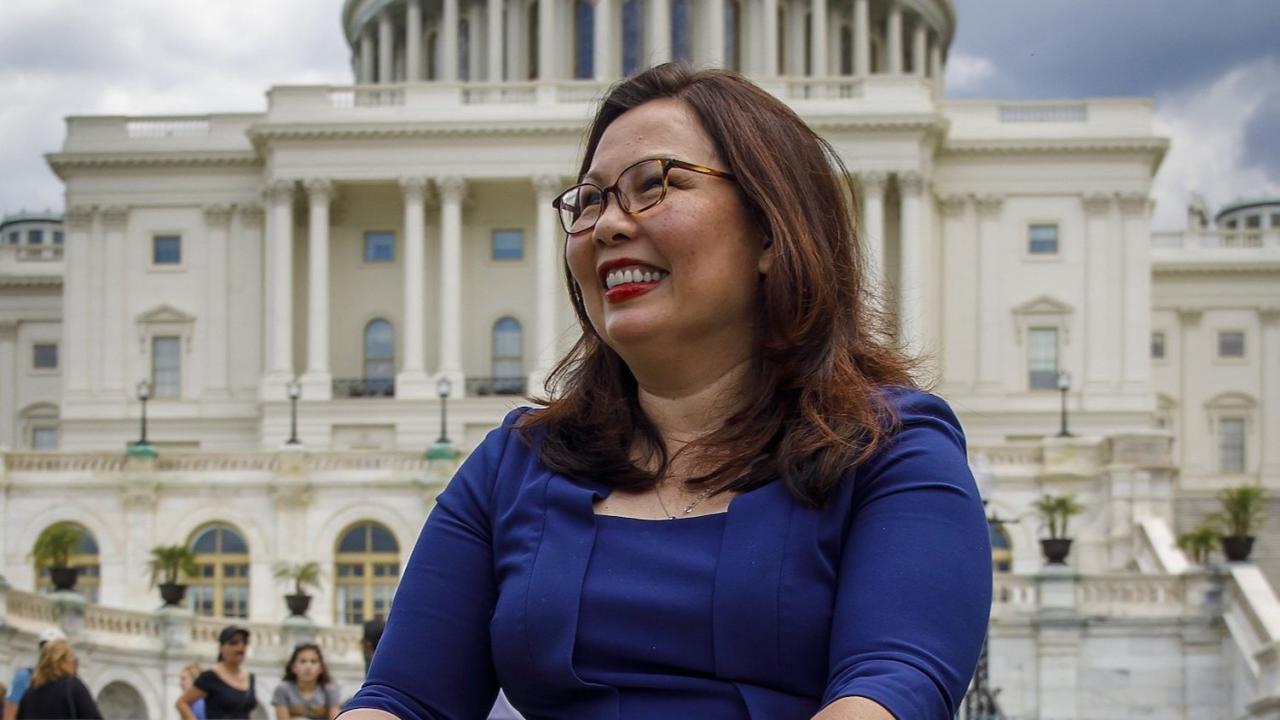
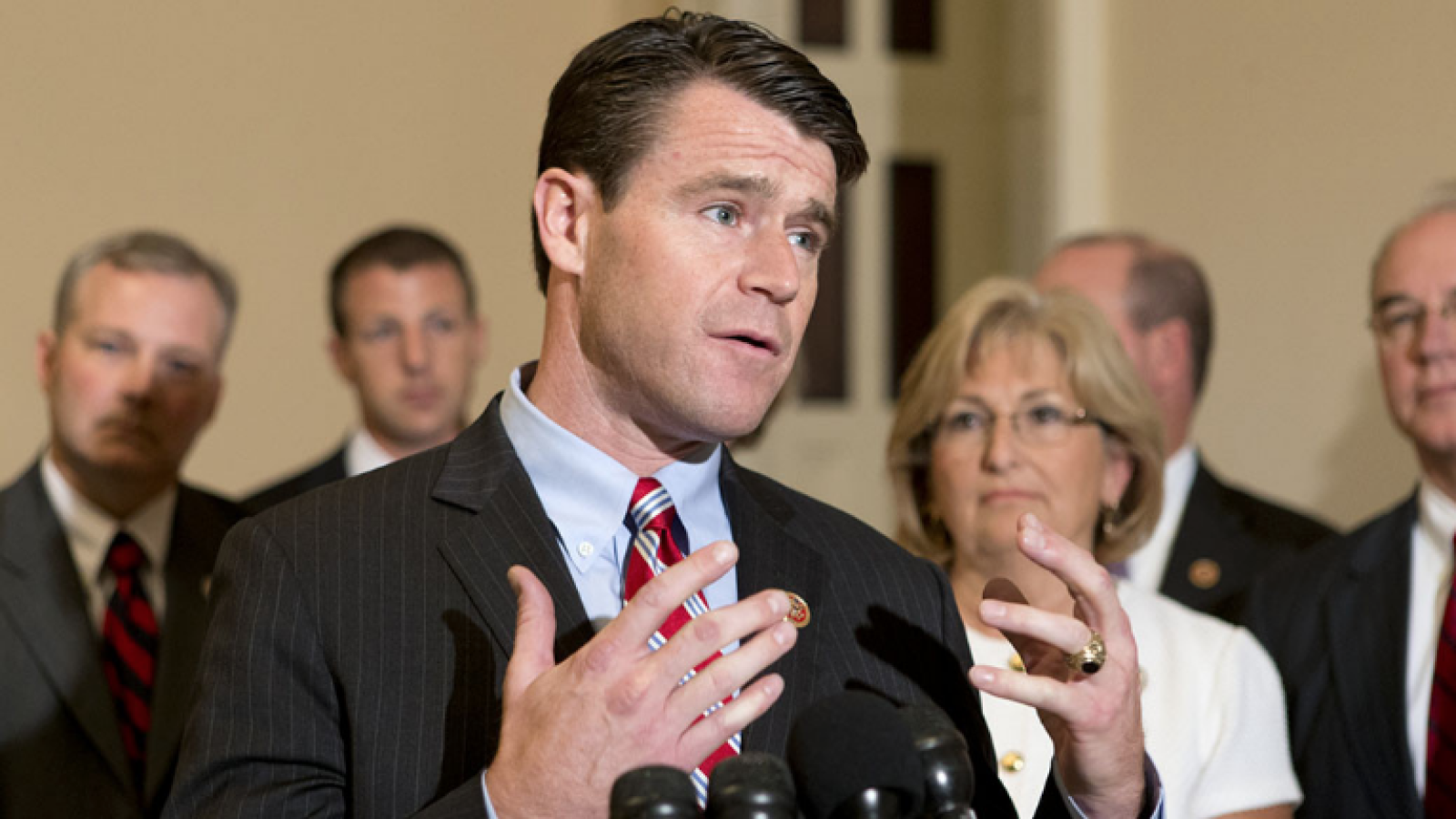
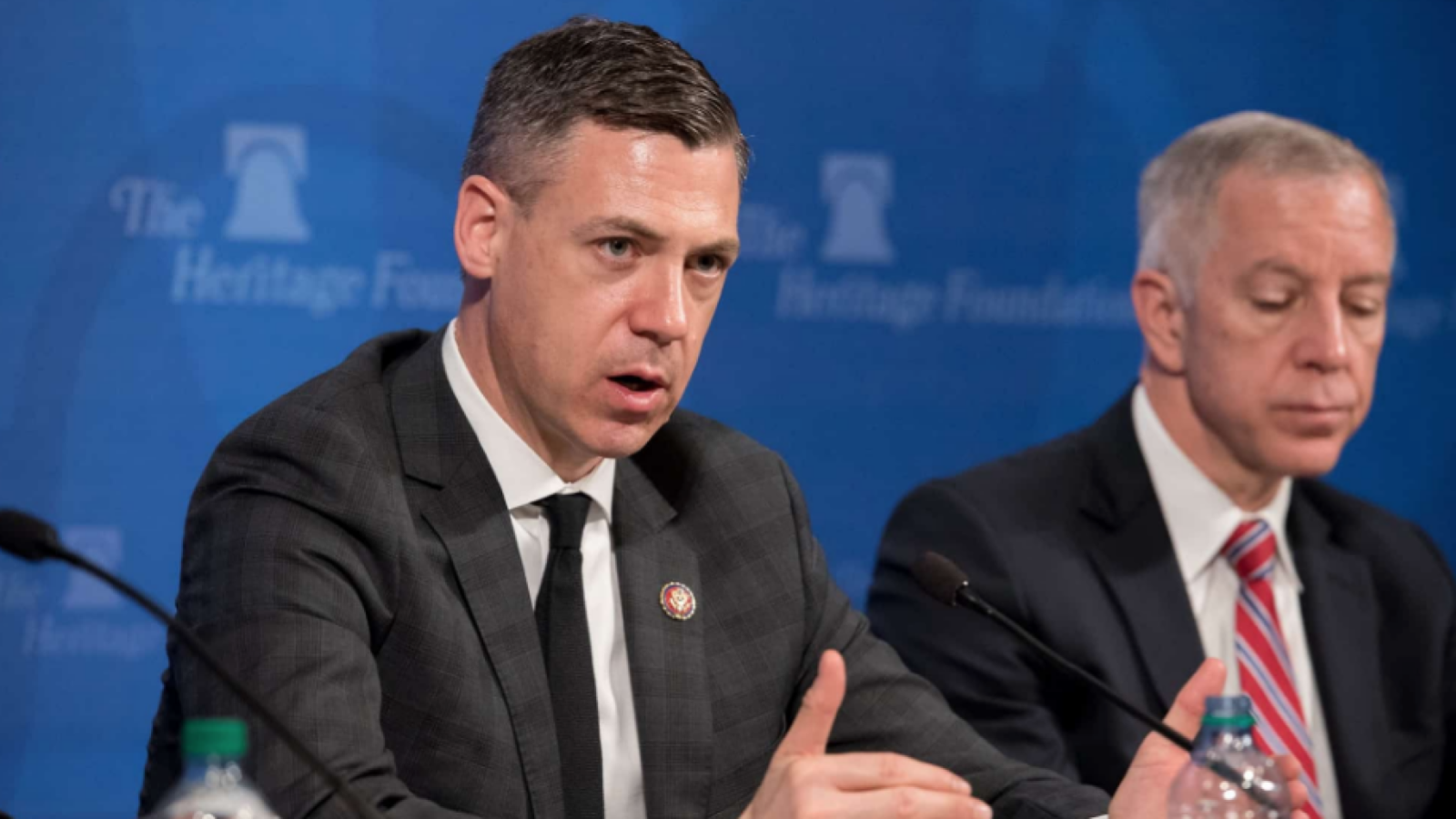
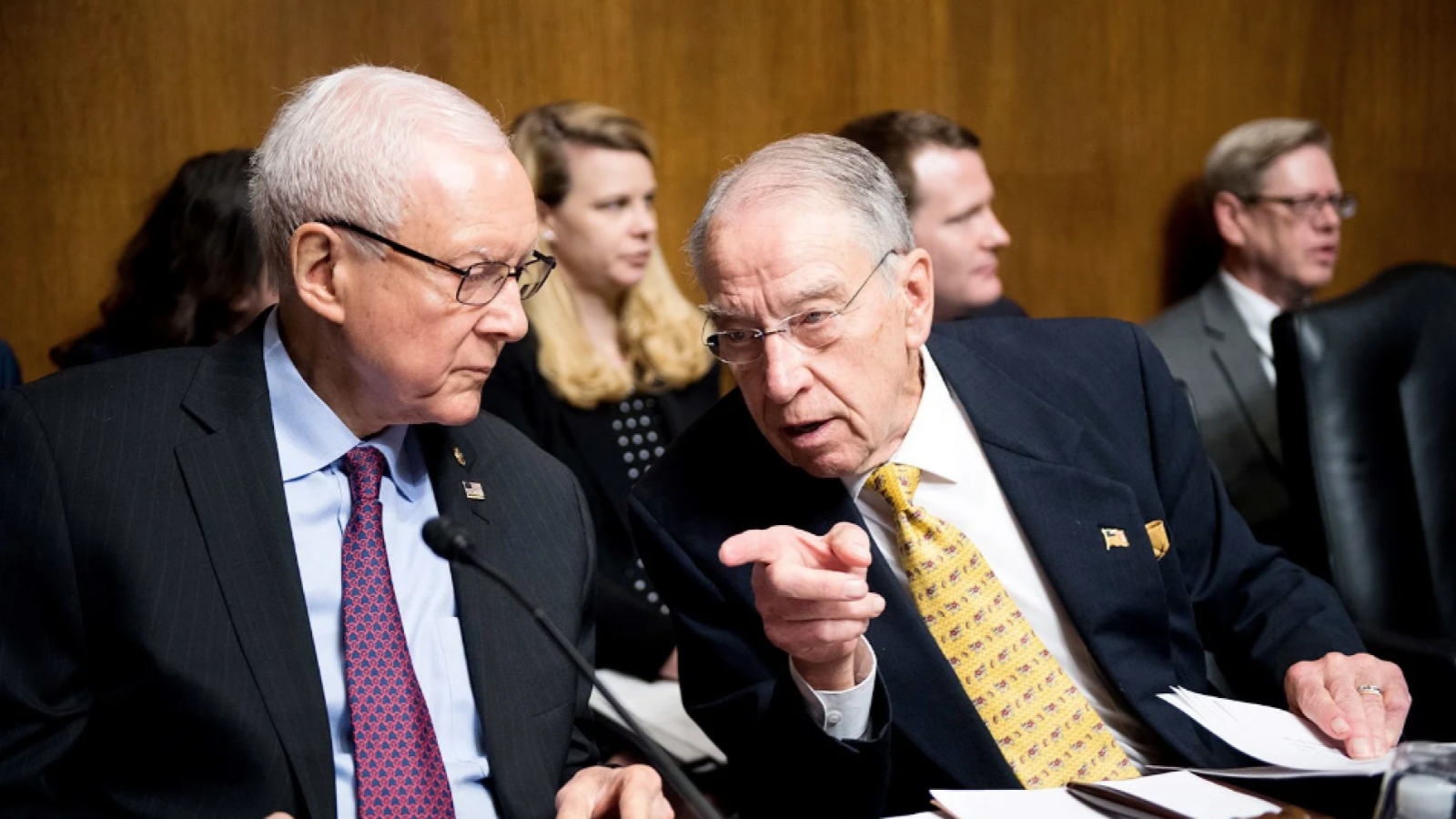
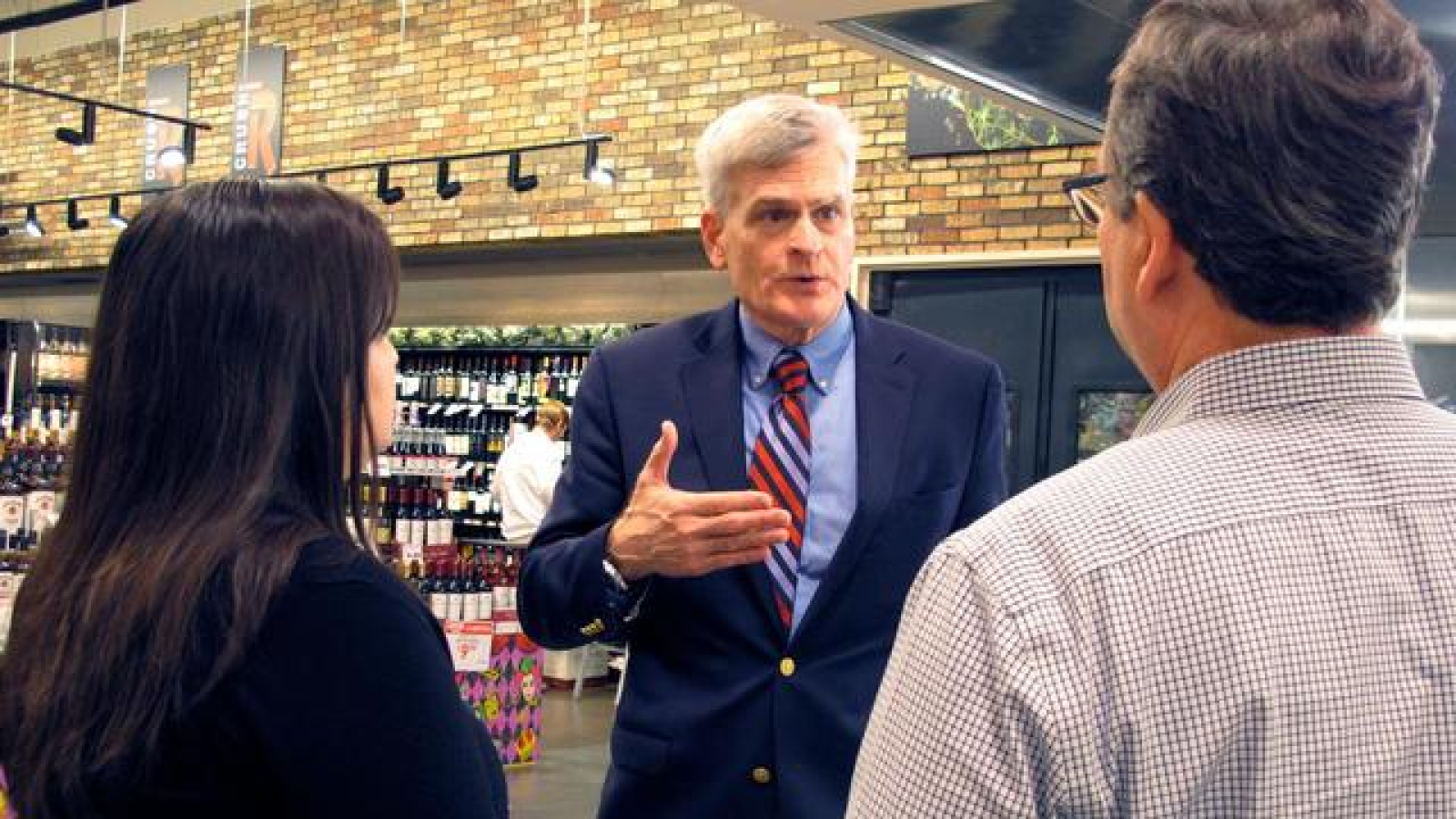
