’s rule, which prevents Medicaid coverage for the replacement of dentures within eight years of initial placement and a ban on coverage of dental implants.[258] In addition, older adults are more likely than those in younger age groups to have medical conditions, such as diabetes and cardiovascular disease, that worsen their oral health.
Medical underwriting and the uninsurable
Prior to the ACA, medical underwriting was common, but, after the law came into effect in 2014, it became effectively prohibited.[259]
Demographic differences

Health disparities are well documented in the United States in ethnic minorities such as African Americans, Native Americans, and Hispanics.[260] When compared to white people, these minority groups have a higher incidence of chronic diseases, higher mortality, poorer health outcomes, and poorer rates of diagnosis and treatment.[261][262] Among the disease-specific examples of racial and ethnic disparities in the US is the cancer incidence rate among African Americans, which is 25% higher than among white people.[263] In addition, adult African Americans and Hispanics have approximately twice the risk as white people of developing diabetes and have higher overall obesity rates.[264] Minorities also have higher rates of cardiovascular disease and HIV/AIDS than white people.[263] In the US, racial demographics are as follows: Asian American (87.1 years), followed by Latino (83.3 years), White (78.9 years), Native American (76.9 years), and African American (75.4 years).[265] A 2001 study found distinguished racial differences exist in healthy life expectancy at lower levels of education.[266]
Public spending is positively correlated with age; average per capita public spending for seniors was more than five times that for children ($6,921 versus $1,225, equivalent to $12,099 versus $2,142 in 2024[32]). Average public spending for non-Hispanic blacks ($2,973, equivalent to $5,197 in 2024[32]) was slightly higher than that for white people ($2,675, equivalent to $4,676 in 2024[32]) while spending for Hispanics ($1,967, equivalent to $3,439 in 2024[32]) was significantly lower than the population average ($2,612, equivalent to $4,566 in 2024[32])). Total public spending is also strongly correlated with self-reported health status ($13,770 [equivalent to $24,073 in 2024[32]] for those reporting “poor” health versus $1,279 [equivalent to $2,236 in 2024[32]] for those reporting “excellent” health).[134] Seniors make up 13% of the population but take one-third of all prescription drugs. The average senior fills 38 prescriptions annually.[267] A new study has also found that older men and women in the South are more likely to be prescribed antibiotics than older Americans elsewhere, even though there is no evidence that the South has higher rates of diseases requiring antibiotics.[268]
There is considerable research into inequalities in healthcare where in certain cases, these inequalities are caused by income disparities that result in lack of health insurance and other barriers, such as medical equipment, to receiving necessary services. In some cases, these inequalities are caused by income disparities that result in lack of health insurance and other barriers, such as medical equipment, to receiving services.[269] According to the 2009 National Healthcare Disparities Report, uninsured Americans are less likely to receive preventive services in healthcare.[270] For example, minorities are not regularly screened for colon cancer and the death rate for colon cancer has increased among African Americans and Hispanic people. In other cases, inequalities in healthcare reflect a systemic bias in the way medical procedures and treatments are prescribed for different racial and ethnic groups. Raj Bhopal, professor emeritus at University of Edinburgh, writes that the history of racism in science and medicine shows that people and institutions behave according to the ethos of their times.[271] Nancy Krieger, professor of social epidemiology at Harvard, wrote that racism underlies unexplained inequities in healthcare, including treatment for heart disease,[272] renal failure,[273] bladder cancer,[274] and pneumonia.[275] Results from a 2023 scoping review of the literature found that in studies conducted in multiracial or multiethnic populations, race or ethnicity variables were rarely included in conceptually thoughtful and analytically informative ways concerning race or ethnicity as markers of exposure to racialized social disadvantage.[276][277] Bhopal writes that these inequalities have been documented in numerous studies whose consistent and repeated findings were that Black Americans received less healthcare than white Americans—particularly when the care involved expensive new technology. The consistent and repeated findings were that Black Americans received less healthcare than white Americans—particularly when the care involved expensive new technology.[278] One recent study has found that when minority and white patients use the same hospital, they are given the same standard of care.[279][280] The lack of equitable access to different resources is intrinsically tied to the field of public health, which works to supplement the traditional medical system with other services and opportunities.
Medical devices are expensive because the process of designing and approving them is extensive and costly, requiring that they be sold at higher than market price. The costs include research, design and development, meeting the U.S. Food and Drug Administration’s regulatory guidelines, manufacture, marketing, distribution, and business plan.[281] Cost, alongside the impact of systematic oppression and inequality of communities of color within healthcare, together make medical equipment inaccessible. Most studies focused on access to medical devices and enhancement of affordable local production have concluded that increasing access to medical devices in an attempt to meet healthcare needs is highly critical.[282] Audio-based telehealth has been identified as a tool for improving healthcare access among underserved populations, including older adults, rural communities, and Black, Indigenous, and People of Color (BIPOC).[283]
The increase of artificial intelligence (AI) in health care raises issues of equity and bias related to how health applications are developed and used. AI expansion is now of serious global interest towards public and private investment. The Harrow Council launched the IBM Watson Care Manager system to match individuals, considering budget, with a provider and develop individual care plans.[284] Within the US, the FDA in 2017 cleared an AI medical imaging platform for clinical use as well as future devices.[285] A recent scoping review identified 18 equity issues with 15 strategies to address them to try to ensure that AI applications equitably meet the needs of the populations intended to benefit from them.[286]
Coverage of social determinants of health
The access to medical care and services in the US is tied to the field of public health, which works to supplement the traditional medical system with other services and opportunities to improve the social determinants of health (SDOH) of populations. SDOH are external factors, systems, and structures that shape the experiences of different individuals and their access to healthcare.[287] Examples of SDOH are poverty, work conditions, exposure to violence, substance abuse history, housing insecurity, and more. Studies have shown that people have adverse SDOH are more likely to experience negative health effects. [288] In order to address these other upstream factors, some states have implemented Section 1115 waivers under Medicaid and Children’s Health Insurance Program (CHIP), which allow for coverage of nontraditional services such as home-delivered meals, medical transportation, and educational services.[289]
Trauma-informed care
Some providers in the US advocate for the use of Trauma-informed care frameworks within their practice. Trauma-informed care frameworks center a patient’s experience with trauma in the treatment plan and view medical care as one aspect of treatment. Advocates argue that doing so fosters more equitable and culturally sensitive care that is especially important when serving patients from marginalized communities.[290] Clinically, trauma-informed care can strengthen the social determinants of health of patients, as well as provide impactful interventions for patients at high risk. [290] In violent trauma care settings, providers have been advocating for the implementation of Hospital-Based Intervention Programs (HVIPs) at all Level 1 trauma centers to deliver trauma-informed care addressing social determinants of health of patients post-injury, in order to better prevent re-injury.[291][290] Others suggest that upstream education during medical training is more beneficial, so healthcare providers themselves can manage clinical medicine and SDOH together. [290]
Drug efficiency and safety

The FDA[292] is the primary institution tasked with the safety and effectiveness of human and veterinary drugs. It also is responsible for making sure drug information is accurately and informatively presented to the public. The FDA reviews and approves products and establishes drug labeling, drug standards, and medical device manufacturing standards. It sets performance standards for radiation and ultrasonic equipment.
One of the more contentious issues related to drug safety is immunity from prosecution. In 2004, the FDA reversed a federal policy, arguing that FDA premarket approval overrides most claims for damages under state law for medical devices. In 2008, this was confirmed by the Supreme Court in Riegel v. Medtronic, Inc.[293]
On June 30, 2006, an FDA ruling went into effect extending protection from lawsuits to pharmaceutical manufacturers, even if it was found that they submitted fraudulent clinical trial data to the FDA in their quest for approval. This left consumers who experience serious health consequences from drug use with little recourse. In 2007, the House of Representatives expressed opposition to the FDA ruling, but the Senate took no action. On March 4, 2009, an important US Supreme Court decision was handed down. In Wyeth v. Levine, the court asserted that state-level rights of action could not be pre-empted by federal immunity and could provide “appropriate relief for injured consumers”.[294] In June 2009, under the Public Readiness and Emergency Preparedness Act, Secretary of Health and Human Services Kathleen Sebelius signed an order extending protection to vaccine makers and federal officials from prosecution during a declared health emergency related to the administration of the swine flu vaccine.[295][296]
Prescription drug prices
During the 1990s, the price of prescription drugs became a major issue in US politics as the prices of many new drugs increased significantly, and many citizens discovered that neither the government nor their insurer would cover the cost of such drugs. Per capita, the US spends more on pharmaceuticals than any other country, although expenditures on pharmaceuticals accounts for a smaller share (13%) of total healthcare costs compared to an OECD average of 18% (2003 figures).[297] Some 25% of out-of-pocket spending by individuals is for prescription drugs.[298] Another study finds that between 1990 and 2016, prescription drug prices in the US increased by 277% while prescription drug prices increased by only 57% in the UK, 13% in Canada, and decreased in France and Japan.[299] A November 2020 study by the West Health Policy Center stated that more than 1.1 million senior citizens in the U.S. Medicare program are expected to die prematurely over the next decade because they will be unable to afford their prescription medications, requiring an additional $17.7 billion to be spent annually on avoidable medical costs due to health complications.[300]
The US government has taken the position (through the Office of the US Trade Representative) that US drug prices are rising because US consumers are effectively subsidizing costs which drug companies cannot recover from consumers in other countries (because many other countries use their bulk-purchasing power to aggressively negotiate drug prices).[301] The US position (consistent with the primary lobbying position of the Pharmaceutical Research and Manufacturers of America) is that the governments of such countries are free riding on the backs of US consumers. Such governments should either deregulate their markets, or raise their domestic taxes in order to fairly compensate US consumers by directly remitting the difference (between what the companies would earn in an open market versus what they are earning now) to drug companies or to the US government. In turn, pharmaceutical companies would be able to continue to produce innovative pharmaceuticals while lowering prices for US consumers. Currently, the US, as a purchaser of pharmaceuticals, negotiates some drug prices but is forbidden by law from negotiating drug prices for the Medicare program due to the Medicare Prescription Drug, Improvement, and Modernization Act passed in 2003. Democrats have charged that the purpose of this provision is merely to allow the pharmaceutical industry to profiteer off of the Medicare program.[302]
Impact of drug companies
The US, along with New Zealand, make up the only countries in the world that allows direct-to-consumer advertising of prescription drugs. The Food and Drug Administration in the United States, mainly under the Federal Food, Drug, and Cosmetic, oversees the advertising of prescription drugs to ensure accurate and truthful communication. In 2015, the American Medical Association called for the banning of direct-to-consumer advertising because it is linked with increased drug prices.[303] Physicians, via various FDA surveys, conveyed varying thoughts regarding ads as they believe while patients were getting more involved in their own healthcare, they felt pressured to prescribe specific drugs or felt concern over methods of communication about risks and benefits of the drug.[304] Still, other evidence cites that there are some benefits to direct-to-consumer advertising, such as encouraging patients to see the doctor, diagnosis of rare diseases, and the removal of stigma associated with the disease.[305]
When healthcare legislation was being written in 2009, the drug companies were asked to support the legislation in return for not allowing importation of drugs from foreign countries.[306] There were and are many complications regarding drug legislation due to the relationship between pharmaceutical companies and the federal government. Legislation relating to drug prices in particular tends to cause several issues.[307] The Inflation Reduction Act of 2022, while still undergoing negotiations for roughly the next two years, attempts to renegotiate drug prices by amending the non-interference clause in the Medicare Part D program.[308] The non-interference clause states that the government is prohibited from interfering in negotiations with drug manufacturers, insurers and pharmacies.[309]

In 2008, prior to the major healthcare reform in 2010, Americans were divided in their views of the US health system; 45% said that the US system was best and 39% said that other countries’ systems are better.[310][311]
Much of the historical debate around healthcare reform centered around single-payer healthcare, and particularly pointing to the hidden costs of treating the uninsured[312] while free-market advocates point to freedom of choice in purchasing health insurance[313][314][315] and unintended consequences of government intervention, citing the Health Maintenance Organization Act of 1973.[316]
According to a 2020 study published in The Lancet, a single-payer universal healthcare system could save 68,000 lives and $450 billion in national healthcare expenditure annually,[317] while another 2022 study published in the PNAS, estimated that a universal healthcare system could have saved more than 338,000 lives during the COVID-19 pandemic in the US from its start until March 2022.[318]
Ultimately, a single-payer healthcare, sometimes called “socialized medicine“,[319][320] was not adopted in the final ACA.