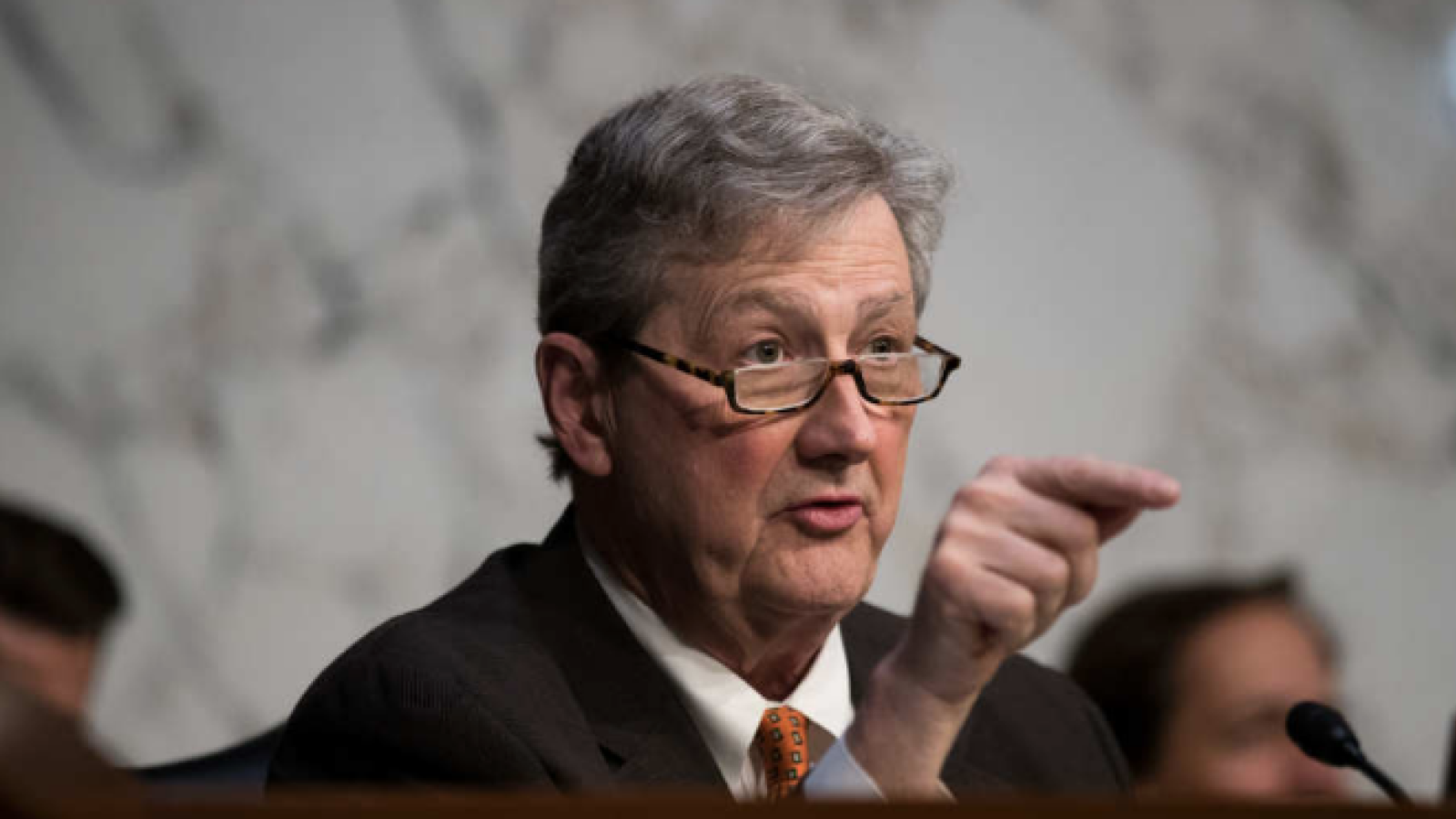
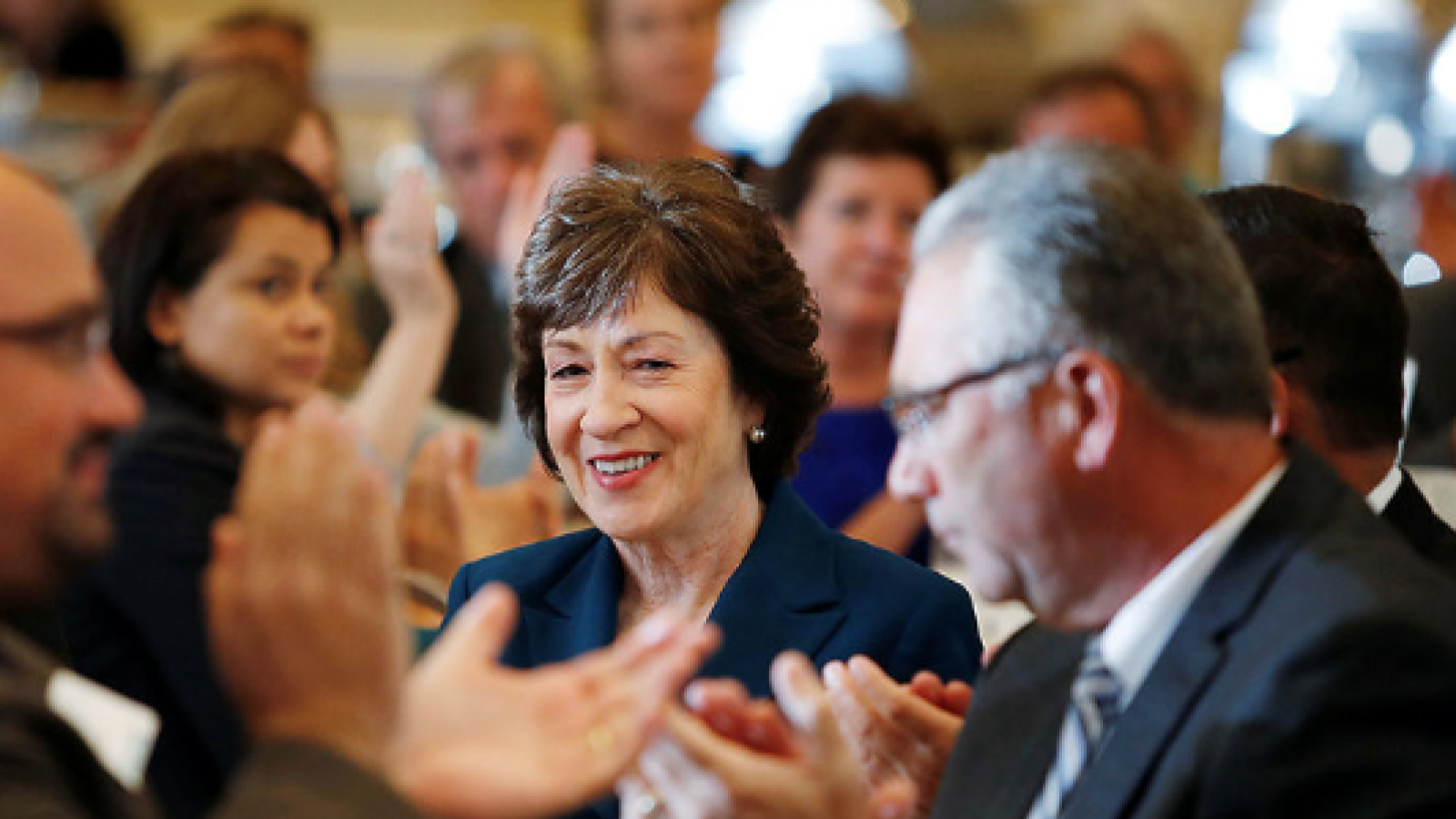
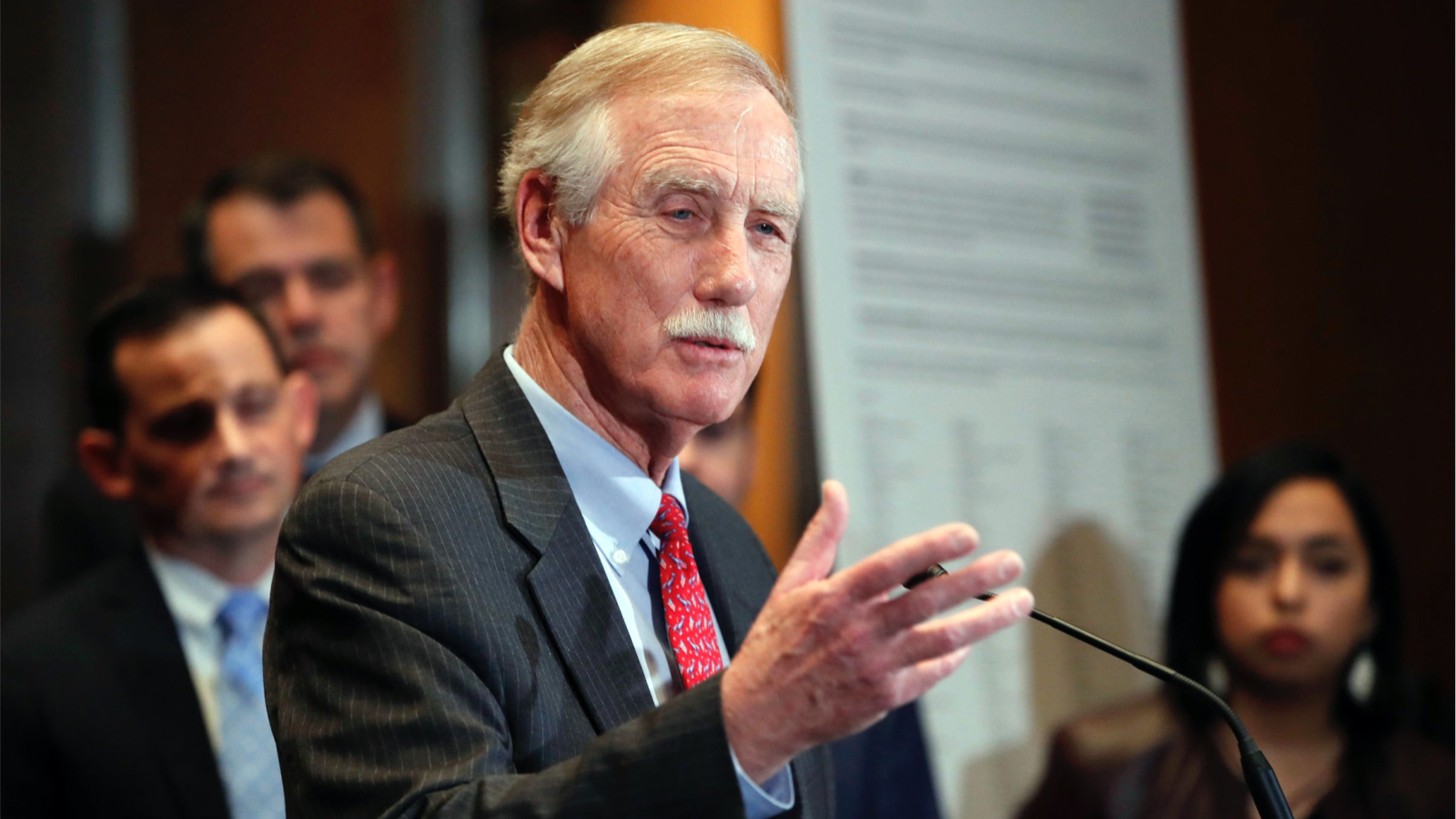
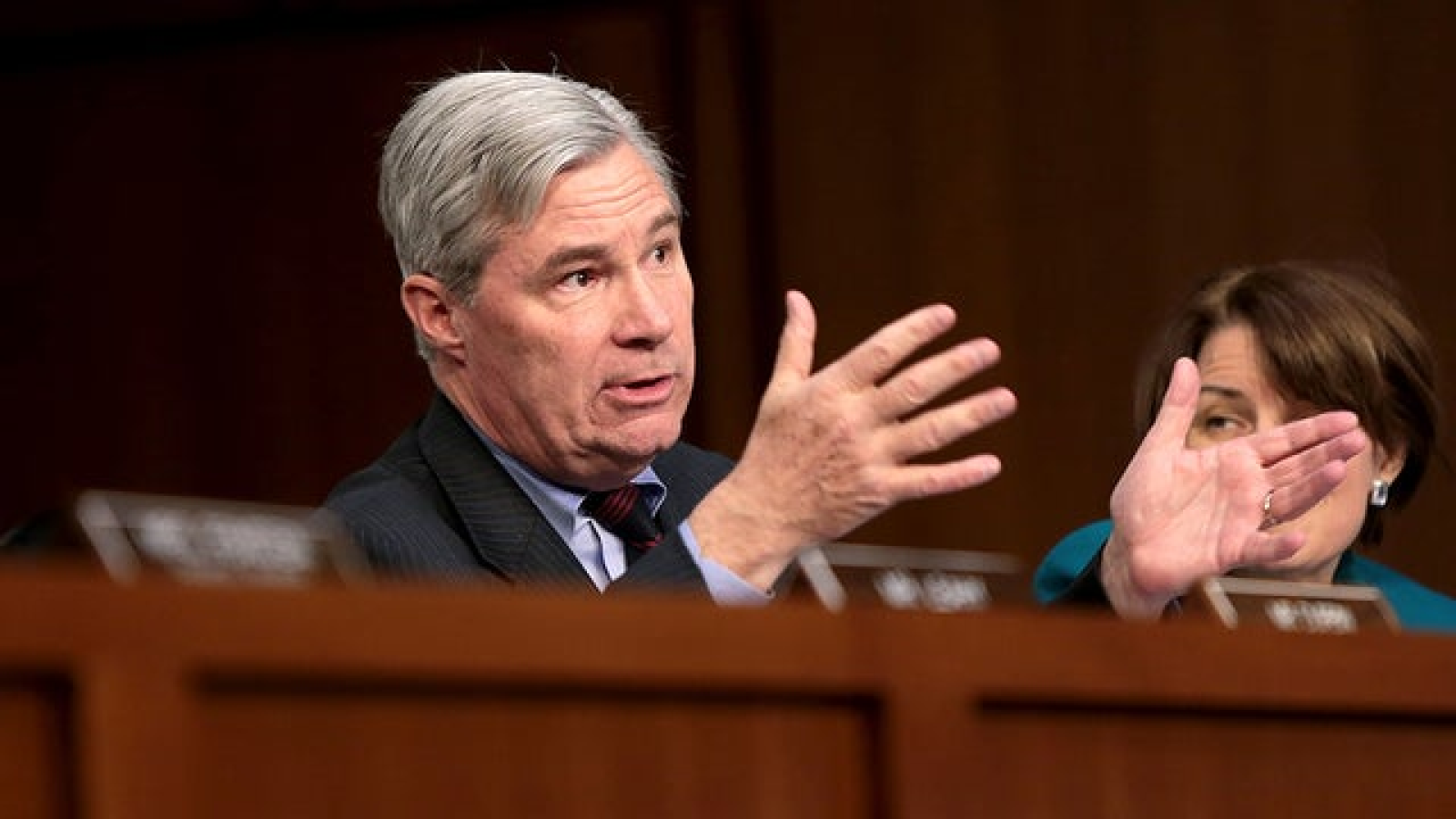
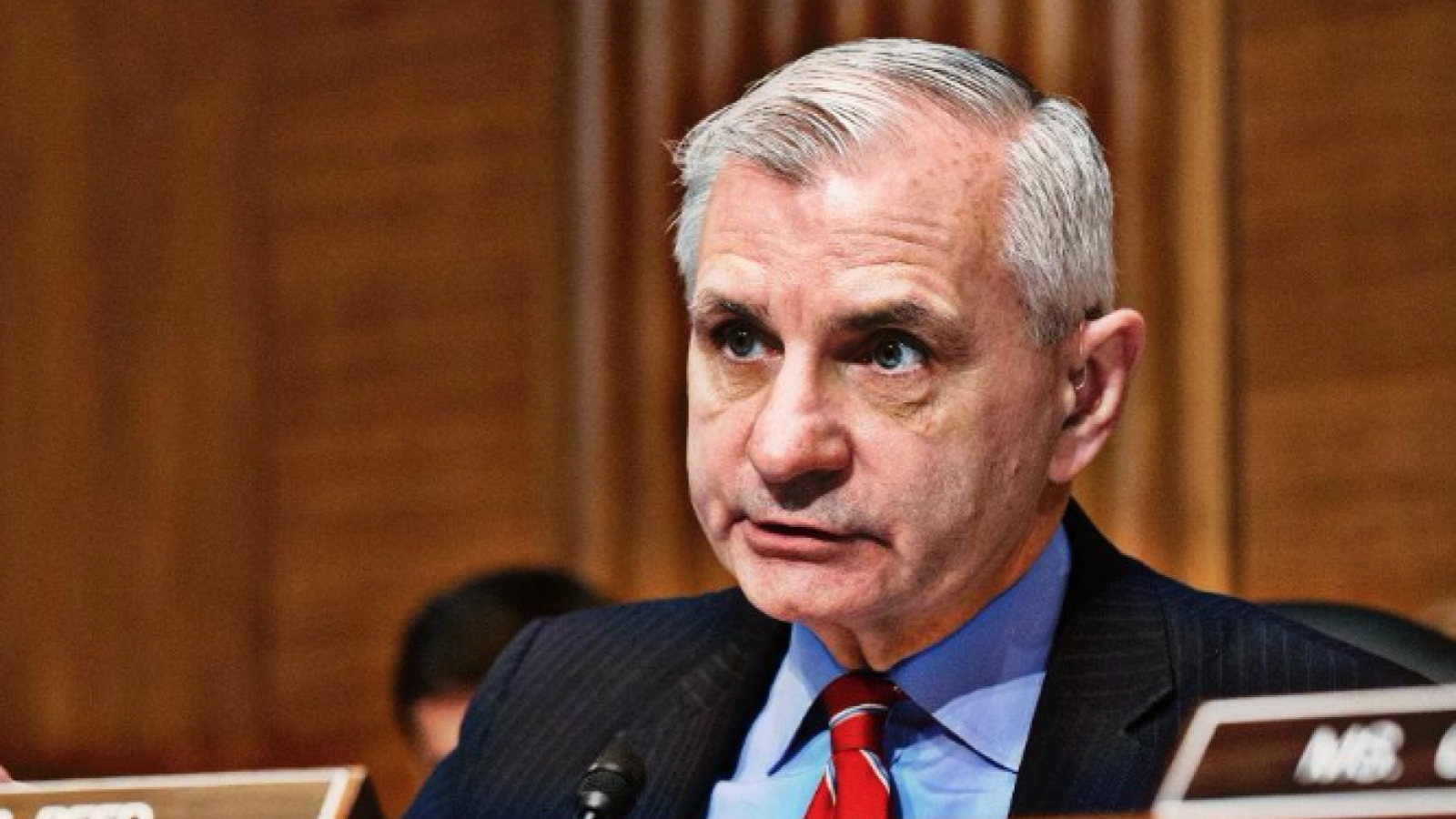
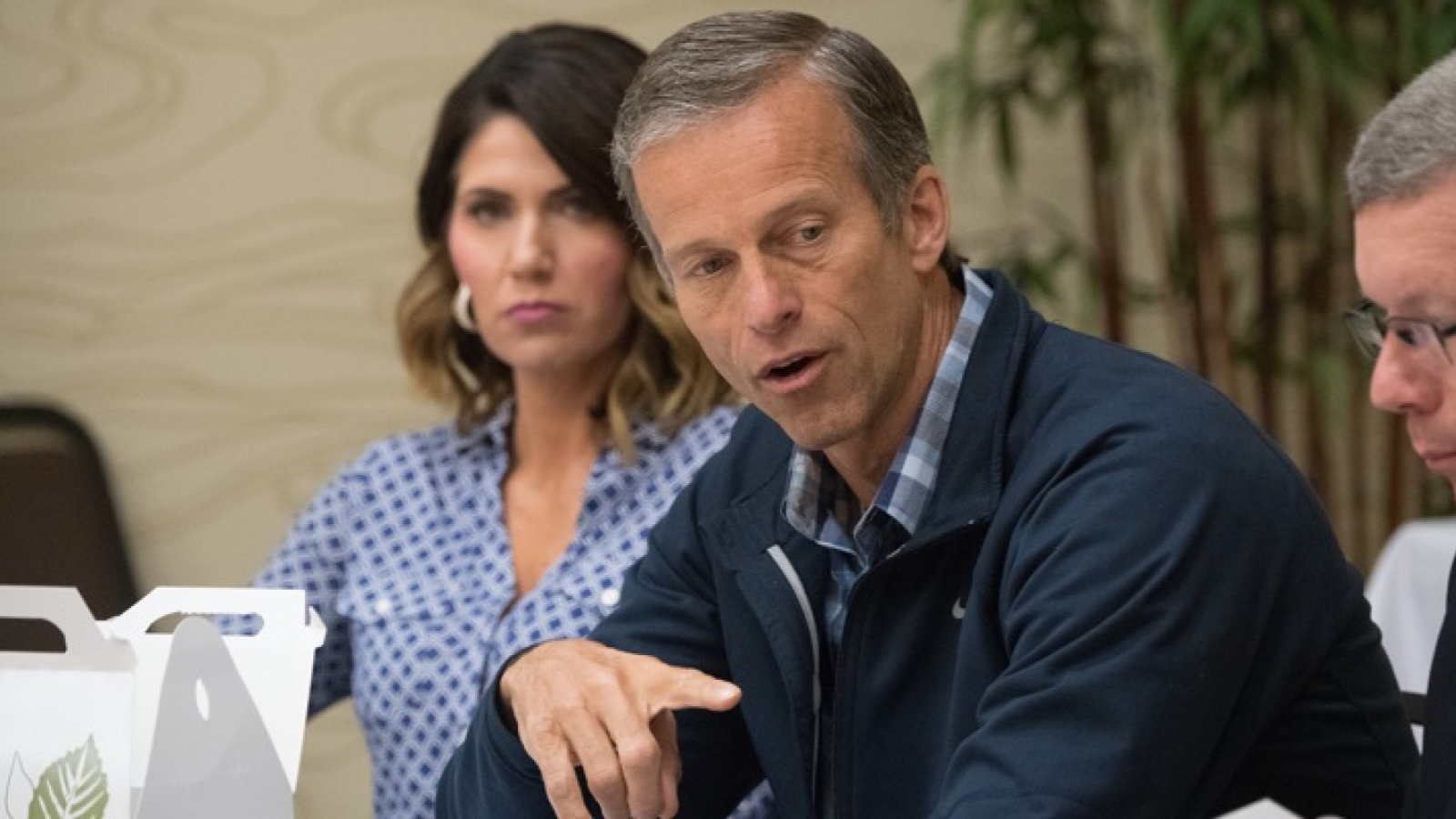
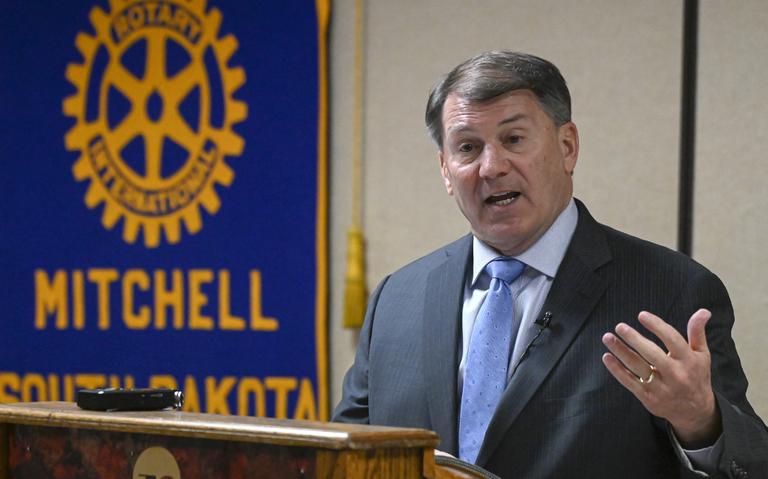
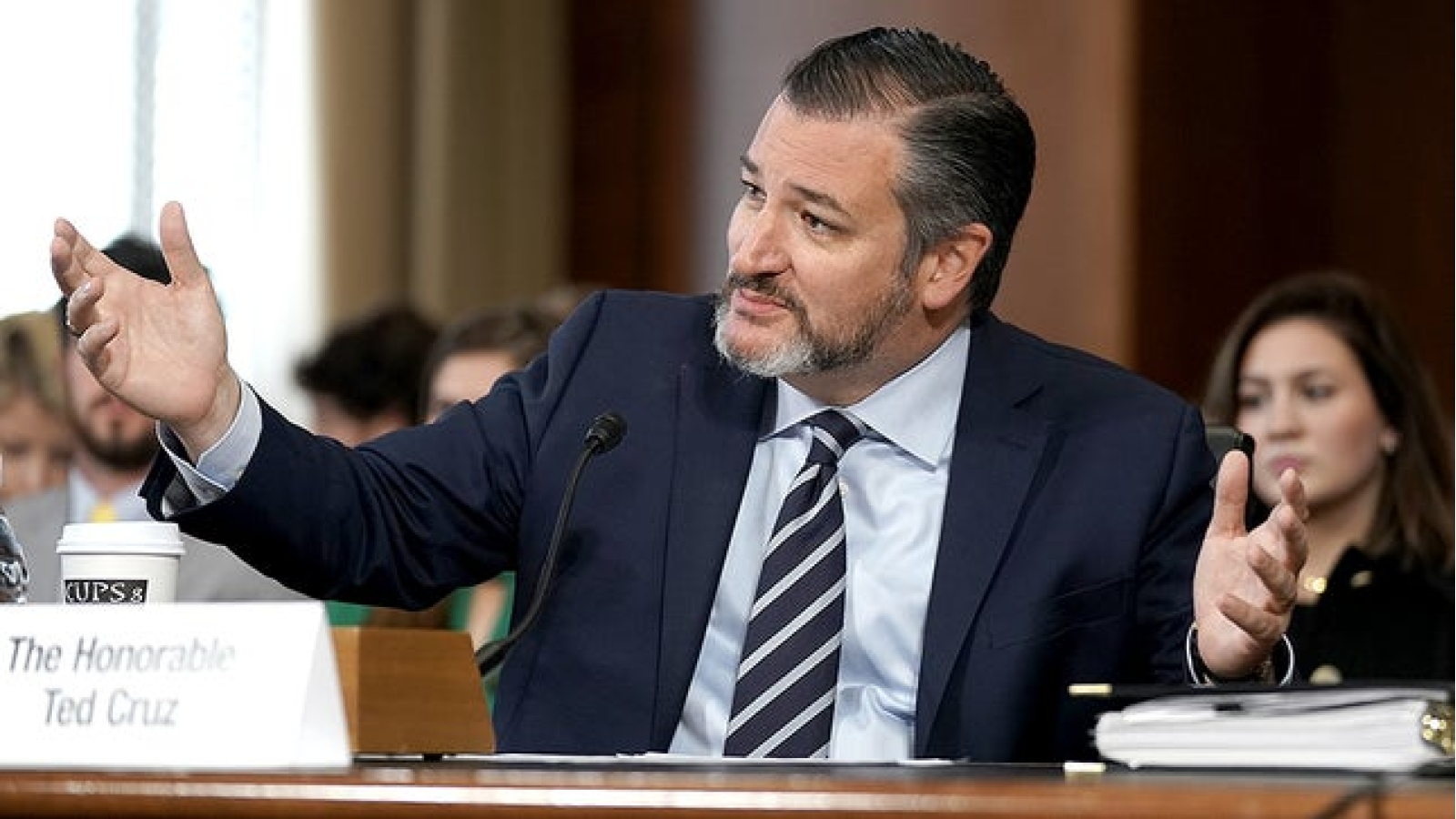
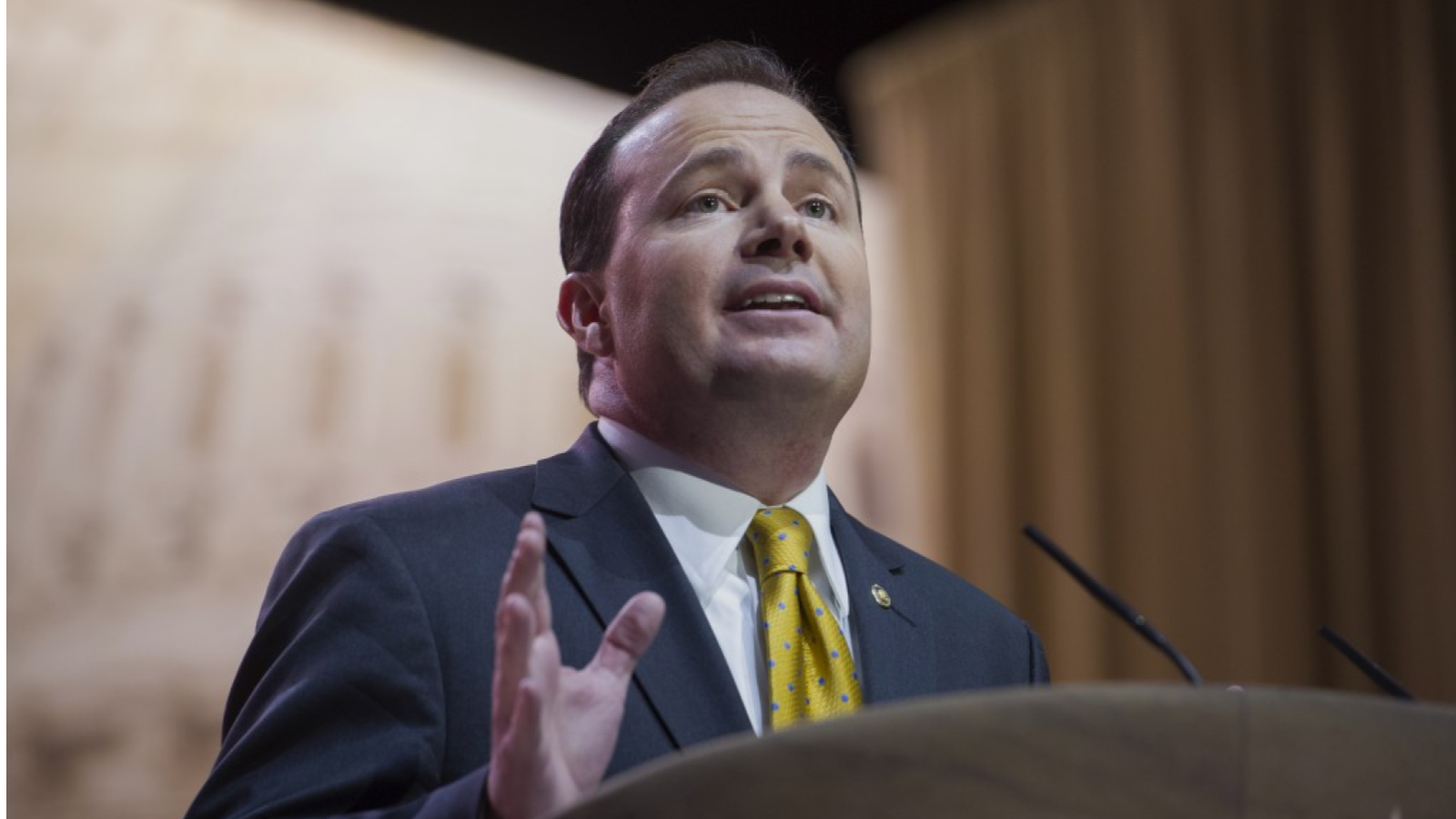
The 119th United States Congress is the current term of the legislative branch of the United States federal government. It convened on January 3, 2025, during the final 17 days of Joe Biden’s presidency, and will end in 2027. It will meet during the first two years of Donald Trump’s second presidency.