Patient Protection and Affordable Care Act (2010)
The ACA (Public Law 111–148) is a healthcare reform bill that was signed into law in the US by President Barack Obama on March 23, 2010. The law includes a large number of health-related provisions, most of which took effect in 2014, including expanding Medicaid eligibility for people making up to 133% of FPL,[321] subsidizing insurance premiums for individuals and families making up to 400% of FPL and capping expenses from 2% to 9.8% of annual income.[322][323] For the first time, all health policies sold in the US must cap an individual’s (or family’s) medical expenses out of pocket annually.[324] Other provisions include providing incentives for businesses to provide healthcare benefits, prohibiting denial of coverage and denial of claims based on pre-existing conditions, establishing health insurance exchanges, prohibiting insurers from establishing annual spending caps and support for medical research. The costs of these provisions are offset by a variety of taxes, fees, and cost-saving measures, such as new Medicare taxes for high-income brackets, taxes on indoor tanning, cuts to the Medicare Advantage program in favor of traditional Medicare, and fees on medical devices and pharmaceutical companies;[325] there is also a tax penalty for citizens who do not obtain health insurance (unless they are exempt due to low income or other reasons).[326] The Congressional Budget Office estimates that the net effect (including the reconciliation act) will be a reduction in the federal deficit by $143 billion over the first decade.[327] However, two months later, the office subsequently acknowledged that there was an additional $115 billion in funds needed that were not originally included in the estimate. Additionally, the CBO estimated that although projected premiums in 2016 would be lower by $100 per person for small and large business health insurance plans with the ACA than without, individual plans would be higher by $1,900 with the bill.[328]
The first open enrollment period of the ACA began in October 2013. Prior to this period, access to healthcare and insurance coverage trends were worsening on a national level. A large, national survey of US adults found that after the act’s first two enrollment periods, self-reported coverage, health, and access to care improved significantly. Furthermore, insurance coverage for low-income adults were significantly greater in states that expanded Medicaid in comparison with states that did not expand Medicaid.[329] However, discrepancies do exist between those covered by Medicaid versus those covered by private insurance. Those insured by Medicaid tend to report fair or poor health, as opposed to excellent or very good health.[330]
On December 22, 2017, the Tax Cuts and Jobs Act of 2017 was signed into law by President Donald Trump. Inside the final version of the bill was a repeal of the individual mandate in the ACA, which required individuals and companies to get healthcare for themselves and their employees. It was this mandate which kept healthcare costs down under the PPACA by promoting cost sharing over a larger pool. Economists believe the repeal of the individual mandate will lead to higher premiums and lower enrollment in the current market though they do not agree with how much.[331] In 2017, the new Republican healthcare bill known as the American Health Care Act was passed by the House of Representatives under President Donald Trump. Although the ACA and the American Health Care Act both propose tax cuts in order to make insurance more affordable for Americans, each of these bills affected Americans in different ways. The people most affected by President Trump’s plan are young people, individuals of a higher socioeconomic status, and people who live in urban areas. Young people because individuals between the age of 20 and 30 will see drops in the premiums they pay within their plans. Individuals with higher socioeconomic status because whereas under Obamacare individuals could only make up to $50,000 annually and still receive tax breaks, now under Trump’s plan that number has been increased so that individuals who make up to $115,000 annually can receive tax breaks. In addition, those in urban areas can also benefit from the plan because under Obamacare tax credits were designated also by the cost of local healthcare, but the American Health Care Act does not take this into consideration although rural healthcare is generally more expensive due to the lack of hospitals and available services.[332]
In May 2023, an international daily, in its article on the US healthcare system, asserted on the need for United States to guarantee healthcare to all its citizens as a basic human right.[333]
Of the 26.2 million foreign immigrants living in the US in 1998, 62.9% were non-US citizens. In 1997, 34.3% of non-US citizens living in the US did not have health insurance coverage opposed to the 14.2% of native-born Americans who do not have health insurance coverage. Among those immigrants who became citizens, 18.5% were uninsured, as opposed to noncitizens, who are 43.6% uninsured. In each age and income group, immigrants are less likely to have health insurance.[334] With the recent healthcare changes, many legal immigrants with various immigration statuses now are able qualify for affordable health insurance.[335]
Undocumented immigrants within the US do not have access to government funded health insurance. Although the ACA allows immigrants to receive insurance at a discounted rate, the same does not go for those without US citizenship.[336] While policies like the Patient Protection Act and Affordable Care Act have aimed at expanding health insurance coverage to also improve refugee health in the US, different states have implemented their health insurance programs differently leading to healthcare access disparities between states.[337] Undocumented immigrants in the US can seek medical help from community centers, or what is termed Safety Net Providers, and participate in fee for service medical assistance, but can only buy health insurance from private health insurers.[338]
- Biomedical research in the United States
- Canadian and American health care systems compared
- Centers for Disease Control and Prevention timeline
- Health in the United States
- Health Care and Education Reconciliation Act of 2010
- Health care compared – tabular comparisons of the US, Canada, and other countries not shown above.
- Health care industry
- Health care politics
- Health care systems (including comparisons)
- Health insurance cooperative
- Healthcare reform in the United States
- Healthy People program
- Health spending as percent of gross domestic product (GDP) by country
- List of countries by total health expenditure per capita
- List of healthcare accreditation organizations in the United States
- Medical centers in the United States
- Medical debt
- Medical education in the United States
- Medicare for All Act
- Medicare Rights Center
- Medicare Sustainable Growth Rate
- Military Health System
- Osteopathic medicine in the United States
- School health services
- Universal Health Care Foundation of Connecticut
- Visitor health insurance
- ^ “Governor Hochul, Mayor Adams Announce Plan for SPARC Kips Bay, First-of-Its-Kind Job and Education Hub for Health and Life Sciences Innovation”. State of New York. October 13, 2022. Retrieved May 29, 2024.
- ^ a b c “How to Improve Access to Health Care: Issues & Potential Solutions”. healthadministrationdegree.usc.edu. Los Angeles and Sacramento, California: USC Price School of Public Policy, University of Southern California. 2023. Archived from the original on April 21, 2023. Retrieved May 12, 2023.
- ^ Vladeck, Bruce (January 2003). “Universal Health Insurance in the United States: Reflections on the Past, the Present, and the Future”. American Journal of Public Health. 93 (1): 16–19. doi:10.2105/AJPH.93.1.16. ISSN 0090-0036. PMC 1447684. PMID 12511377.
- ^ Fisher M (June 28, 2012). “Here’s a Map of the Countries That Provide Universal Health Care (America’s Still Not on It)”. The Atlantic.
- ^ “The U.S. Health Care System: An International Perspective – DPEAFLCIO”. dpeaflcio.org. August 15, 2016.
- ^ Papanicolas, Irene. “Health Care Spending in the United States and Other High-Income Countries”. National Library of Medicine. US Department of Health and Services. Retrieved March 12, 2025.
- ^ Fullman N, Yearwood J, Abay SM, Abbafati C, Abd-Allah F, Abdela J, et al. (GBD 2016 Healthcare Access and Quality Collaborators) (June 2018). “Measuring performance on the Healthcare Access and Quality Index for 195 countries and territories and selected subnational locations: a systematic analysis from the Global Burden of Disease Study 2016”. Lancet. 391 (10136): 2236–2271. doi:10.1016/S0140-6736(18)30994-2. PMC 5986687. PMID 29893224.
- ^ Murdock, Christopher J.; Laurencin, Lynne; Christensen, Donna M.; Laurencin, Cato T. (June 2018). “HIV/AIDS and the African-American Community 2018: A Decade Call To Action”. Journal of Racial and Ethnic Health Disparities. 5 (3). Springer Nature: 449–458. doi:10.1007/s40615-018-0491-0. ISSN 2196-8837. PMC 8224540. PMID 29869005.
- ^ Guilamo-Ramos, V; Thimm-Kaiser, M; Benzekri, A; Chacón, G; Rios, E; Scaccabarrozzi, L (January 2020). “The Invisible US Hispanic/Latino HIV Crisis: Addressing Gaps in the National Response”. American Journal of Public Health. 110 (1). American Public Health Association: 27–31. doi:10.2105/AJPH.2019.305309. ISSN 0090-0036. PMC 6893335. PMID 31725313.
- ^ Lee, S.; Martinez, G.; Ma, G.; Hsu, C. E.; Robinson, E. S.; Bawa, J.; Juon, H.-S. (January–February 2010). Glover, Elbert D. (ed.). “Barriers to Health Care Access in 13 Asian American Communities”. American Journal of Health Behavior. 34 (1). PNG Publications and Scientific Research Limited: 21–30. doi:10.5993/AJHB.34.1.3. ISSN 1945-7359. PMC 6628721. PMID 19663748. S2CID 31669071.
- ^ Armstrong, Katrina; Putt, Mary; Halbert, Chanita H.; Grande, David; Schwartz, Jerome Sanford; Liao, Kaijun; Marcus, Noora; Demeter, Mirar B.; Shea, Judy A. (February 2013). “Prior Experiences of Racial Discrimination and Racial Differences in Health Care System Distrust”. Medical Care. 51 (2). Lippincott Williams & Wilkins on behalf of the American Public Health Association: 144–150. doi:10.1097/mlr.0b013e31827310a1. ISSN 0025-7079. PMC 3552105. PMID 23222499. S2CID 46125799.
- ^ Kliff, Sarah; Katz, Josh (August 22, 2021). “Hospitals and Insurers Didn’t Want You to See These Prices. Here’s Why”. The Upshot. The New York Times. eISSN 1553-8095. ISSN 0362-4331. OCLC 1645522. Archived from the original on December 31, 2021. Retrieved July 18, 2022.
- ^ Rosenthal E (December 21, 2013). “News Analysis – Health Care’s Road to Ruin”. New York Times. Retrieved December 22, 2013.
- ^ a b c d “Improving Europe’s competitiveness”. EFPIA. Archived from the original on August 23, 2009. Retrieved November 6, 2016.
- ^ a b c d Stats from 2007 Europ.Fed.of Pharm.Indust.and Assoc. Retrieved June 17, 2009, from [1][permanent dead link]
- ^ Grant Rigney (March 3, 2023). “United States: #11 in the 2022 World Index of Healthcare Innovation. America’s runaway leadership in science and technology is marred by a fiscally unsustainable system of costly health care”. freopp.org. Retrieved April 27, 2023.
- ^ Health, Institute of Medicine (US) Committee for the Study of the Future of Public (1988). A History of the Public Health System. National Academies Press (US).
- ^ “AMA (AMA History) 1847 to 1899”. American Medical Association. Archived from the original on February 9, 2009. Retrieved February 16, 2009.
- ^ a b Adams, Tracey L. (October 20, 2020). “Health professional regulation in historical context: Canada, the USA and the UK (19th century to present)”. Human Resources for Health. 18 (1): 72. doi:10.1186/s12960-020-00501-y. ISSN 1478-4491. PMC 7572238. PMID 33076923.
- ^ Michael, Jerrold M (2011). “The National Board of Health: 1879–1883”. Public Health Reports. 126 (1): 123–129. doi:10.1177/003335491112600117. ISSN 0033-3549. PMC 3001811. PMID 21337938.
- ^ Shi; Singh (2019). Delivering health care in America : a systems approach (7th ed.). Jones & Bartlett Learning.
- ^ Raffel, M. W. (1980). The U.S. health system : origins and functions. New York : Wiley.
- ^ Carl Bridenbaugh, Cities in the Wilderness: The First Century of Urban Life in America 1625-1742 (1938) p 401
- ^ Robinson, Martha. 2005. New Worlds, New Medicines: Indian Remedies and English Medicine in Early America. Early American Studies (Spring): 94-110.
- ^ Jacob Ernest Cooke, ed. Encyclopedia of the North American colonies (3 vol 1992) 1:214
- ^ Richard Morris Encyclopedia of American History (1976) p 806.
- ^ Breslaw, Elaine G. (March 2014). Lotions, Potions, Pills, and Magic: Health Care in Early America. NYU Press. ISBN 978-1479807048.
- ^ Thomasson MA (July 2002). “From Sickness to Health: The Twentieth-Century Development of U.S. Health Insurance”. Explorations in Economic History. 39 (3): 233–253. doi:10.1006/exeh.2002.0788. S2CID 30393803.
- ^ Gruber, Jonathan (2011). “The Impacts of the Affordable Care Act: How Reasonable Are the Projections?”. National Tax Journal. 64 (3): 893–908. doi:10.17310/ntj.2011.3.06. hdl:1721.1/72971. S2CID 232213290. Archived from the original on June 20, 2016. Retrieved July 23, 2017.
- ^ a b c “Overview of U.S. Hospital Stays in 2016: Variation by Geographic Region #246”. www.hcup-us.ahrq.gov. Retrieved November 10, 2019.
- ^ “Overview of Hospital Stays in the United States, 2011 – Statistical Brief #166”. www.hcup-us.ahrq.gov. Retrieved November 10, 2019.
- ^ a b c d e f g h i j k l m n o p q r s t 1634–1699:McCusker, J. J. (1997). How Much Is That in Real Money? A Historical Price Index for Use as a Deflator of Money Values in the Economy of the United States: Addenda et Corrigenda (PDF). American Antiquarian Society. 1700–1799:McCusker, J. J. (1992). How Much Is That in Real Money? A Historical Price Index for Use as a Deflator of Money Values in the Economy of the United States (PDF). American Antiquarian Society. 1800–present:Federal Reserve Bank of Minneapolis. “Consumer Price Index (estimate) 1800–”. Retrieved February 29, 2024.
- ^ Weiss AJ, Elixhauser A (2006). “Overview of Hospital Stays in the United States, 2012: Statistical Brief #180”. Healthcare Cost and Utilization Project (HCUP) Statistical Briefs. Agency for Healthcare Research and Quality (US). PMID 25506966. Retrieved November 10, 2019.
- ^ “FastStats”. www.cdc.gov. September 4, 2019. Retrieved November 10, 2019.
- ^ Alemayehu B, Warner KE (June 2004). “The lifetime distribution of health care costs”. Health Services Research. 39 (3): 627–642. doi:10.1111/j.1475-6773.2004.00248.x. PMC 1361028. PMID 15149482.
- ^ a b Institute of Medicine. Committee on the Consequences of Uninsurance (January 13, 2004). Insuring America’s health: principles and recommendations. Washington, DC: National Academies Press. p. 25. ISBN 978-0-309-52826-9.
- ^ Health Care Problems in Rural and Small Communities (Macon, Ga., and Atlanta, Ga.) Joint Hearings Before the Subcommittee on Health of the Committee on Finance and Committee on Governmental Affairs, United States Senate, Ninety-fifth Congress, First Session, August 16 and 18, 1977 By United States. Congress, Senate, Committee on Finance, Subcommittee on Health, 1978, P.126
- ^ The Book of Numbers, compiled by the Editors of Heron House, 1978, P.231
- ^ Access to health care in America. Institute of Medicine, Committee on Monitoring Access to Personal Health Care Services. Millman M, editor. Washington: National Academies Press; 1993.
- ^ a b c Blumenthal, David (2017). “The Decline of Employer-Sponsored Health Insurance”. commonwealthfund.org. doi:10.26099/dnqz-4g48. Retrieved November 25, 2018.
- ^ Himmelstein DU, Woolhandler S (March 2016). “The Current and Projected Taxpayer Shares of US Health Costs”. American Journal of Public Health. 106 (3): 449–52. doi:10.2105/AJPH.2015.302997. PMC 4880216. PMID 26794173.
Government’s share of overall health spending was 64% of national health expenditures in 2013
- ^ Leonard K (January 22, 2016). “Could Universal Health Care Save U.S. Taxpayers Money?”. U.S. News & World Report. Retrieved July 12, 2016.
- ^ “How FEHB Relates to Other Government Health Insurance”. FEDweek. May 25, 2017. Retrieved May 26, 2017.
- ^ “National Center for Health Statistics”. Cdc.gov. Retrieved December 1, 2016.
- ^ Docteur E, Oxley H (October 19, 2004). “Health-system reform: lessons from experience”. Towards high-performing health systems: policy studies. The OECD health project. Paris: OECD. pp. 25, 74. ISBN 978-92-64-01559-3.
- ^ “New study finds 45,000 deaths annually linked to lack of health coverage”. Harvard Gazette. September 17, 2009. Retrieved February 28, 2018.
- ^ a b Witters D (January 23, 2019). “U.S. Uninsured Rate Rises to Four-Year High”. Gallup News: Well-being. Retrieved August 13, 2019.
- ^ “Health Insurance Coverage in the United States: 2017”. census.gov. Retrieved November 25, 2018.
- ^ DeNavas-Walt C, Proctor BD, Smith JC (September 13, 2011). Income, poverty, and health insurance coverage in the United States: 2010 (PDF). U.S. Census Bureau: Current Population Reports, P60-239. Washington, DC: U.S. Government Printing Office.
- ^ Johnson, Avery (September 17, 2010). “Recession swells number of uninsured to 50.7 million”. The Wall Street Journal. p. A4. Retrieved November 21, 2010.
- Wolf R (September 17, 2010). “Number of uninsured Americans rises to 50.7 million”. USA Today. p. 8A. Retrieved November 21, 2010.
- DeNavas-Walt C, Proctor BD, Smith, Jessica C. (September 16, 2010). “Income, poverty, and health insurance coverage in the United States: 2009” (PDF). Washington, D.C.: U.S. Census Bureau. Retrieved November 21, 2010.
- Roberts M, Rhoades JA (August 19, 2010). “The uninsured in America, first half of 2009: estimates for the United States civilian noninstitutionalized population under age 65. Medical Expenditure Panel Survey, Statistical Brief #291” (PDF). Rockville, Md.: Agency for Healthcare Research and Quality (AHRQ). Retrieved November 21, 2010.
- Cohen RA, Martinez MA (September 22, 2010). “Health insurance coverage: early release of estimates from the National Health Interview Survey, January–March 2010” (PDF). Hyattsville, Md.: National Center for Health Statistics (NCHS). Retrieved November 21, 2010.
- “Comparing federal government surveys that count uninsured people in America” (PDF). Minneapolis, Minn.: State Health Access Data Assistance Center, School of Public Health, University of Minnesota. August 26, 2008. Archived from the original (PDF) on March 29, 2012. Retrieved November 21, 2010.
- ^ Dickman SL, Woolhandler S, Bor J, McCormick D, Bor DH, Himmelstein DU (July 2016). “Health Spending For Low-, Middle-, And High-Income Americans, 1963-2012” (PDF). Health Affairs. 35 (7): 1189–96. doi:10.1377/hlthaff.2015.1024. PMID 27385233.
- ^ a b c Dickman SL, Himmelstein DU, Woolhandler S (April 2017). “Inequality and the health-care system in the USA”. Lancet. 389 (10077): 1431–1441. doi:10.1016/s0140-6736(17)30398-7. PMID 28402825. S2CID 13654086.
- ^ “Status of State Medicaid Expansion Decisions: Interactive Map”. KFF. Map is updated as changes occur. Click on states for details. March 20, 2024.
- ^ a b Sommers BD, Gawande AA, Baicker K (August 2017). “Health Insurance Coverage and Health – What the Recent Evidence Tells Us”. The New England Journal of Medicine. 377 (6): 586–593. doi:10.1056/nejmsb1706645. PMID 28636831. S2CID 2653858.
- ^ Gaffney, Adam; McCormick, Danny (April 8, 2017). “The Affordable Care Act: implications for health-care equity”. The Lancet. 389 (10077): 1442–1452. doi:10.1016/S0140-6736(17)30786-9. ISSN 0140-6736. PMID 28402826.
- ^ Frean M, Gruber J, Sommers BD (May 2017). “Premium subsidies, the mandate, and Medicaid expansion: Coverage effects of the Affordable Care Act” (PDF). Journal of Health Economics. 53: 72–86. doi:10.1016/j.jhealeco.2017.02.004. hdl:1721.1/129483. PMID 28319791. S2CID 3759121.
- ^ Sommers BD (May 11, 2017). “State Medicaid Expansions and Mortality, Revisited: A Cost-Benefit Analysis” (PDF). American Journal of Health Economics. 3 (3): 392–421. doi:10.1162/ajhe_a_00080. ISSN 2332-3493. S2CID 53488456.
- ^ “Medical Debt Huge Bankruptcy Culprit – Study: It’s Behind Six-In-Ten Personal Filings”. CBS. June 5, 2009. Archived from the original on June 8, 2009. Retrieved June 22, 2009.
- ^ Kavilanz PB (March 5, 2009). “Underinsured Americans: Cost to you”. CNN.
- ^ Kelley AS, McGarry K, Fahle S, Marshall SM, Du Q, Skinner JS (February 2013). “Out-of-pocket spending in the last five years of life”. Journal of General Internal Medicine. 28 (2): 304–9. doi:10.1007/s11606-012-2199-x. PMC 3614143. PMID 22948931.
- ^ Groman R (2004). “The Cost of Lack of Health Insurance” (PDF). American College of Physicians. Archived from the original (PDF) on July 7, 2016. Retrieved October 22, 2017.
- ^ Schoen C, Doty MM, Collins SR, Holmgren AL (June 14, 2005). “Insured but not protected: how many adults are underinsured?”. Health Affairs. 24 (Suppl 1 Web Exclusives): W5-289-W5-302. doi:10.1377/hlthaff.w5.289. PMID 15956055.
- ^ Davis K, Ballreich J (October 2014). “Equitable access to care–how the United States ranks internationally”. The New England Journal of Medicine. 371 (17): 1567–1570. doi:10.1056/nejmp1406707. PMID 25337745. S2CID 205110579.
- ^ Link between health spending and life expectancy: US is an outlier. May 26, 2017. By Max Roser at Our World in Data. Click the sources tab under the chart for info on the countries, healthcare expenditures, and data sources. See the later version of the chart here.
- ^ a b Kenworthy L (July 10, 2011). “America’s inefficient health-care system: another look”. Consider the Evidence (blog). Retrieved September 11, 2012.
- ^ a b c “Country Comparison: Life Expectancy at Birth”. The World Factbook. CIA. Archived from the original on January 2, 2018. Retrieved April 22, 2017.
- ^ a b c Murray CJ, Atkinson C, Bhalla K, Birbeck G, Burstein R, Chou D, et al. (August 2013). “The state of US health, 1990-2010: burden of diseases, injuries, and risk factors” (PDF). JAMA. 310 (6): 591–608. doi:10.1001/jama.2013.13805. PMC 5436627. PMID 23842577.
- ^ Noguchi, Yuki (December 22, 2022). “American life expectancy is now at its lowest in nearly two decades”. NPR. Retrieved June 22, 2023.
- ^ Mortality rate, under-5 (per 1,000 live births). World Bank Data. World Development Indicators. World DataBank.
- ^ a b “Global Health Observatory (GHO) data: Maternal mortality ratio (per 100 000 live births), by WHO region, 2015”. World Health Organization. Retrieved September 5, 2017.
- ^ Morello C (May 2, 2014). “Maternal deaths in childbirth rise in the U.S.” Washington Post. Retrieved May 5, 2015.
- ^ a b “Global Health Observatory (GHO) data: Life expectancy data by country”. World Health Organization. Retrieved September 5, 2017.
- ^ a b c “World Health Statistics 2016 Monitoring health for the SDGs: Annex B, Tables of health statistics by country, WHO region, and globally” (PDF). World Health Organization. Retrieved September 5, 2017.