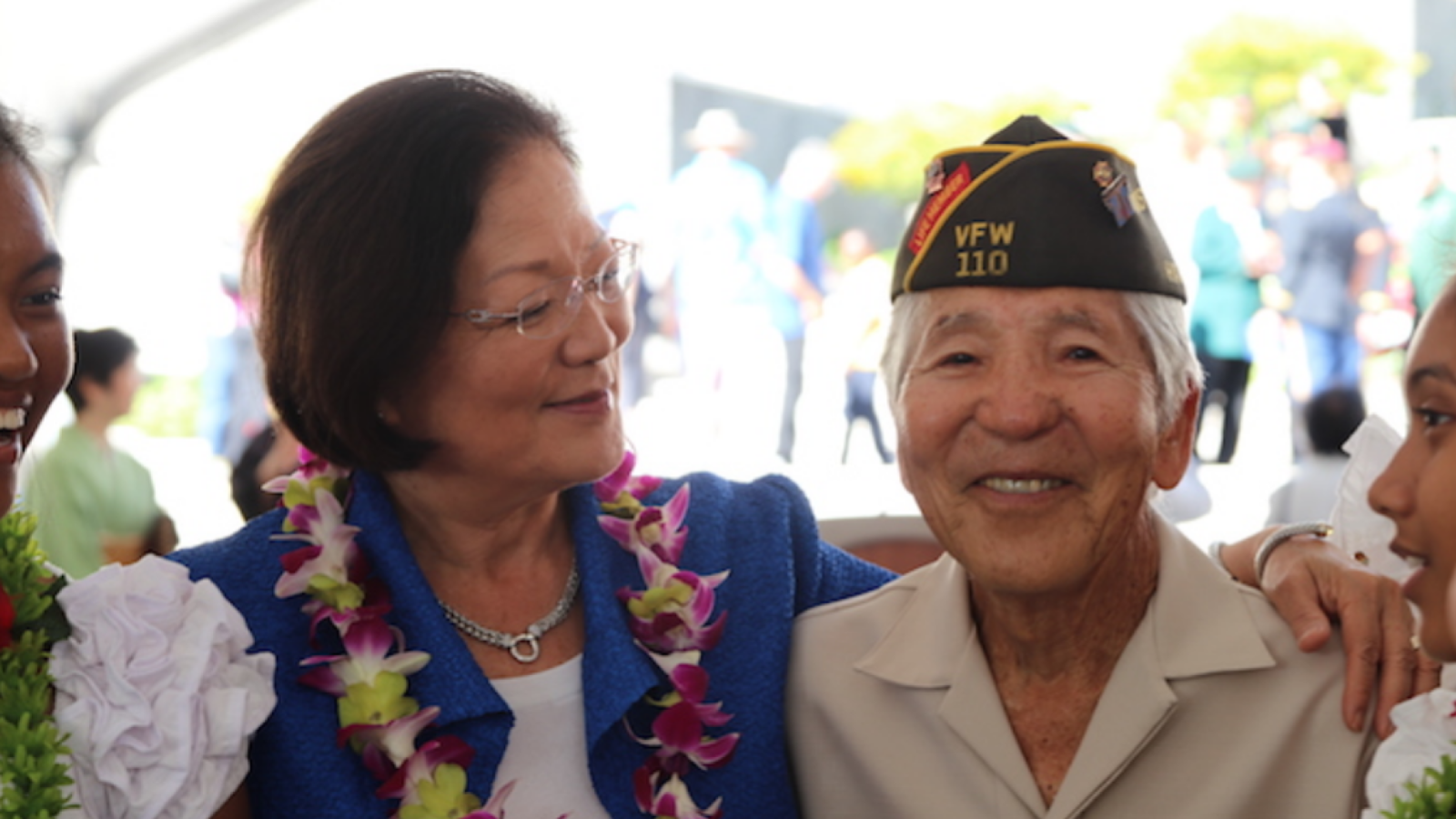
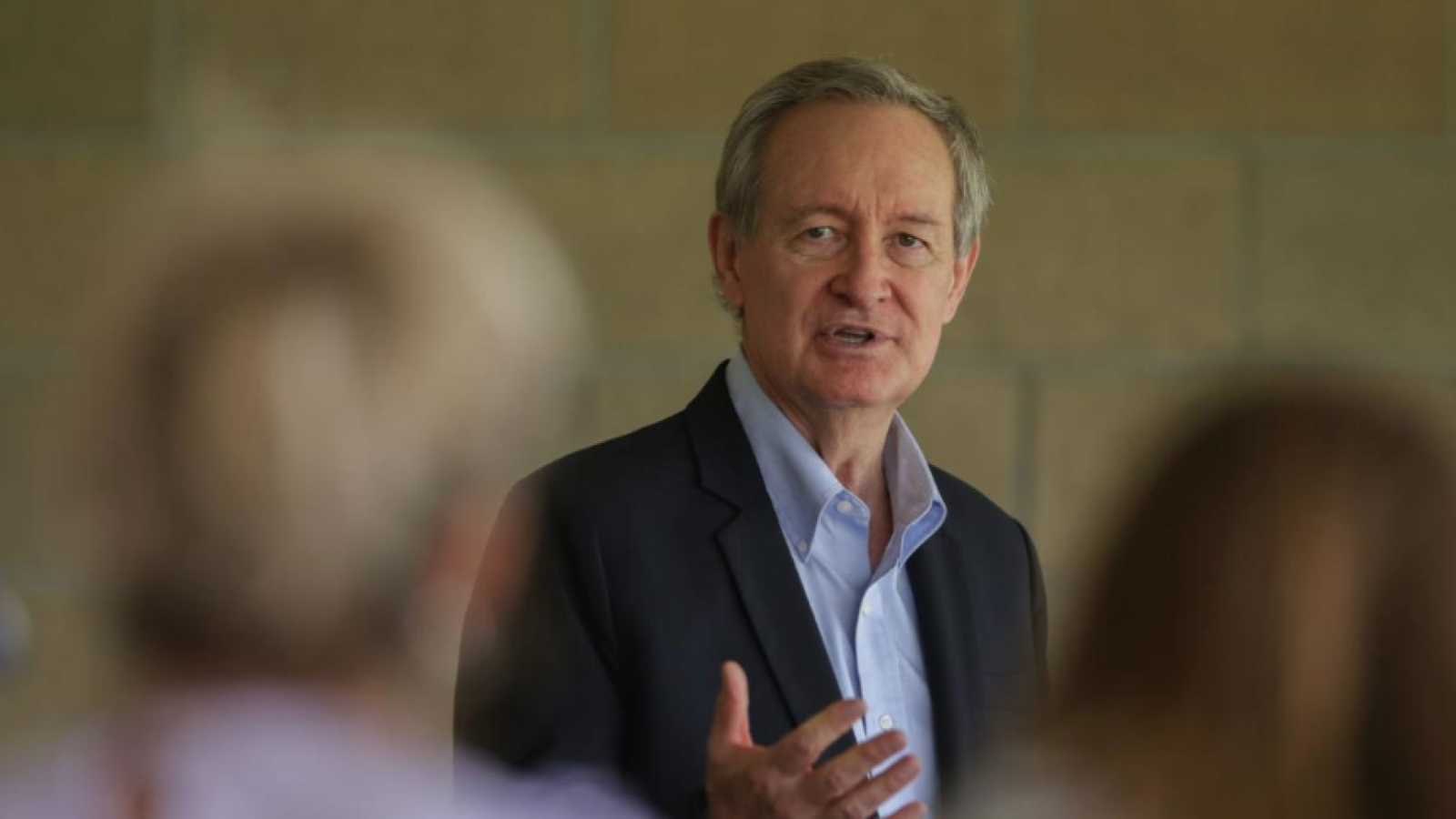
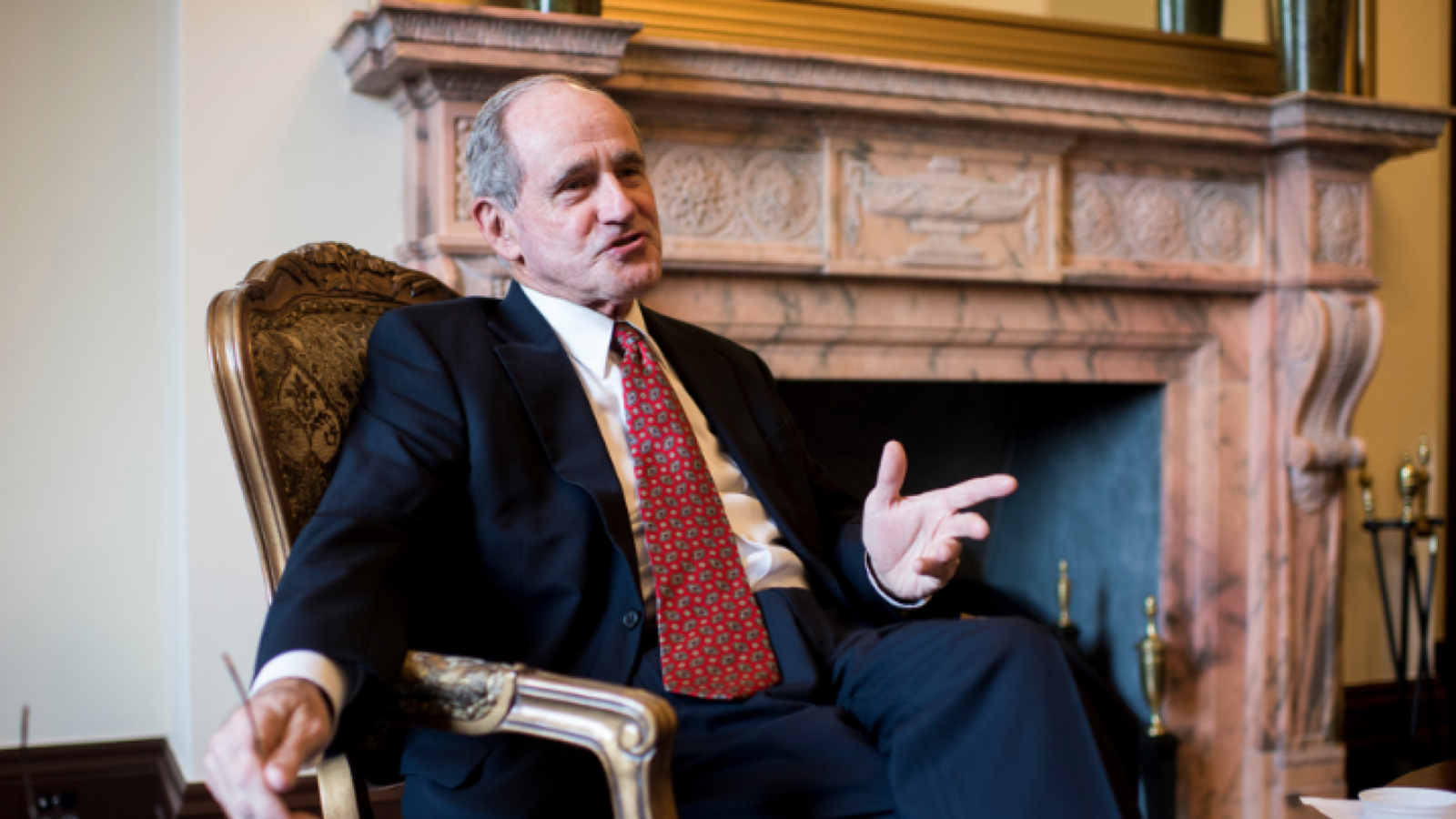
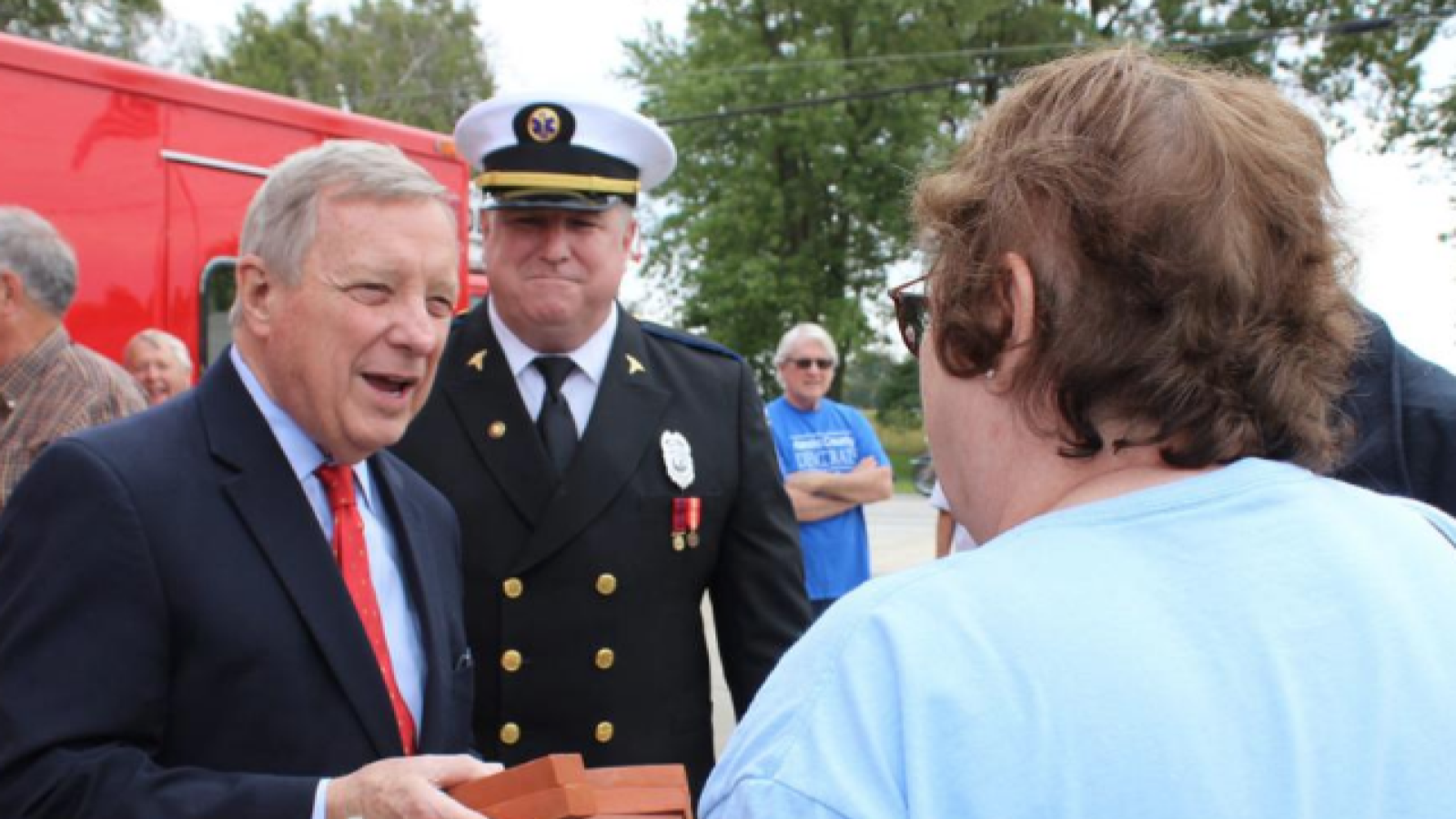
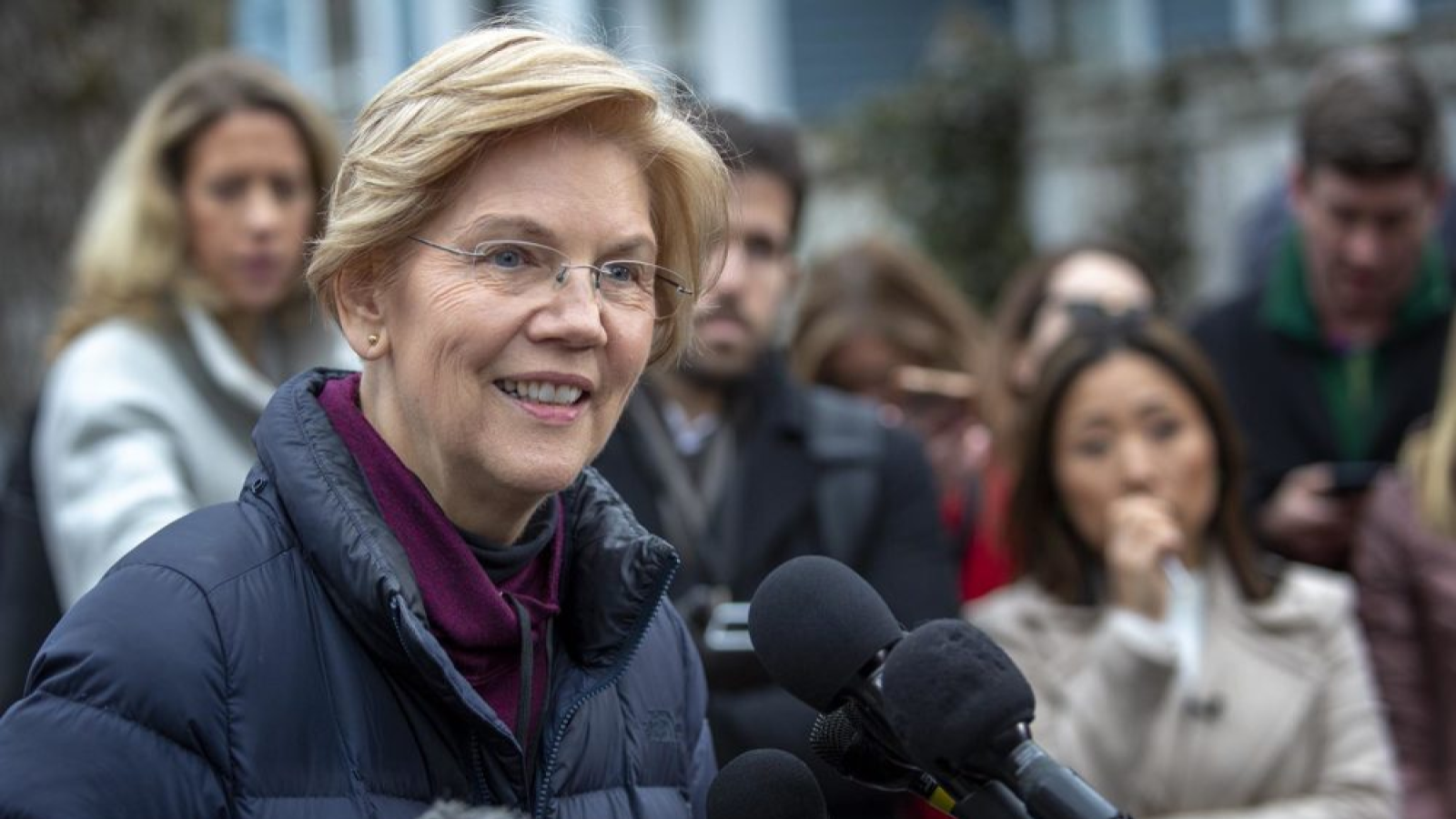
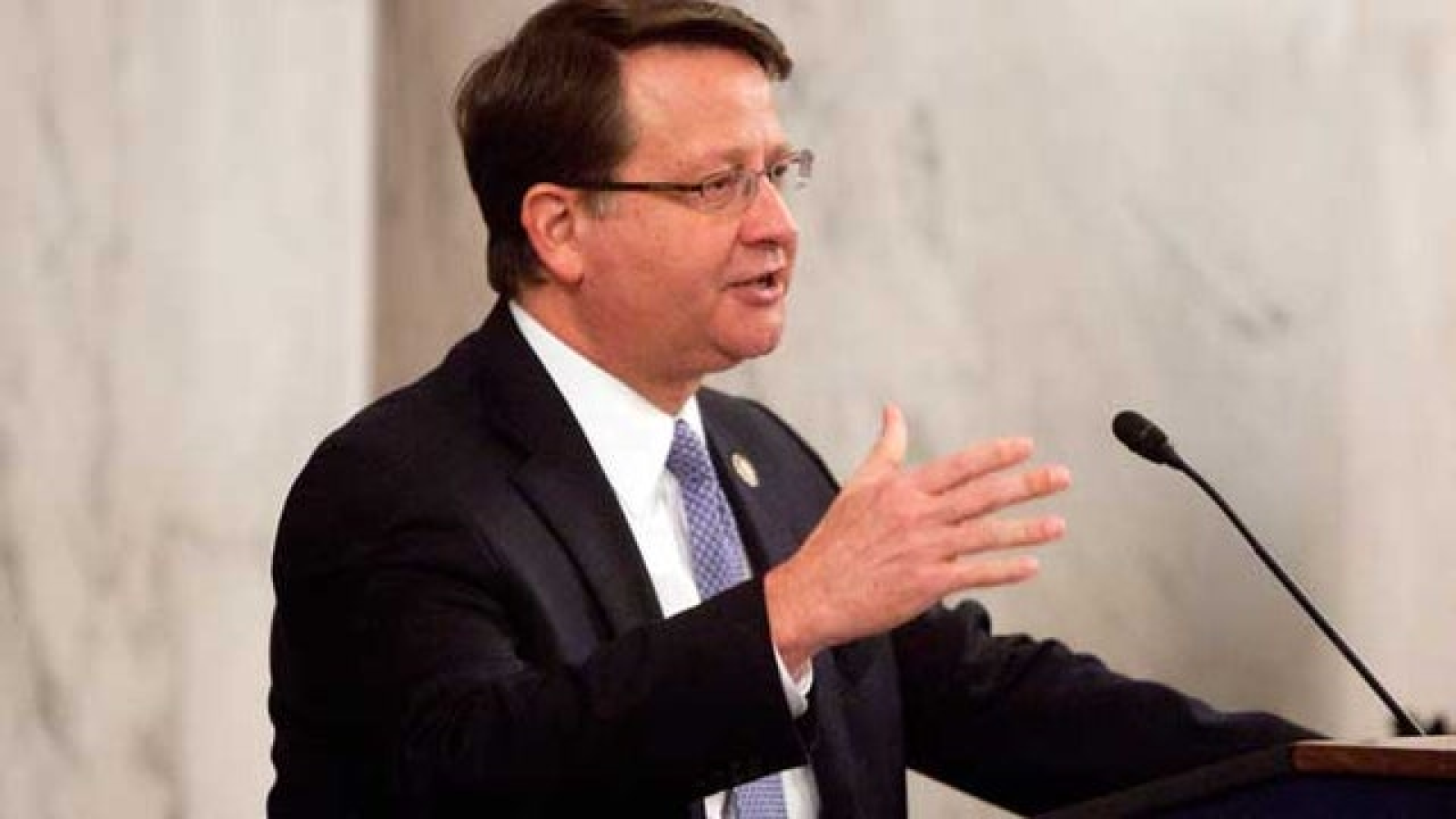
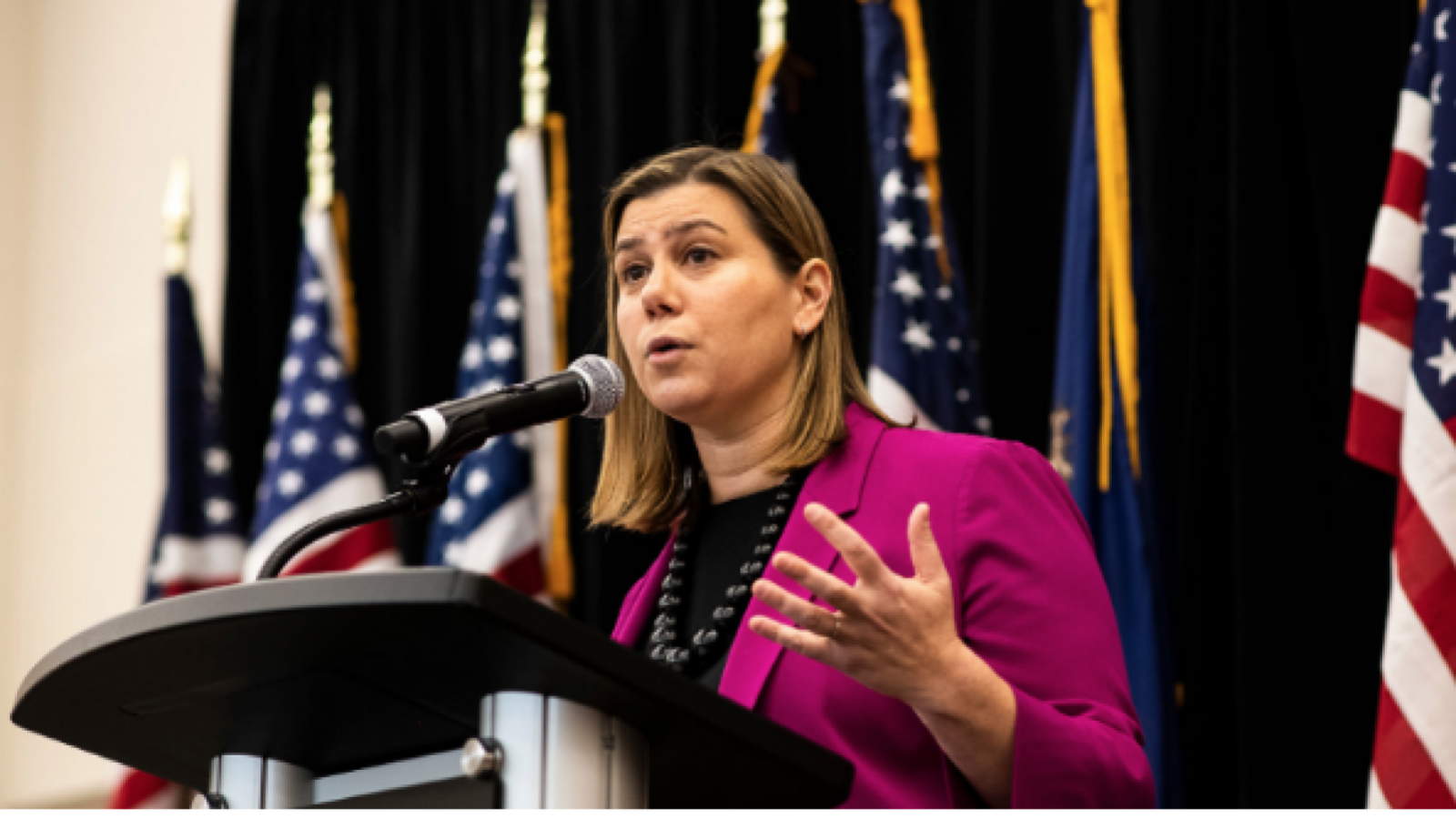