- ^ National Research Council and Institute of Medicine. (2013) “U.S. Health in International Perspective: Shorter Lives, Poorer Health” Panel on Understanding Cross-National Health Differences Among High-Income Countries, Steven H. Woolf and Laudan Aron, Eds. Committee on Population, Division of Behavioral and Social Sciences and Education, and Board on Population Health and Public Health Practice, Institute of Medicine. Washington, DC: The National Academies Press.
- ^ a b c “Institute for Health Metrics and Evaluation: United States both sexes, all ages, deaths per 100,000”. healthdata.org. Retrieved September 5, 2017.
- ^ “FastStats”. cdc.gov. August 3, 2017. Retrieved February 28, 2018.
- ^ “U.S. Ranks Below 16 Other Rich Countries In Health Report”. Npr.org. January 9, 2013. Retrieved December 1, 2016.
- ^ Case, Anne; Deaton, Angus (2021). Deaths of Despair and the Future of Capitalism. Princeton University Press. p. ix. ISBN 978-0691217079.
- ^ “Suicides in the U.S. reached all-time high in 2022, CDC data shows”. NBC News. August 10, 2023. Retrieved August 15, 2023.
- ^ Mateus, Benjamin (August 11, 2023). “Deaths of despair and suicides in the US at historic levels”. World Socialist Web Site. Retrieved August 15, 2023.
- ^ Danelski, David (April 17, 2023). “Poverty is the 4th greatest cause of U.S. deaths”. news.ucr.edu. Retrieved June 23, 2023.
- ^ Brady, David; Kohler, Ulrich; Zheng, Hui (2023). “Novel Estimates of Mortality Associated With Poverty in the US”. The Journal of the American Medical Association. 183 (6): 504–628. doi:10.1001/jamainternmed.2023.0276. PMC 10111231. PMID 37067817.
- ^ Murez, Cara (April 18, 2023). “America’s 4th Leading Cause of Death: Poverty”. U.S. News & World Report. Retrieved August 15, 2023.
- ^ Jarow, Oshan (July 14, 2023). “Poverty is a major public health crisis. Let’s treat it like one”. Vox. Retrieved August 24, 2023.
- ^ “Products – Data Briefs – Number 427 – December 2021”. www.cdc.gov. December 21, 2021. doi:10.15620/cdc:112079. S2CID 54466506. Retrieved March 3, 2022.
- ^ Noguchi, Yuki (December 22, 2022). “American life expectancy is now at its lowest in nearly two decades”. NPR. Retrieved December 27, 2022.
The new numbers also speak to the acute mental health crisis that’s run parallel to the pandemic: Deaths from drug overdoses reached over 106,000 last year — another major factor reducing life expectancy, according to the second CDC analysis released on Thursday. Deaths by suicide and from liver disease, or cirrhosis, caused by alcohol also increased — shortening the average American life span.
- ^ Diamond, Dan (December 28, 2023). “America has a life expectancy crisis. But it’s not a political priority”. The Washington Post. Retrieved December 29, 2023.
While recent federal data suggests that life expectancy ticked up in 2022, a partial rebound from the ravages of the coronavirus pandemic, no national strategy exists to reverse a years-long slide that has left the United States trailing peers, such as Canada and Germany, and rivals, such as China.
- ^ Trani, Olivia (March 13, 2023). “Child and teen mortality in the U.S. experiences largest increase in decades”. VCU News. Retrieved June 15, 2023.
- ^ de Visé, Daniel (March 22, 2023). “Child mortality is rising at the fastest rate in 50 years”. The Hill. Retrieved June 15, 2023.
- ^ Hameed, Ishaque; Nusrat, Khushboo; Jamil, Adeena; Fatima, Kaneez; Minhas, Abdul Mannan Khan; Greene, Stephen J.; Sauer, Andrew J.; Butler, Javed; Khan, Muhammad Shahzeb (2024). “Demographic and Regional Trends of Cardiovascular Disease and Obesity-Related Mortality in the United States From 1999 to 2021”. The American Journal of Cardiology. 233: 51–54. doi:10.1016/j.amjcard.2024.09.028. PMID 39374685.
- ^ “Obesity-related deaths on the rise in US—but there is good news for cardiologists”. cardiovascularbusiness.com. October 10, 2024. Retrieved October 12, 2024.
- ^ “100 of the largest hospitals and health systems in America”, Becker’s Hospital Review
- ^ “Fast Facts on U.S. Hospitals, 2018 | AHA”. American Hospital Association. Retrieved February 28, 2018.
- ^ David G (May 2005). “The Convergence between For-Profit and Nonprofit Hospitals in the United States” (PDF). Archived from the original (PDF) on February 26, 2006.
- ^ “The Hill–Burton Act | The Center On Congress at Indiana University”. Congress.indiana.edu. Archived from the original on November 3, 2014. Retrieved December 1, 2016.
- ^ “15 largest health systems in the U.S.” beckershospitalreview.com. June 15, 2016. Retrieved May 17, 2019.
- ^ “Dignity-CHI merger creates largest nonprofit health system by revenue”. Healthcare Dive. Retrieved May 17, 2019.
- ^ Cohen GR, Jones DJ, Heeringa J, Barrett K, Furukawa MF, Miller D, et al. (December 2017). “Leveraging Diverse Data Sources to Identify and Describe U.S. Health Care Delivery Systems”. eGEMs. 5 (3): 9. doi:10.5334/egems.200 (inactive February 28, 2025). PMC 5983023. PMID 29881758.
{{cite journal}}: CS1 maint: DOI inactive as of February 2025 (link) - ^ “Boosting competition among hospitals, health systems will improve health care”. STAT. September 20, 2017. Retrieved May 22, 2019.
- ^ Diamond D (November 8, 2017). “A nation of McHospitals?”. The Agenda. Retrieved May 24, 2019.
- ^ Casalino LP, Pesko MF, Ryan AM, Mendelsohn JL, Copeland KR, Ramsay PP, et al. (September 2014). “Small primary care physician practices have low rates of preventable hospital admissions”. Health Affairs. 33 (9): 1680–8. doi:10.1377/hlthaff.2014.0434. PMID 25122562.
- ^ “About the Military Health System”. Military Health System. Retrieved March 8, 2021.
- ^ Poghosyan, Lusine (August 2, 2017). “The Untapped Potential of the Nurse Practitioner Workforce in Reducing Health Disparities”. Policy, Politics, & Nursing Practice. 18 (2): 84–94. doi:10.1177/1527154417721189. PMID 28766986. Retrieved October 3, 2024.
- ^ Nadkarni MM, Philbrick JT (July 2005). “Free clinics: a national survey”. The American Journal of the Medical Sciences. 330 (1): 25–31. doi:10.1097/00000441-200507000-00005. PMID 16020996. S2CID 20380812.
- ^ “FastStats: Nursing Home Care”. National Center for Health Statistics (U.S.). March 2021.
- ^ “19 hospital closures, bankruptcies in 2022”. Beckers Hospital Review. November 11, 2022. Retrieved November 14, 2022.
- ^ “Home – Doctors That DO | Doctors of Osteopathic Medicine”. Doctors That DO | Doctors of Osteopathic Medicine. Retrieved February 28, 2018.
- ^ Young A, Chaudhry HJ, Pei X, Arnhart K, Dugan M, Snyder GB (2017). “A census of actively licensed physicians in the United States, 2016” (PDF). Journal of Medical Regulation. 103 (2): 7–21. doi:10.30770/2572-1852-103.2.7.
- ^ a b c d e f Johnston, Louis; Williamson, Samuel H. (2023). “What Was the U.S. GDP Then?”. MeasuringWorth. Retrieved November 30, 2023. United States Gross Domestic Product deflator figures follow the MeasuringWorth series.
- ^ “(Open using Adobe reader) p. 16” (PDF). Archived from the original (PDF) on October 4, 2009.
- ^ Medical Research Spending Doubled Over Past Decade, Neil Osterweil, MedPage Today, September 20, 2005
- ^ “U.S. pharmaceutical R&D expenditure 1995-2015 | Statistic”. Statista. Retrieved February 28, 2018.
- ^ “2008 Annual Report” (PDF). PHRMA. Archived from the original (PDF) on December 30, 2008. Retrieved June 20, 2009.
- ^ a b Houlton S (September 2012). “Debating Obamacare”. Chemistry and Industry. 76 (9): 23. doi:10.1002/cind.7609_5.x.
- ^ “The world will need to stop piggybacking on US pharma”. Financial Times. 2023.
- ^ “Health Care”. The Economist. November 13, 2014. ISSN 0013-0613. Retrieved November 10, 2019.
- ^ Kessler G (July 24, 2014). “Do 10,000 baby boomers retire every day?”. Washington Post. ISSN 0190-8286. Retrieved November 10, 2019.
- ^ “How has U.S. spending on healthcare changed over time?”. Peterson-Kaiser Health System Tracker. Retrieved November 11, 2019.
- ^ Prowle MJ, Araali NA (2017). “Meeting The Escalating Demands For Health And Social Care Services Of Elderly Populations In Developing Countries: A Strategic Perspective” (PDF). American Journal of Medical Research. 4 (2): 127. doi:10.22381/ajmr4220175.
- ^ Wilkins T. “Cryotherapy, cupping and TMS: New forms of alternative medicine treatment in St. George”. The Spectrum & Daily News. Retrieved November 11, 2019.
- ^ “29 CFR § 825.125 – Definition of health care provider”. LII / Legal Information Institute. Retrieved November 13, 2020.
- ^ “Latest Survey Shows More Hospitals Offering Complementary and Alternative Medicine Services”. September 2, 2012. Archived from the original on September 2, 2012. Retrieved November 11, 2019.
- ^ a b “The Use of Complementary and Alternative Medicine in the United States: Cost Data”. NCCIH. Retrieved November 11, 2019.
- ^ Davis MA, Martin BI, Coulter ID, Weeks WB (January 2013). “US spending on complementary and alternative medicine during 2002-08 plateaued, suggesting role in reformed health system”. Health Affairs. 32 (1): 45–52. doi:10.1377/hlthaff.2011.0321. PMC 3644505. PMID 23297270.
- ^ “US Healthcare Expenditure”. Our World in Data. Retrieved March 6, 2020.
- ^ Leonhardt, David (December 4, 2023). “Big Profits in Caring for the Elderly”. The New York Times. Archived from the original on December 4, 2023.
- ^ Marmor T, Oberlander J, White J (April 2009). “The Obama administration’s options for health care cost control: hope versus reality”. Annals of Internal Medicine. 150 (7): 485–9. doi:10.7326/0003-4819-150-7-200904070-00114. PMID 19258549.Free full-text.
- ^ “National Health Expenditures 2016 Highlights” (PDF).
- ^ “What Country Spends The Most (And Least) On Health Care Per Person?”. NPR.org. Retrieved February 28, 2018.
- ^ Papanicolas I, Woskie LR, Jha AK (March 2018). “Health Care Spending in the United States and Other High-Income Countries” (PDF). JAMA. 319 (10): 1024–1039. doi:10.1001/jama.2018.1150. PMID 29536101. S2CID 4293977.
- ^ “Why Are U.S. Health Costs The World’s Highest? Study Affirms ‘It’s The Prices, Stupid’“. WBUR. March 13, 2018.
- ^ Emanuel EJ (March 2018). “The Real Cost of the US Health Care System”. JAMA. 319 (10): 983–985. doi:10.1001/jama.2018.1151. PMID 29536081.
- ^ Pfuntner A., Wier L.M., Elixhauser A. Overview of Hospital Stays in the United States, 2011. HCUP Statistical Brief #166. November 2013. Agency for Healthcare Research and Quality, Rockville, MD. [2] Archived November 10, 2019, at the Wayback Machine.
- ^ a b Thomas M. Selden and Merrile Sing, “The Distribution Of Public Spending For Health Care In The United States, 2002,” Health Affairs 27, no. 5 (2008): w349–59 (published online July 29, 2008)
- ^ Weiss AJ, Barrett ML, Steiner CA (July 2014). “Trends and Projections in Inpatient Hospital Costs and Utilization, 2003–2013”. HCUP Statistical Brief (175). Rockville, MD: Agency for Healthcare Research and Quality. PMID 25165806.