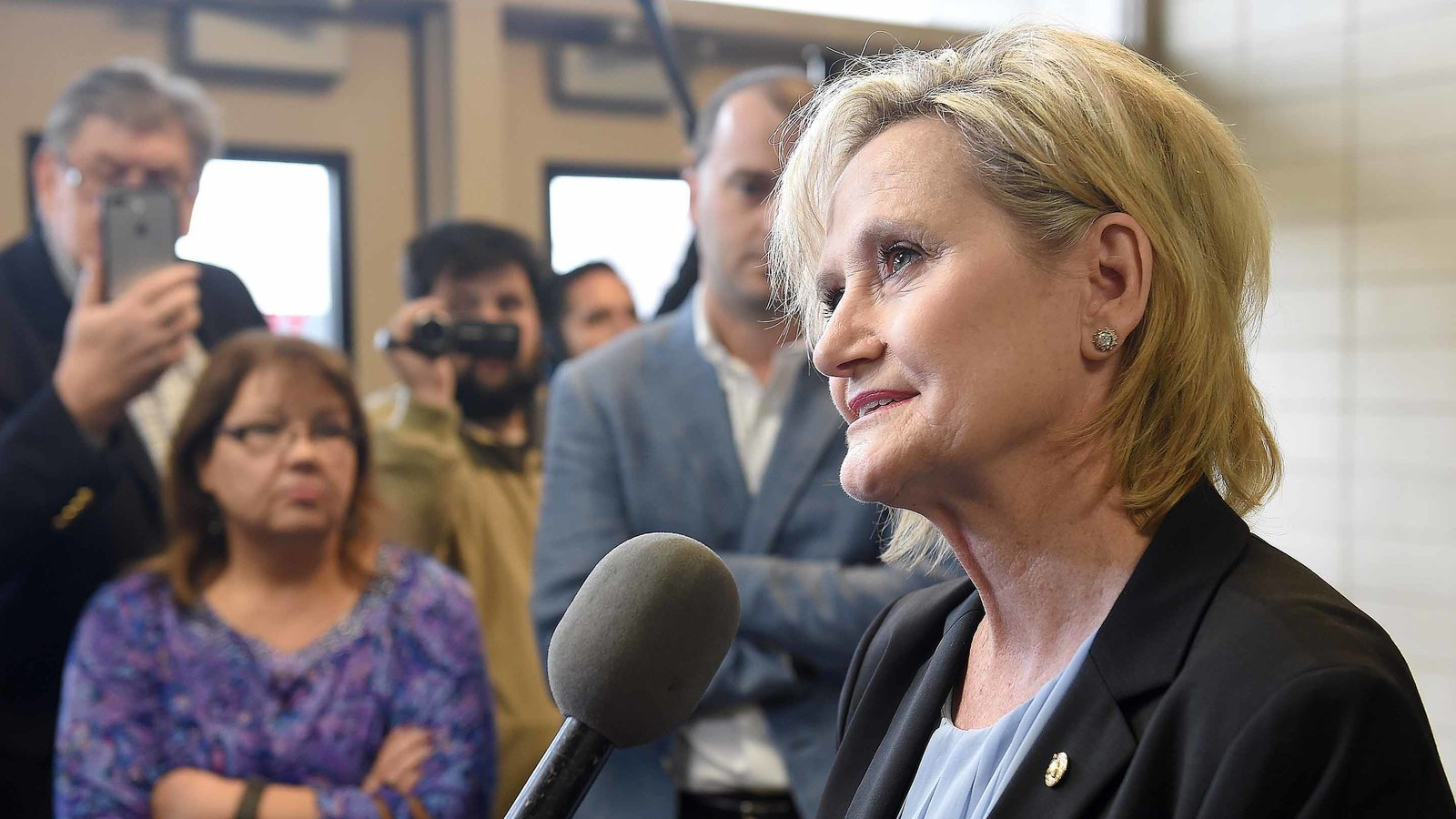
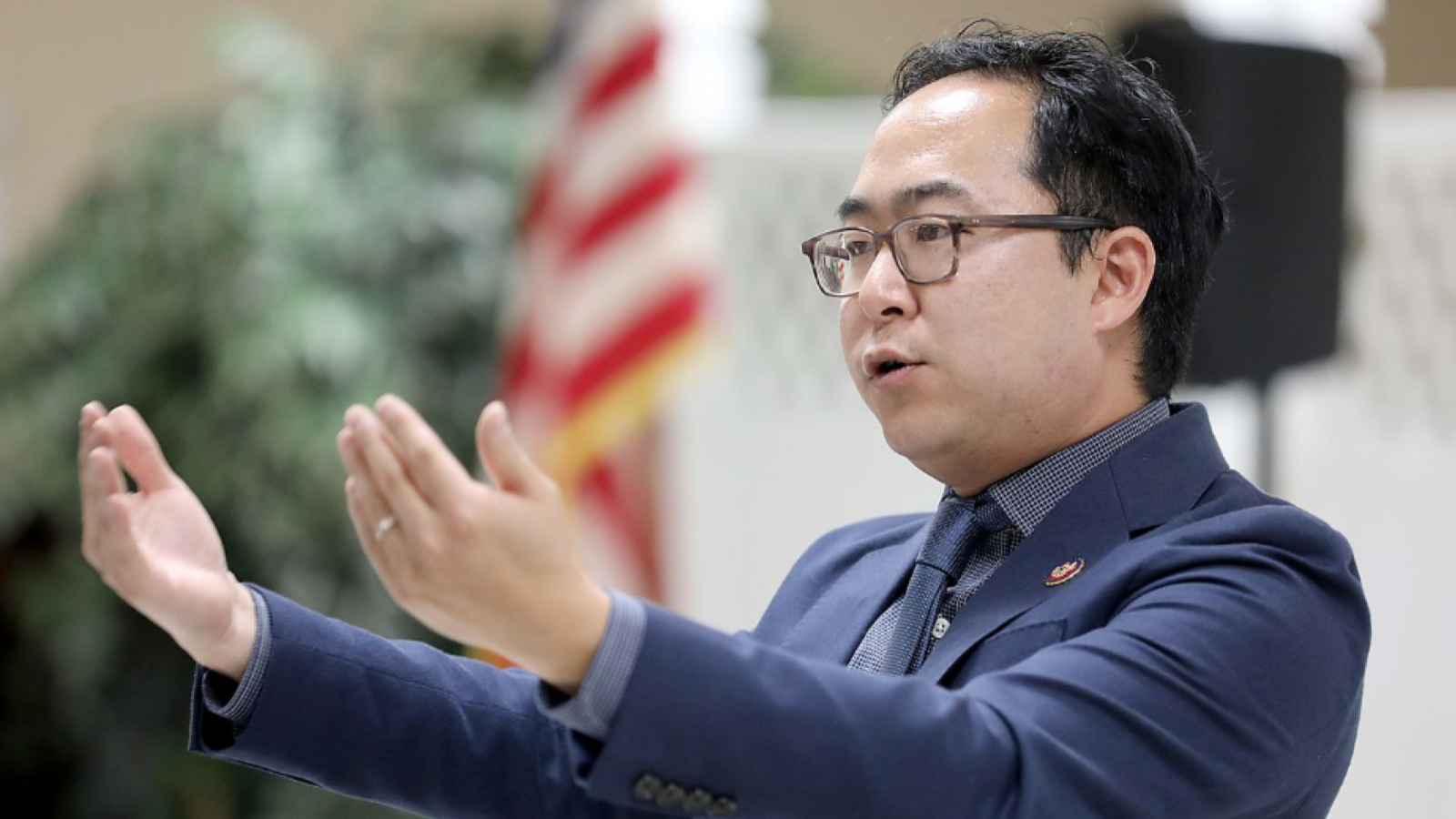
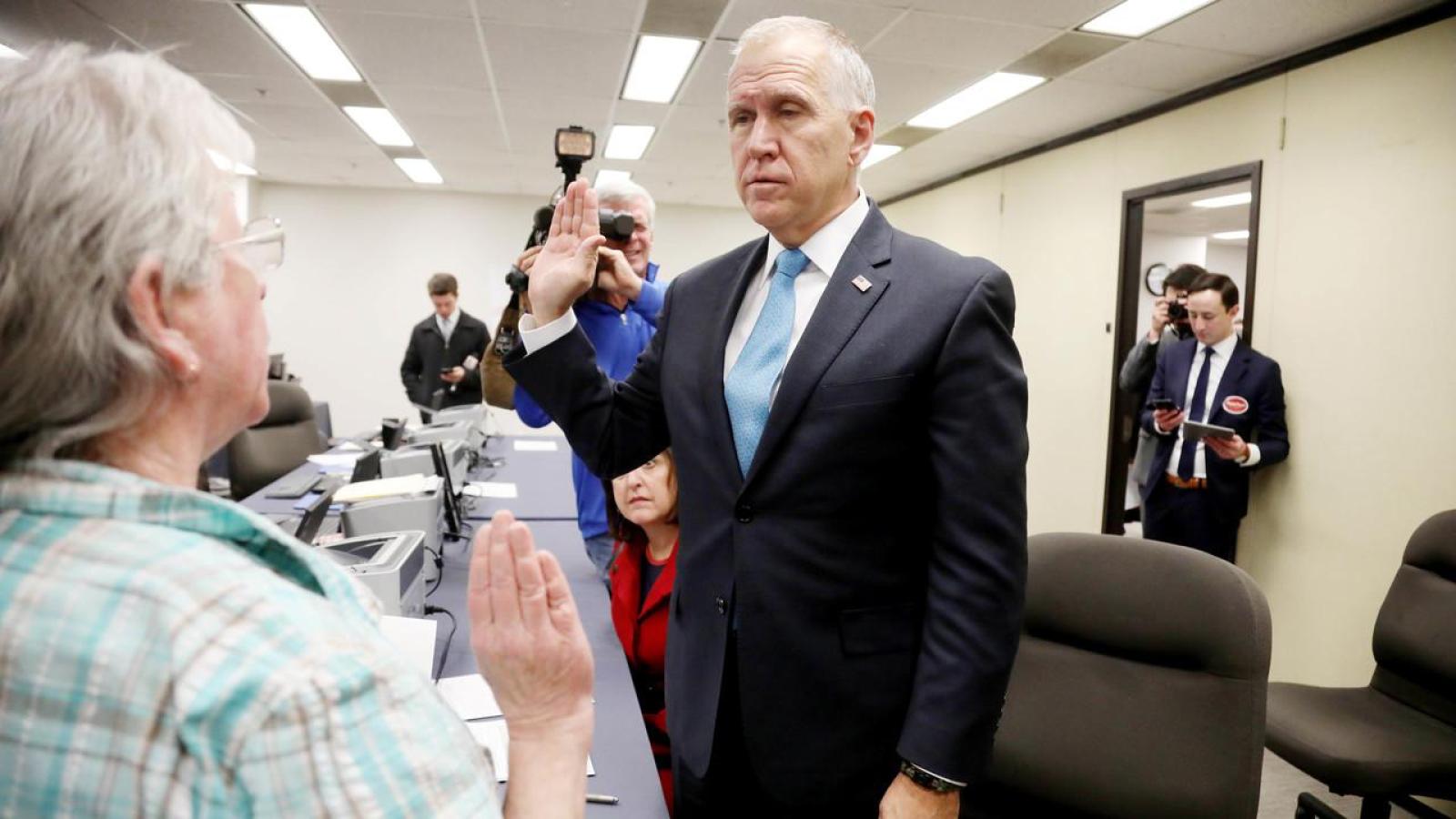
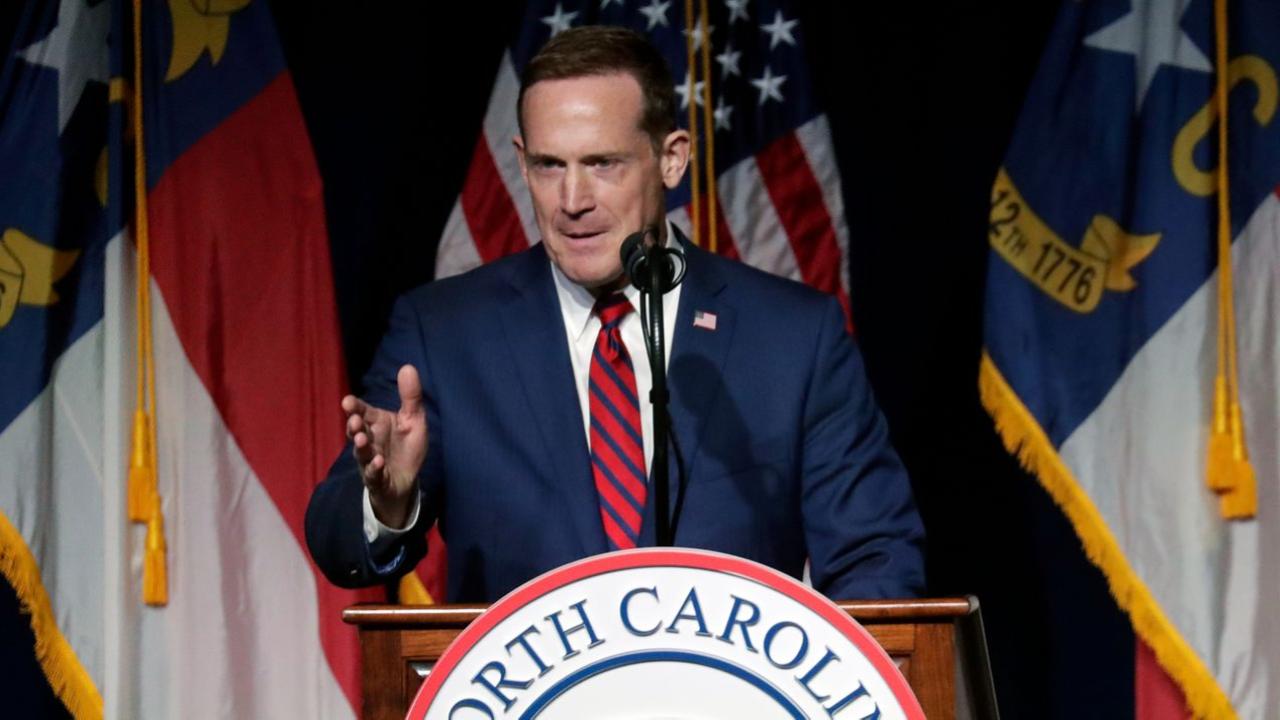
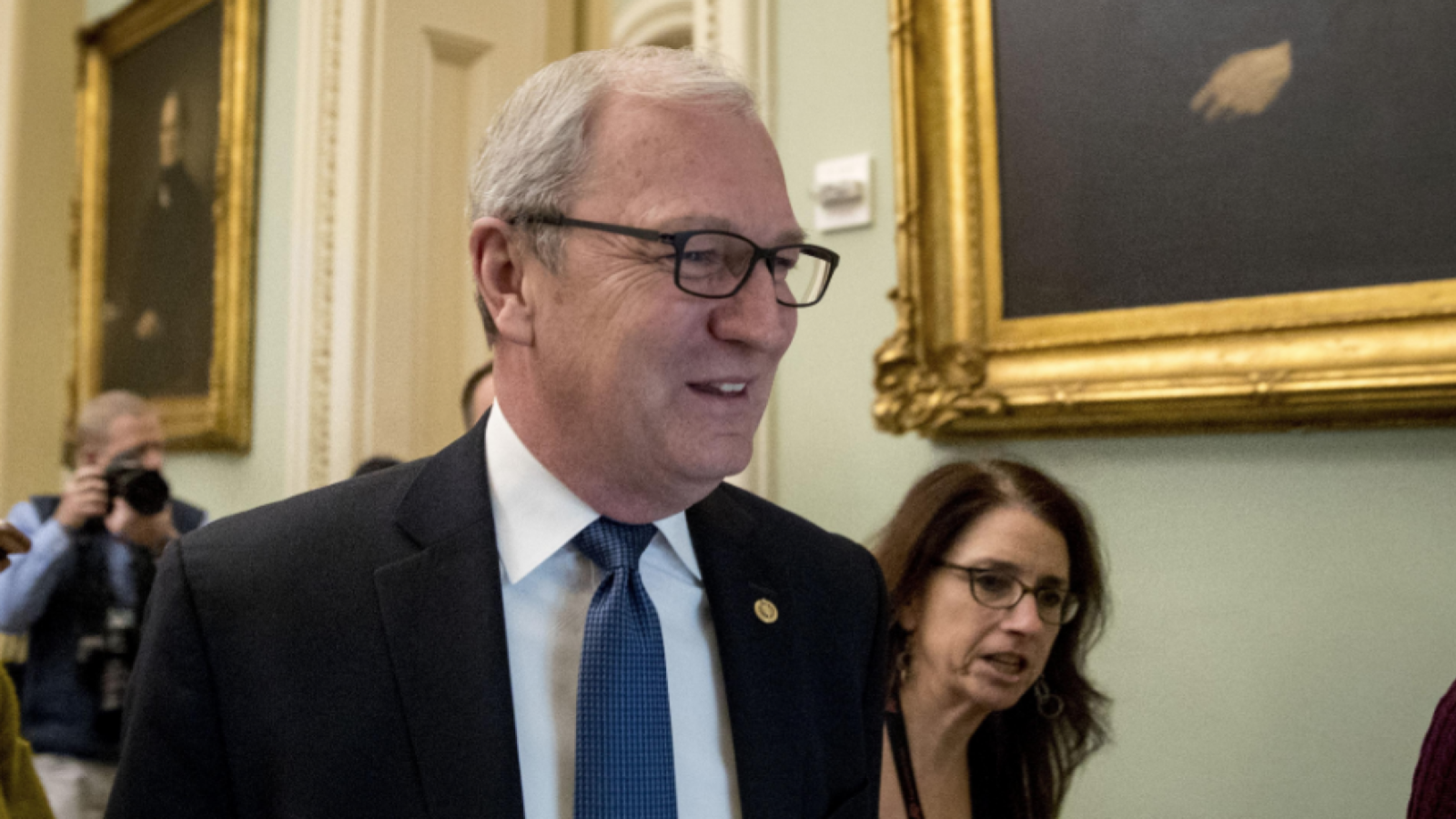
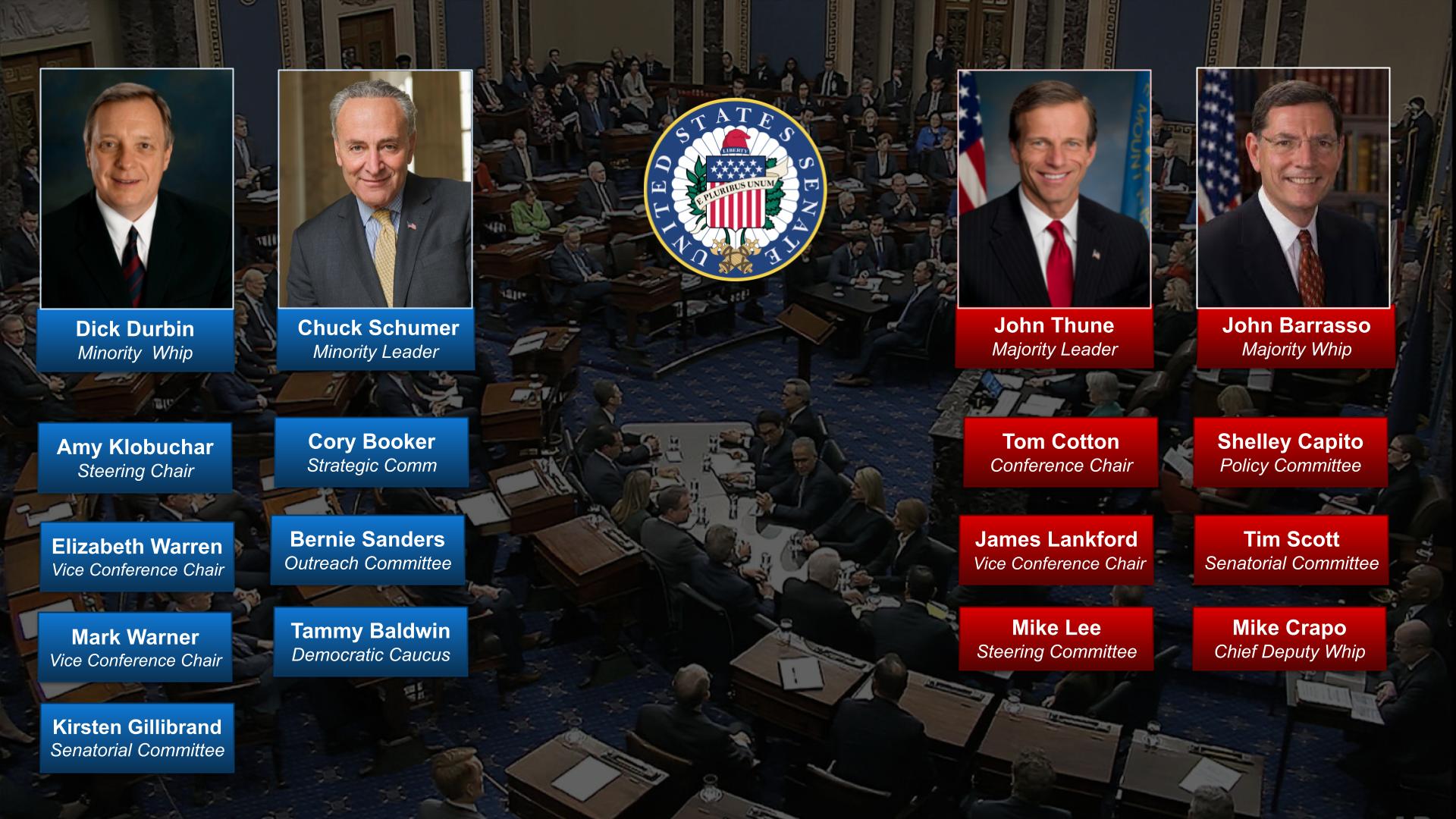
Following the 2024 elections, the Republican Party won the majority in the Senate with 53 Republicans winning their races and 47 Democrats winning their races. See this slider of posts on the new leaders of the Republican senators and this slider of post on the leaders of the Democratic senators. To view all the Republican senators, go this slider of their posts and to view all the Democratic senators, go this slider of their posts. All the senators can be found in this slider organized alphabetically by state name.
OnAir Post: US Senate- 119th Congress