- ^ WHO (2011). World health statistics 2011. Geneva: World Health Organization. ISBN 978-92-4-156419-9. Archived from the original on October 22, 2011.
- ^ “National Health Expenditure Data: NHE Fact Sheet,” Centers for Medicare and Medicaid Services, referenced February 26, 2008
- ^ Sean Keehan, Andrea Sisko, Christopher Truffer, Sheila Smith, Cathy Cowan, John Poisal, M. Kent Clemens, and the National Health Expenditure Accounts Projections Team, “Health Spending Projections Through 2017: The Baby-Boom Generation Is Coming To Medicare”, Health Affairs Web Exclusive, February 26, 2008. Retrieved February 27, 2008.
- ^ “Health Costs”. Kaiseredu.org. The Henry J. Kaiser Family Foundation. October 3, 2016. Archived from the original on September 10, 2013. Retrieved December 1, 2016.
- ^ Marcozzi D, Carr B, Liferidge A, Baehr N, Browne B (April 2018). “Trends in the Contribution of Emergency Departments to the Provision of Hospital-Associated Health Care in the USA”. International Journal of Health Services. 48 (2): 267–288. doi:10.1177/0020731417734498. PMID 29039720. S2CID 206411788.
- ^ French EB, McCauley J, Aragon M, Bakx P, Chalkley M, Chen SH, et al. (July 2017). “End-Of-Life Medical Spending In Last Twelve Months Of Life Is Lower Than Previously Reported” (PDF). Health Affairs. 36 (7): 1211–1217. doi:10.1377/hlthaff.2017.0174. PMID 28679807.
- ^ Pfeffer J (April 10, 2013). “The Reason Health Care Is So Expensive: Insurance Companies”. Bloomberg News. Retrieved January 17, 2016.
- ^ Liebowitz, Stan Policy Analysis: Why Health Care Costs So Much, Cato Institute, June 23, 1994
- ^ a b The Factors Fueling Rising Healthcare Costs 2006 Archived November 27, 2007, at the Wayback Machine, PriceWaterhouseCoopers for America’s Health Insurance Plans, 2006. Retrieved October 8, 2007.
- ^ “Confronting The Medicare Cost Shift”. Managed Care Magazine. December 2006. Retrieved June 28, 2007.
- ^ a b Health Care Cost Trends. Massachusetts Office of Health and Human Services. See Appendix B: Preliminary Report of the Massachusetts Attorney General (PDF) Archived May 9, 2010, at the Wayback Machine, pp. 1–2, for quote and summary.
- ^ Helland E, Tabarrok A (May 2019). “Why Are the Prices So Damn High?” (PDF). Retrieved May 26, 2019.
- ^ “How Would Authorizing Medicare to Cover Anti-Obesity Medications Affect the Federal Budget? | Congressional Budget Office”. www.cbo.gov. October 8, 2024. Retrieved October 9, 2024.
- ^ a b c d e f Improving Health Care: A Dose of Competition, Report by the Federal Trade Commission and the Department of Justice, 2004
- ^ Victoria Craig Bunce and JP Wieske, “Health Insurance Mandates in the States 2008”, The Council for Affordable Health Insurance, 2008
- ^ “Coverage & Access: Disciplinary Action Against Physicians Dropped 6% From 2006 to 2007, Report Finds,” Final Expense insurance.
- ^ Nursing Home Compare, Centers for Medicare and Medicaid Services (accessed April 24, 2008). Note, CMS also publishes a list of Special Focus Facilities – nursing homes with “a history of serious quality issues” at Special Focus Facility (“SFF”) Initiative.
- ^ a b Conover CJ (October 4, 2004). “Health Care Regulation: A $169 Billion Hidden Tax” (PDF). Cato Policy Analysis. 527: 1–32. Retrieved February 19, 2014.
- ^ a b c Ho V, Ku-Goto MH, Jollis JG (April 2009). “Certificate of Need (CON) for cardiac care: controversy over the contributions of CON”. Health Services Research. 44 (2 Pt 1): 483–500. doi:10.1111/j.1475-6773.2008.00933.x. PMC 2677050. PMID 19207590.
- ^ a b c Dalmia S (August 26, 2009). “The Evil-Mongering of the American Medical Association”. Forbes. Retrieved January 17, 2014.
- ^ Medical miscalculation creates doctor shortage, USA Today, March 2, 2005
- ^ Blomqvist, Ake; Busby, Colin (2013). “Paying Hospital-Based Doctors: Fee for Whose Service?”. SSRN Electronic Journal. doi:10.2139/ssrn.2345417. ISSN 1556-5068.
- ^ Sending Back the Doctor’s Bill, The New York Times July 29, 2007
- ^ Data from 2006, presented in: Criminal Background Checks for Entering Medical Students(registration required) Archived May 15, 2013, at the Wayback Machine by James Kleshinski, MD; Steven T. Case, PhD; Dwight Davis, MD; George F. Heinrich, MD; Robert A. Witzburg, MD. Posted: August 2, 2011; Academic Medicine. 2011;86(7):795–98.
- ^ The Uninsured: Access to Medical Care Archived March 4, 2010, at the Wayback Machine, American College of Emergency Physicians. Retrieved October 30, 2007.
- ^ Fact Sheet: The Future of Emergency Care: Key Findings and Recommendations Archived September 22, 2011, at the Wayback Machine, Institute of Medicine, 2006. Retrieved October 7, 2007.
- ^ “National Library of Medicine – Medical Subject Headings, 2011 MeSH, MeSH Descriptor Data, Quality Assurance, Health Care”. U.S. National Library of Medicine. Bethesda, MD: National Institutes of Health. Retrieved February 19, 2015.
- ^ Herper M. “Should Big Data Pick Your Next Doctor?”. Forbes. Retrieved May 26, 2017.
- ^ Metcalfe, David; Rios Diaz, Arturo J.; Olufajo, Olubode A.; Massa, M. Sofia; Ketelaar, Nicole Abm; Flottorp, Signe A.; Perry, Daniel C. (September 6, 2018). “Impact of public release of performance data on the behaviour of healthcare consumers and providers”. The Cochrane Database of Systematic Reviews. 2018 (9): CD004538. doi:10.1002/14651858.CD004538.pub3. ISSN 1469-493X. PMC 6513271. PMID 30188566.
- ^ Gunja, Munira Z.; Gumas, Evan D.; Williams II, Reginald D. (January 31, 2023). “U.S. Health Care from a Global Perspective, 2022: Accelerating Spending, Worsening Outcomes”. www.commonwealthfund.org. doi:10.26099/8ejy-yc74. Retrieved December 11, 2024.
- ^ Corrigan, Janet M. “Crossing the quality chasm.” Building a Better Delivery System (2005).
- ^ “Strategic Plan and Priorities”. HHS.gov. August 26, 2013. Archived from the original on August 26, 2013.
- ^ a b “National Prevention Strategy” (PDF). National Prevention Council. Washington, DC: U.S. Department of Health and Human Services, Office of the Surgeon General. 2011. Archived from the original (PDF) on April 12, 2019. Retrieved October 22, 2017.
- ^ “About”. January 13, 2013. Archived from the original on January 13, 2013.
- ^ “Commonwealth Fund 2010 Health Policy Survey in 11 Countries” (PDF). The Commonwealth Fund. November 2010. pp. 19–20.
- ^ Coyte PC, Wright JG, Hawker GA, Bombardier C, Dittus RS, Paul JE, et al. (October 1994). “Waiting times for knee-replacement surgery in the United States and Ontario”. The New England Journal of Medicine. 331 (16): 1068–71. doi:10.1056/nejm199410203311607. PMID 8090168.
- ^ “Patient’s Wait Time from Decision to Having Orthopedic Surgery – Health Quality Ontario”. hqontario.ca. Retrieved June 13, 2019.
- ^ Roser, Max; Ortiz-Ospina, Esteban; Ritchie, Hannah (May 23, 2013). “Life Expectancy”. Our World in Data.
- ^ “Measure Details”. February 15, 2013. Archived from the original on February 15, 2013.
- ^ “Health, United States, 2013” (PDF). Cdc.gov. Retrieved December 1, 2016.
- ^ “The Surgeon General’s Vision for a Healthy and Fit Nation”. Rockville, Maryland: U.S. Department of Health and Human Services, Office of the Surgeon General. January 2010.
- ^ IOM (Institute of Medicine). 2012. How far have we come in reducing health disparities?: Progress since 2000: Workshop summary. Washington, DC: The National Academies Press.
- ^ “Topic Area”. February 14, 2013. Archived from the original on February 14, 2013.
- ^ ASPE (July 23, 2012). “Health Care Cost Containment and Medical Innovation”. Aspe.hhs.gov. Retrieved December 1, 2016.
- ^ a b OECD Data. Health resources – Health spending.doi:10.1787/8643de7e-en. 2 bar charts: For both: From bottom menus: Countries menu > choose OECD. Check box for “latest data available”. Perspectives menu > Check box to “compare variables”. Then check the boxes for government/compulsory, voluntary, and total. Click top tab for chart (bar chart). For GDP chart choose “% of GDP” from bottom menu. For per capita chart choose “US dollars/per capita”. Click fullscreen button above chart. Click “print screen” key. Click top tab for table, to see data.
- ^ Schneider, Eric C.; Sarnak, Dana O.; Squires, David; Shah, Arnav; Doty, Michelle M. (June 14, 2017). Mirror, Mirror 2017: International Comparison Reflects Flaws and Opportunities for Better U.S. Health Care (Report). The Commonwealth Fund. doi:10.26099/0mh5-a632.
- ^ Kliff S (June 16, 2014). “Five ways the American health care system is literally the worst”. Vox. Retrieved June 17, 2014.
- ^ “Country Comparison: Infant Mortality Rate”. The World Factbook. Cia.gov. Archived from the original on June 13, 2007. Retrieved December 14, 2018.
- ^ Atlas SW (2011). In excellent health: setting the record straight on America’s health care and charting a path for future reform. Stanford, California: Hoover Institution Press, Stanford University. pp. 199–205. ISBN 978-0-8179-1444-8.
- ^ Ellen Nolte and C. Martin McKee, “Measuring the Health of Nations: Updating an Earlier Analysis,”, Health Affairs, January 8, 2008, Volume 98
- ^ Dunham W (January 8, 2008). “France best, U.S. worst in preventable death ranking”. Reuters. Retrieved April 3, 2012.
- ^ Case, Anne; Deaton, Angus (2020). Deaths of Despair and the Future of Capitalism. Princeton University Press. pp. 9–10. ISBN 978-0691190785.
- ^ Ezzati M, Friedman AB, Kulkarni SC, Murray CJ (April 2008). Novotny T (ed.). “The reversal of fortunes: trends in county mortality and cross-county mortality disparities in the United States”. PLOS Medicine. 5 (4): e66. doi:10.1371/journal.pmed.0050066. PMC 2323303. PMID 18433290.
- ^ Jemal A, Ward E, Anderson RN, Murray T, Thun MJ (May 2008). “Widening of socioeconomic inequalities in U.S. death rates, 1993-2001”. PLOS ONE. 3 (5): e2181. Bibcode:2008PLoSO…3.2181J. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0002181. PMC 2367434. PMID 18478119.
- ^ “Healthy Living”. The Huffington Post. Retrieved December 1, 2016.
- ^ Doheny K (July 16, 2008). “Cancer survival rates vary by country. Study shows U.S., Japan, and France have highest cancer survival rates”. WebMD.Coleman MP, Quaresma M, Berrino F, Lutz JM, De Angelis R, Capocaccia R, et al. (August 2008). “Cancer survival in five continents: a worldwide population-based study (CONCORD)” (PDF). The Lancet. Oncology. 9 (8): 730–56. doi:10.1016/S1470-2045(08)70179-7. PMID 18639491.
In the CONCORD study, Cuba had the highest five-year relative survival rates for breast cancer and for colorectal cancer in women, but problems with data quality might have led to over-estimations. - ^ World Health Organization assesses the world’s health system. Press Release WHO/44 21 June 2000.
- ^ “The World Health Report 2000: Annex Table 1 Health system attainment and performance in all Member States, ranked by eight measures, estimates for 1997” (PDF). Who.int. Retrieved December 1, 2016.
- ^ David Gratzer, Why Isn’t Government Health Care The Answer? Archived March 12, 2009, at the Wayback Machine, Free Market Cure, July 16, 2007
- ^ a b c Robert J. Blendon, Minah Kim and John M. Benson, “The Public Versus The World Health Organization On Health System Performance,” Health Affairs, May/June 2001
- ^ Christopher J.L. Murray, Kei Kawabata, and Nicole Valentine, “People’s Experience Versus People’s Expectations”, Health Affairs, May/June 2001
- ^ Fenton JJ, Jerant AF, Bertakis KD, Franks P (March 2012). “The cost of satisfaction: a national study of patient satisfaction, health care utilization, expenditures, and mortality” (PDF). Archives of Internal Medicine. 172 (5): 405–11. doi:10.1001/archinternmed.2011.1662. PMID 22331982.
- ^ Maratt, Jennifer K.; Kerr, Eve A.; Klamerus, Mandi L.; Lohman, Shannon E.; Froehlich, Whit; Bhatia, R. Sacha; Saini, Sameer D. (2019). “Measures Used to Assess the Impact of Interventions to Reduce Low-Value Care: a Systematic Review”. Journal of General Internal Medicine. 34 (9): 1857–1864. doi:10.1007/s11606-019-05069-5. ISSN 0884-8734. PMC 6712188. PMID 31250366.
- ^ Donna St. George, “For Children, a Better Beginning,” The Washington Post, April 24, 2008
- ^ Kenneth C. Land, Project Coordinator, “2008 Special Focus Report: Trends in Infancy/Early Childhood and Middle Childhood Well-Being, 1994–2006,” The Foundation for Child Development Child and Youth Well-Being Index (CWI) Project, Foundation for Child Development (FCD), April 24, 2008
- ^ Office of health Economics. “International Comparison of Medicines Usage: Quantitative Analysis” (PDF). Association of the British Pharmaceutical Industry. Archived from the original (PDF) on November 11, 2015. Retrieved July 2, 2015.
- ^ a b “Stan Brock: the British cowboy turned movie star who rescued millions of uninsured Americans”. The Independent. Archived from the original on May 9, 2022. Retrieved May 19, 2019.
- ^ Maternal deaths and mortality rates by state, 2018-2021. Listed at Data Files and Resources. National Vital Statistics System (NVSS). National Center for Health Statistics. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention.
- ^ Maternal Mortality Rates in the United States, 2021. Listed at Data Files and Resources. US Center for Disease Control. National Center for Health Statistics. National Vital Statistics System, Natality and Mortality.doi:10.15620/cdc:124678.
- ^ “Dartmouth Atlas of Health Care”. Dartmouthatlas.org. December 30, 2015. Retrieved December 1, 2016.
- ^ Lowrey A, Pear R (July 28, 2012). “Doctor Shortage Likely to Worsen With Health Law”. The New York Times. Retrieved July 29, 2012.
- ^ Gill PS (2013). “Five Product Engineering Methods That Can Be Applied to Health Care Management”. Managed Care. 3: 21–26.
- ^ “U.S. health-care system ranks last among 11 high-income countries, researchers say”. Washington Post. August 5, 2021. Retrieved May 23, 2022.
- ^ Cecere D (September 17, 2009). “New study finds 45,000 deaths annually linked to lack of health coverage”. Harvard Gazette. Retrieved August 27, 2013.
- ^ Wilper AP, Woolhandler S, Lasser KE, McCormick D, Bor DH, Himmelstein DU (December 2009). “Health insurance and mortality in US adults”. American Journal of Public Health. 99 (12): 2289–95. doi:10.2105/AJPH.2008.157685. PMC 2775760. PMID 19762659.
- ^ Woolhandler S, et al. (September 12, 2012). “Despite slight drop in uninsured, last year’s figure points to 48,000 preventable deaths”. Physicians for a National Health Program. Archived from the original on September 24, 2012. Retrieved September 26, 2012.
- ^ Goodman J (September 21, 2009). “Does Lack Of Insurance Cause Premature Death?”. Health Affairs. doi:10.1377/forefront.20090921.002196.
- ^ Kronick R (August 2009). “Health insurance coverage and mortality revisited”. Health Services Research. 44 (4): 1211–31. doi:10.1111/j.1475-6773.2009.00973.x. PMC 2739025. PMID 19453392.
- ^ Gerard F. Anderson, Uwe E. Reinhardt, Peter S. Hussey and Varduhi Petrosyan, “It’s The Prices, Stupid: Why The United States Is So Different From Other Countries”, Health Affairs, Volume 22, Number 3, May/June 2003. Retrieved February 27, 2008.
- ^ Kliff, Sarah (October 12, 2023). “Mary Lou Retton Crowdfunded Her Medical Debt, Like Many Thousands of Others”. The New York Times. ISSN 0362-4331. Retrieved December 19, 2024.
- ^ Ross, Martha (October 12, 2023) [2023-10-11]. “Mary Lou Retton’s lack of insurance raises questions as crowdfunding passes $330,000”. The Mercury News. Retrieved December 19, 2024.
- ^ Hadley J (March 2007). “Insurance coverage, medical care use, and short-term health changes following an unintentional injury or the onset of a chronic condition”. JAMA. 297 (10): 1073–84. doi:10.1001/jama.297.10.1073. PMID 17356028.
- ^ “Advance Data From Vital and Health Statistics No. 388” (PDF). Cdc.gov. June 28, 2007. Retrieved December 1, 2016.
- ^ Halpern MT, Ward EM, Pavluck AL, Schrag NM, Bian J, Chen AY (March 2008). “Association of insurance status and ethnicity with cancer stage at diagnosis for 12 cancer sites: a retrospective analysis”. The Lancet. Oncology. 9 (3): 222–31. doi:10.1016/S1470-2045(08)70032-9. PMID 18282806. Lay summary: Study Finds Cancer Diagnosis Linked to Insurance, New York Times.
- ^ Ulene V (May 5, 2008). “Care that goes too far”. Los Angeles Times.
- ^ Emily Cox, Doug Mager, Ed Weisbart, “Geographic Variation Trends in Prescription Use: 2000 to 2006,” Express Scripts, January 2008 Archived February 27, 2008, at the Wayback Machine
- ^ “Effective Care,” Archived February 16, 2008, at the Wayback Machine The Dartmouth Atlas of Health Care, January 15, 2007
- ^ Laurence C. Baker, Elliott S. Fisher, and John E. Wennberg, “Variations In Hospital Resource Use For Medicare And Privately Insured Populations In California,” Health Affairs web exclusive, February 2008
- ^ John E. Wennberg, Elliott S. Fisher, David C. Goodman, and Jonathan S. Skinner, “Tracking the Care of Patients with Severe Chronic Illness: the Dartmouth Atlas of Health Care 2008.” Archived October 29, 2008, at the Wayback Machine The Dartmouth Institute for Health Policy and Clinical Practice, May 2008,ISBN 978-0-9815862-0-5 (Executive Summary Archived April 8, 2008, at the Wayback Machine)
- ^ “Medicare: End-of-Life Hospital Spending for Medicare Beneficiaries With Chronic Health Conditions Varies Widely, Study Finds,”[permanent dead link] Kaiser Daily Health Policy Report, Kaiser Family Foundation, April 7, 2008
- ^ California HealthCare Foundation, “Uncoordinated Care: A Survey of Physician and Patient Experience” Archived February 14, 2008, at the Wayback Machine, Harris Interactive. 2007. Retrieved March 20, 2008.
- ^ a b Tare Parker-Pople, “Well: Doctor and Patient, Now at Odds,” The New York Times, July 29, 2008
- ^ Hospitalists and the family physician [3] Archived October 26, 2011, at the Wayback Machine by Bruce Bagley, M.D.; American Family Physician
- ^ “Use of mandatory hospitalists blasted, ACP Observer May 99”. Acpinternist.org. February 16, 1999. Archived from the original on October 19, 2016. Retrieved December 1, 2016.
- ^ “Facts + Statistics: Industry overview | III”. www.iii.org. Retrieved June 24, 2019.
- ^ “Annual Report on the Insurance Industry (September 2018)” (PDF). Federal Insurance Office, U.S. Department of the Treasury.
- ^ Woolhandler S, Campbell T, Himmelstein DU (August 2003). “Costs of health care administration in the United States and Canada”. The New England Journal of Medicine. 349 (8): 768–75. doi:10.1056/NEJMsa022033. PMID 12930930. S2CID 2313231.
- ^ Jeff Lemieux, “Perspective: Administrative Costs of Private Health Insurance Plans”[usurped], America’s Health Insurance Plans, 2005
- ^ “Understanding Health Plan Administrative Costs”, Blue Cross Blue Shield Association, 2003 Archived October 26, 2007, at the Wayback Machine
- ^ Sacia KJ, Dobson RH (February 20, 2003). Health Plan Administrative Cost Trends. Milliman USA (Report). BlueCross BlueShield Association.
- ^ Reinhardt UE (November 21, 2008). “Why Does U.S. Health Care Cost So Much? (Part II: Indefensible Administrative Costs)”. The New York Times. Retrieved May 4, 2010.
- ^ U.S. Congressional Budget Office, Key Issues in Analyzing Major Health Insurance Proposals, December 2008
- ^ a b Sherlock DB (2009). “Administrative Expenses of Health Plans” (PDF). Blue Cross Blue Shield Association – via s3.amazonaws.com.
- ^ Kahn JG, Kronick R, Kreger M, Gans DN (2005). “The cost of health insurance administration in California: estimates for insurers, physicians, and hospitals”. Health Affairs. 24 (6): 1629–39. doi:10.1377/hlthaff.24.6.1629. PMID 16284038.
- ^ Weech-Maldonado, R.; Pradhan, R.; Dayama, N.; Lord, J.; Gupta, S. (2019). “Nursing Home Quality and Financial Performance: Is There a Business Case for Quality?”. Inquiry: The Journal of Medical Care Organization, Provision and Financing. 56: 0046958018825191. doi:10.1177/0046958018825191. PMC 6376502. PMID 30739511.
- ^ Stewart, K. A.; Grabowski, D. C.; Lakdawalla, D. N. (2009). “Annual expenditures for nursing home care: Private and public payer price growth, 1977–2004”. Medical Care. 47 (3): 295–301. doi:10.1097/MLR.0b013e3181893f8e. PMC 2763425. PMID 19194339.
- ^ Stewart, K. A.; Grabowski, D. C.; Lakdawalla, D. N. (2009). “Annual expenditures for nursing home care: Private and public payer price growth, 1977–2004”. Medical Care. 47 (3): 295–301. doi:10.1097/MLR.0b013e3181893f8e. PMC 2763425. PMID 19194339.
- ^ Scandlen G (2005). “Consumer-driven health care: just a tweak or a revolution?”. Health Affairs. 24 (6): 1554–8. doi:10.1377/hlthaff.24.6.1554. PMID 16284028.
- ^ “Colorado proposes running public health care option through private insurers”. The Denver Post. October 7, 2019. Retrieved November 21, 2019.
- ^ “Federal Subsidies for Health Insurance Coverage for People Under Age 65”. CBO. March 24, 2016.
- ^ “NIMH » Mental Illness”. nimh.nih.gov. Retrieved February 28, 2018.
- ^ “Data on behavioral health in the United States”. apa.org. Archived from the original on March 30, 2019. Retrieved February 28, 2018.
- ^ “The Carter Center Mental Health Program: Combating the Stigma of Mental Illness”. The Carter Center. Retrieved July 30, 2008.
- ^ Weiss R (June 7, 2005). “Study: U.S. Leads In Mental Illness, Lags in Treatment”. The Washington Post. Retrieved July 30, 2008.
- ^ Kuehn, Bridget M. (May 25, 2022). “Clinician Shortage Exacerbates Pandemic-Fueled “Mental Health Crisis”“. Medical News & Perspectives. JAMA. 327 (22): 2179–81. doi:10.1001/jama.2022.8661. PMID 35612873.
- ^ Madden, Jeanne M.; Adams, Alyce S.; LeCates, Robert F.; Ross-Degnan, Dennis; Zhang, Fang; Huskamp, Haiden A.; Gilden, Daniel M.; Soumerai, Stephen B. (February 1, 2015). “Changes in Drug Coverage Generosity and Untreated Serious Mental Illness: Transitioning From Medicaid to Medicare Part D”. JAMA Psychiatry. 72 (2): 179–188. doi:10.1001/jamapsychiatry.2014.1259. ISSN 2168-622X. PMC 4505620. PMID 25588123.
- ^ “8 Best Affordable Online Therapy Options for 2023”. PsychCentral. November 16, 2023. Archived from the original on November 24, 2023. Retrieved November 22, 2023.
- ^ Pear R (March 6, 2008). “House Approves Bill on Mental Health Parity”. The New York Times. Retrieved July 29, 2009.
- ^ “Sedgwick Ignores Medical Records and Denies Disability Benefits” on YouTube
- ^ Pinto, Rita Del; Monaco, Annalisa; Ortu, Eleonora; Czesnikiewicz-Guzik, Marta; Aguilera, Eva Muñoz; Giannoni, Mario; D’Aiuto, Francesco; Guzik, Tomasz J.; Ferri, Claudio; Pietropaoli, Davide (November 2, 2021). “Access to dental care and blood pressure profiles in adults with high socioeconomic status”. Journal of Periodontology. 93 (7): 1060–1071. doi:10.1002/JPER.21-0439. ISSN 1943-3670. PMC 9542004. PMID 34726790. S2CID 240422102.
- ^ Northridge, Mary E.; Kumar, Anjali; Kaur, Raghbir (2020). “Disparities in Access to Oral Health Care”. Annual Review of Public Health. 41: 513–535. doi:10.1146/annurev-publhealth-040119-094318. PMC 7125002. PMID 31900100.
- ^ Committee, U.S. Department of Health and Human Services Oral Health Coordinating (March 2016). “U.S. Department of Health and Human Services Oral Health Strategic Framework, 2014–2017”. Public Health Reports. 131 (2): 242–257. doi:10.1177/003335491613100208. PMC 4765973. PMID 26957659.
- ^ “New York State Medicaid program – dental policy and procedure code manual” (PDF). www.emedny.org/. February 1, 2022. Retrieved October 23, 2022.
- ^ “How Buying Insurance Will Change Under Obamacare”. Kff.org. The Henry J. Kaiser Family Foundation. September 24, 2013. Retrieved December 1, 2016.
- ^ Goldberg, J., Hayes, W., and Huntley, J. “Understanding Health Disparities.” Archived May 15, 2008, at the Wayback Machine Health Policy Institute of Ohio (November 2004), p. 3.
- ^ Smedley, Brian D.; Stith, Adrienne Y.; Nelson, Alan R. (2003). Unequal treatment: confronting racial and ethnic disparities in health care. National Academy Press. ISBN 978-0-309-21582-4. OCLC 853283904.
- ^ Atdjian, Sylvia; Vega, William A. (December 2005). “Disparities in Mental Health Treatment in U.S. Racial and Ethnic Minority Groups: Implications for Psychiatrists”. Psychiatric Services. 56 (12): 1600–1602. doi:10.1176/appi.ps.56.12.1600. ISSN 1075-2730. PMID 16339626.
- ^ a b American Public Health Association (APHA), Eliminating Health Disparities: Toolkit (2004).
- ^ Campanile C (November 23, 2012). “Americans are getting fatter: poll”. Nypost.com. New York Post. Retrieved December 1, 2016.
- ^ Sarah Burd-Sharps and Kristen Lewis. Geographies of Opportunity: Ranking Well-Being by Congressional District. 2015. Measure of America of the Social Science Research Council.
- ^ Trends in healthy life expectancy in the united states, 1970–1990: gender, racial, and educational differences Archived March 17, 2010, at the Wayback Machine
- ^ Tronetti P (January 11, 2011). “Senior consult:Check drugs supplements to avoid interactions”. Florida Today. Melbourne, Florida. p. 1D.
- ^ O’Connor A (September 25, 2012). “Well: Antibiotic Prescription? It May Depend on Where You Live”. The New York Times.
- ^ “How Trends in the Health Care System Affect Low-Income Adults: Identifying Access Problems and Financial Burdens”, Issue Brief: Kaiser Commission on Medicaid and the Uninsured, December 21, 2007. Retrieved February 26, 2008.
- ^ Habib JL (2010). “Progress lags in infection prevention and health disparities”. Drug Benefit Trends. 22 (4): 112. Archived from the original on January 20, 2013. Retrieved June 11, 2010.
- ^ Bhopal R (June 1998). “Spectre of racism in health and health care: lessons from history and the United States”. BMJ. 316 (7149): 1970–3. doi:10.1136/bmj.316.7149.1970. PMC 1113412. PMID 9641943.
- ^ Oberman A, Cutter G (September 1984). “Issues in the natural history and treatment of coronary heart disease in black populations: surgical treatment”. American Heart Journal. 108 (3 Pt 2): 688–94. doi:10.1016/0002-8703(84)90656-2. PMID 6332513.
- ^ Kjellstrand CM (June 1988). “Age, sex, and race inequality in renal transplantation”. Archives of Internal Medicine. 148 (6): 1305–9. doi:10.1001/archinte.1988.00380060069016. PMID 3288159.
- ^ Mayer WJ, McWhorter WP (June 1989). “Black/white differences in non-treatment of bladder cancer patients and implications for survival”. American Journal of Public Health. 79 (6): 772–5. doi:10.2105/ajph.79.6.772. PMC 1349641. PMID 2729474.
- ^ Yergan J, Flood AB, LoGerfo JP, Diehr P (July 1987). “Relationship between patient race and the intensity of hospital services”. Medical Care. 25 (7): 592–603. doi:10.1097/00005650-198707000-00003. PMID 3695664. S2CID 11637921.
- ^ Cené, Crystal W.; Viswanathan, Meera; Fichtenberg, Caroline M.; Sathe, Nila A.; Kennedy, Sara M.; Gottlieb, Laura M.; Cartier, Yuri; Peek, Monica E. (January 19, 2023). “Racial Health Equity and Social Needs Interventions: A Review of a Scoping Review”. JAMA Network Open. 6 (1): e2250654. doi:10.1001/jamanetworkopen.2022.50654. ISSN 2574-3805. PMC 9857687. PMID 36656582.
- ^ Cené, Crystal W.; Viswanathan, Meera; Fichtenberg, Caroline M.; Sathe, Nila A.; Kennedy, Sara M.; Gottlieb, Laura M.; Cartier, Yuri; Peek, Monica E. (January 2023). “Racial Health Equity and Social Needs Interventions: Rapid Review”.
- ^ Council on Ethical Judicial Affairs (May 1990). “Black-white disparities in health care”. JAMA. 263 (17): 2344–6. doi:10.1001/jama.263.17.2344. PMID 2182918.
- ^ Darrell J. Gaskin, Christine S. Spencer, Patrick Richard, Gerard F. Anderson, Neil R. Powe, and Thomas A. LaVeist, “Do Hospitals Provide Lower-Quality Care To Minorities Than To Whites?,” Health Affairs, March/April 2008
- ^ “In the Literature: Do Hospitals Provide Lower-Quality Care To Minorities Than To Whites?,” Archived March 16, 2008, at the Wayback Machine The Commonwealth Fund, March 11, 2008
- ^ “Thought Leadership Archives”. Sterling Medical Devices. Retrieved April 27, 2023.
- ^ “Towards improving access to medical devices through local production”. www.who.int. Retrieved April 27, 2023.
- ^ Albritton, Jordan A.; Booth, Graham; Kugley, Shannon; Reddy, Shivani; Coker-Schwimmer, Manny; Fujita, Miku; Crotty, Karen (2025). “Audio-Based Care for Managing Chronic Conditions in Adults: A Systematic Review”. Medical Care. 63 (2): 164–182. doi:10.1097/MLR.0000000000002097. ISSN 0025-7079. PMC 11708983. PMID 39791849.
- ^ “AI in healthcare and research”. The Nuffield Council on Bioethics. Retrieved May 10, 2024.
- ^ Gerke, Sara; Minssen, Timo; Cohen, Glenn (January 1, 2020), Bohr, Adam; Memarzadeh, Kaveh (eds.), “Chapter 12 – Ethical and legal challenges of artificial intelligence-driven healthcare”, Artificial Intelligence in Healthcare, Academic Press, pp. 295–336, ISBN 978-0-12-818438-7, retrieved May 10, 2024
- ^ Berdahl, Carl Thomas; Baker, Lawrence; Mann, Sean; Osoba, Osonde; Girosi, Federico (February 7, 2023). “Strategies to Improve the Impact of Artificial Intelligence on Health Equity: Scoping Review”. JMIR AI. 2: e42936. doi:10.2196/42936. ISSN 2817-1705. PMC 11041459. PMID 38875587. S2CID 256681439.
- ^ Jang, Angie; Thomas, Arielle; Slocum, John; Tesorero, Kaithlyn; Danna, Giovanna; Saklecha, Anjay; Wafford, Eileen; Regan, Sheila; Stey, Anne M. (October 1, 2023). “The gap between hospital-based violence intervention services and client needs: A systematic review”. Surgery. 174 (4): 1008–1020. doi:10.1016/j.surg.2023.07.011. ISSN 0039-6060. PMID 37586893.
- ^ Thornton, Rachel L. J.; Glover, Crystal M.; Cené, Crystal W.; Glik, Deborah C.; Henderson, Jeffrey A.; Williams, David R. (August 2016). “Evaluating Strategies For Reducing Health Disparities By Addressing The Social Determinants Of Health”. Health Affairs. 35 (8): 1416–1423. doi:10.1377/hlthaff.2015.1357. ISSN 0278-2715. PMC 5524193. PMID 27503966.
- ^ Costello, Anne Marie (January 7, 2021). “SHO# 21-001 RE:Opportunities in Medicaid and CHIP to Address Social Determinants of Health (SDOH)” (PDF). United States Department of Health and Human Services. Medicaid. Baltimore, Maryland: Centers for Medicare & Medicaid Services.
- ^ a b c d Irvin, Nathan (November 1, 2019). “Commentary: Using a Trauma-Informed Care Framework to Address the Upstream and Downstream Correlates of Youth Violence”. Annals of Emergency Medicine. Inventing Social Emergency Medicine. 74 (5, Supplement): S55 – S58. doi:10.1016/j.annemergmed.2019.08.451. ISSN 0196-0644. PMID 31655678.
- ^ Jang, Angie; Thomas, Arielle; Slocum, John; Tesorero, Kaithlyn; Danna, Giovanna; Saklecha, Anjay; Wafford, Eileen; Regan, Sheila; Stey, Anne M. (October 1, 2023). “The gap between hospital-based violence intervention services and client needs: A systematic review”. Surgery. 174 (4): 1008–1020. doi:10.1016/j.surg.2023.07.011. ISSN 0039-6060. PMID 37586893.
- ^ “What FDA Regulates”. Food and Drug Administration. June 4, 2009. Archived from the original on June 4, 2009.
- ^ Glantz LH, Annas GJ (May 2008). “The FDA, preemption, and the Supreme Court”. The New England Journal of Medicine. 358 (18): 1883–5. doi:10.1056/NEJMp0802108. PMID 18450601.
- ^ “Wyeth v. Levine”. Oyez. Chicago-Kent College of Law at Illinois Tech. n.d.
- ^ 74 FR 30294, Federal Register: June 25, 2009 (Volume 74, Number 121), pp. 30294–97.
- ^ Coverage Under the Public Readiness and Emergency Preparedness (PREP) Act for H1N1 Vaccination Flu.gov, retrieved November 11, 2009
- ^ “OECD Health Data 2005: How Does the United States Compare” (PDF). Organisation for Economic Co-operation and Development. Retrieved April 14, 2007.
- ^ Heffler S, Smith S, Keehan S, Clemens MK, Zezza M, Truffer C (2004). “Health spending projections through 2013”. Health Affairs. 23 (Suppl 1 Web Exclusives): W4–79–93. doi:10.1377/hlthaff.w4.79. PMID 15451969.
- ^ Stelzner, Mark Joseph; Nam, Daniel Taekmin (August 11, 2020). “The big cost of big medicine – calculating the rent in private healthcare”. Review of Social Economy. 80 (4): 491–513. doi:10.1080/00346764.2020.1804607. ISSN 0034-6764. S2CID 225500668.
- ^ “High Drug Prices and Patient Costs: Millions of Lives and Billions of Dollars Lost”. West Health Council for Informed Drug Spending Analysis. November 18, 2020. Retrieved February 20, 2023.
- ^ See the summary of the official U.S. position in the “Pharmaceutical Research and Manufacturers of America (PhRMA) Special 301 Submission of 2008”, February 11, 2008, 10–20 (Archived November 21, 2008, at the Wayback Machine).
- ^ Berenson A (November 6, 2006). “As Drug Prices Climb, Democrats Find Fault With Medicare Plan”. The New York Times. Retrieved May 4, 2010.
- ^ AMA (November 17, 2015). “AMA calls for ban on direct to consumer advertising of prescription drugs and medical devices” (Press release).
- ^ “The Impact of Direct-to-Consumer Advertising”. FDA. November 3, 2018.
- ^ Ventola CL (October 2011). “Direct-to-Consumer Pharmaceutical Advertising: Therapeutic or Toxic?”. P & T. 36 (10): 669–84. PMC 3278148. PMID 22346300.
- ^ Hook J, Levey NN (December 16, 2009). “Senate healthcare bill advances with rejection of imported drugs”. Los Angeles Times. Retrieved May 4, 2010.
- ^ Ahmadiani, Saeed; Nikfar, Shekoufeh (May 4, 2016). “Challenges of access to medicine and the responsibility of pharmaceutical companies: a legal perspective”. DARU Journal of Pharmaceutical Sciences. 24 (1): 13. doi:10.1186/s40199-016-0151-z. ISSN 2008-2231. PMC 4855755. PMID 27141958.
- ^ Cubanski, Juliette; Neuman, Tricia; Published, Meredith Freed (January 24, 2023). “Explaining the Prescription Drug Provisions in the Inflation Reduction Act”. KFF. Retrieved May 10, 2024.
- ^ “Medicare – Part D Non-Interference Clause | Chronic Care Policy Alliance”. September 6, 2022. Retrieved May 10, 2024.
- ^ “Most Republicans Think the U.S. Health Care System is the Best in the World. Democrats Disagree.,” Press Release, Harvard School of Public Health and Harris Interactive, March 20, 2008
- ^ “Americans’ Views on the U.S. Health Care System Compared to Other Countries,” Archived April 8, 2008, at the Wayback Machine Harvard School of Public Health and Harris Interactive, March 20, 2008
- ^ “Insuring America’s Health: Principles and Recommendations”. Institute of Medicine of the National Academies. Archived from the original on October 19, 2009. Retrieved October 27, 2007.
- ^ Reynolds A (October 3, 2002). “No Health Insurance? So What?”. The Cato Institute. Archived from the original on October 14, 2007. Retrieved October 27, 2007.
- ^ Center for Economic and Social Rights. “The Right to Health in the United States of America: What Does it Mean?” October 29, 2004. Archived February 14, 2008, at the Wayback Machine
- ^ Sade RM (December 1971). “Medical care as a right: a refutation”. The New England Journal of Medicine. 285 (23): 1288–92. doi:10.1056/NEJM197112022852304. PMID 5113728.
- Reproduced asSade, Robert. “The Political Fallacy that Medical Care is a Right”. Association of American Physicians and Surgeons.
- ^ Bailey R (November 2004). “Mandatory Health Insurance Now! It will save private medicine – and spur medical innovation”. Reason Magazine. Archived from the original on June 18, 2006. Retrieved June 21, 2006.
- ^ Galvani, Alison P; Parpia, Alyssa S; Foster, Eric M; Singer, Burton H; Fitzpatrick, Meagan C (February 13, 2020). “Improving the prognosis of health care in the USA”. The Lancet. 395 (10223): 524–533. doi:10.1016/S0140-6736(19)33019-3. PMC 8572548. PMID 32061298. S2CID 211105345.
- ^ Nuwer, Rachel (June 13, 2022). “Universal Health Care Could Have Saved More Than 330,000 U.S. Lives during COVID”. Scientific American. Retrieved June 22, 2022.
- ^ Reinhardt UE (May 8, 2009). “What Is ‘Socialized Medicine’?: A Taxonomy of Health Care Systems”. The New York Times. Retrieved May 4, 2010.
- ^ “Health Reform for Beginners: The Difference Between Socialized Medicine, Single-Payer Health Care, and What We’ll Be Getting”. The Washington Post. Archived from the original on July 17, 2012. Retrieved May 4, 2010.
- ^ Rice S (March 25, 2010). “5 key things to remember about health care reform”. CNN.
- ^ “Policies to Improve Affordability and Accountability”. whitehouse.gov. Archived from the original on February 8, 2017 – via National Archives.
- ^ Grier P (March 20, 2010). “Health Care Reform Bill 101: Who gets subsidized insurance?”. The Christian Science Monitor.
- ^ “How do out-of-pocket maximums work? | FAQs”. Bcbsm.com. Retrieved December 1, 2016.
- ^ Peter Grier, Health care reform bill 101: Who will pay for reform?, Christian Science Monitor (March 21, 2010).
- ^ Grier P (March 19, 2010). “Health care reform bill 101: Who must buy insurance?”. Christian Science Monitor. Washington, D.C. Retrieved April 7, 2010.
- ^ Congressional Budget Office, Cost Estimates for H.R. 4872, Reconciliation Act of 2010 (Final Health Care Legislation) (March 20, 2010).
- ^ Manchikanti L (January 2011). “Patient Protection and Affordable Care Act of 2010: Reforming the Health Care Reform for the New Decade”. Pain Physician. 14 (1): E35 – E67. doi:10.36076/ppj.2011/14/E35. PMID 21267047.
- ^ Sommers BD, Gunja MZ, Finegold K, Musco T (July 2015). “Changes in Self-reported Insurance Coverage, Access to Care, and Health Under the Affordable Care Act” (PDF). JAMA. 314 (4): 366–74. doi:10.1001/jama.2015.8421. PMID 26219054.
- ^ Hadley J, Holahan J (2003). “Is health care spending higher under Medicaid or private insurance?”. Inquiry. 40 (4): 323–42. doi:10.5034/inquiryjrnl_40.4.323. PMID 15055833.
- ^ Pear R (December 18, 2017). “Without the Insurance Mandate, Health Care’s Future May Be in Doubt”. The New York Times. ISSN 0362-4331. Retrieved February 28, 2018.
- ^ “Trump health bill: Winners and losers”. BBC News. May 4, 2017. Retrieved February 28, 2018.
- ^ Sanders, Bernie (May 18, 2023). “It’s time to guarantee healthcare to all Americans as a human right”. The Guardian. Retrieved May 23, 2023.
- ^ Carrasquillo O, Carrasquillo AI, Shea S (June 2000). “Health insurance coverage of immigrants living in the United States: differences by citizenship status and country of origin”. American Journal of Public Health. 90 (6): 917–23. doi:10.2105/AJPH.90.6.917. PMC 1446276. PMID 10846509.
- ^ “Find out what immigration statuses qualify for coverage in the Health Insurance Marketplace”. HealthCare.gov. Retrieved December 1, 2016.
- ^ “Obamacare: Visitors, International students, immigrants & US citizens”. VisitorGuard.com. December 24, 2013. Retrieved November 17, 2016.
- ^ Agrawal, Pooja; Venkatesh, Arjun Krishna (2016). “Refugee Resettlement Patterns and State-Level Health Care Insurance Access in the United States”. American Journal of Public Health. 106 (4): 662–663. doi:10.2105/AJPH.2015.303017. ISSN 0090-0036. PMC 4816078. PMID 26890186.
- ^ “Health Insurance for Immigrants | Covered California™”. coveredca.com. Retrieved November 17, 2016.
- Breslow L, ed. (2002). Encyclopedia of Public Health. MacMillan Reference. Four volumes.
- Burnham JC (2005). What Is Medical History?. Polity. p. 163. ISBN 0745632254.
- Burnham JC (2015). Health Care in America: A History. Johns Hopkins University Press. ISBN 978-1421416076. A standard comprehensive scholarly history.
- Byrd WM, Clayton LA (2012). An American health dilemma: A medical history of African Americans and the problem of race: Beginnings to 1900. Routledge.
- Christensen C, Hwang J, Grossman J (2009). The Innovator’s Prescription. McGraw Hill. ISBN 978-0-07-159208-6. Archived from the original on November 10, 2013. Retrieved August 22, 2010.
- Deutsch A (1937). The Mentally Ill in America: A History of Their Care and Treatment from Colonial Times.
- Gaffney, Adam, David U. Himmelstein, and Steffie Woolhandler, “The Only Way to Fix US Health Care” (partly a review of Liran Einav and Amy Finkelstein, We’ve Got You Covered: Rebooting American Health Care, Portfolio, 2023, 275 pp.), The New York Review of Books, vol. LXXI, no. 17 (7 November 2024), pp. 34, 36–38.
- Johnston RD (2004). The politics of healing: histories of alternative medicine in twentieth-century North America. Routledge.
- Judd D, Sitzman K (2013). A history of American nursing (2nd ed.). Jones & Bartlett Publishers.
- Leavitt JW, Numbers RL (1997). Sickness and health in America: Readings in the history of medicine and public health (3rd ed.).
- Mahar M (2006). Money-Driven Medicine: The Real Reason Health Care Costs So Much. Harper/Collins. ISBN 978-0-06-076533-0.
- McBride, David (2018). Caring for Equality: A History of African American Health and Healthcare. Lanham, MD: Rowman and Littlefield.
- Numbers RL (1982). “The History of American medicine: A Field in Ferment”. Reviews in American History. 10 (4): 245–63. doi:10.2307/2701830. JSTOR 2701830. PMID 11611756.
- Risse GB, Numbers RL, Leavitt JW (1977). Medicine Without Doctors: Home Health Care in American History. New York: Science History Publications/USA. ISBN 9780882021652.
- Starr P (1982). The Social Transformation of American Medicine. Basic Books. ISBN 0-465-07934-2.
- Reid, T. R. (2009). The Healing of America: A Global Quest for Better, Cheaper and Fairer Health Care. New York: The Penguin Press. ISBN 978-1-59420-234-6. Online (registration required).
- Warner JH, Tighe JA (2001). Major Problems in the History of American Medicine and Public Health.
- Howard Zucker, M.D., “Where Have All the Doctors Gone? Physicians quitting medicine: It’s a crisis that’s shaking our health care system. Here’s how you can protect yourself”, AARP Bulletin, vol. 66, no. 1 (January/February 2025), pp. 7–8, 10–12, 14–15.
- National Center for Health Statistics from the CDC
- National Health Expenditure Data (US) from the HHS
- US profile from the WHO
- And Pharma Market Research Report Archived April 12, 2023, at the Wayback Machine
- Healthcare Market Resources
| Professions | |
|---|---|
| Settings | |
| Care | |
| Skills / training | |
| Technology | |
| Health informatics |
|
| By country | |
Healthcare in North America | |
|---|---|
| Sovereign states | |
Dependencies and other territories | |
Health care by country | |
|---|---|
External links
Further reading
References
See also
Health insurance coverage for immigrants
Healthcare reform debate
Prescription drug issues
System efficiency and equity
Overall system effectiveness
Regulation and oversight
Spending
Providers
Statistics
History
Contents