Summary
Current Position: US Representative of TN District 7 since 2019
Affiliation: Republican
Former Position: State Senator from 2013 – 2018
District: parts of Middle and West Tennessee. most of the area is rural, more than half of the district’s vote is cast in either Montgomery County (Clarksville) or Williamson County (Franklin, Brentwood).
Upcoming Election:
Green has chaired the Committee on Homeland Security since 2023. After graduating from West Point, Green was an infantry officer. He then graduated from Boonshoft School of Medicine at Wright State University and became a flight surgeon, serving tours of duty in the War in Afghanistan and Iraq War.
Green became the CEO of a hospital emergency department staffing company.
Featured Quote:
We cannot allow the American dream to be destroyed by socialism. RT if you agree!
Fighting Tyranny with Rep. Mark Green
OnAir Post: Mark E. Green TN-07
News
About
 Congressman Mark Green first took the oath of office to represent the 7th District of Tennessee in Congress on January 3, 2019. It is the exact oath he first took as a cadet, on the historic Plain at West Point more than thirty years earlier. As a successful business leader, decorated combat veteran, ER physician, and former Tennessee State Senator, Green is uniquely equipped to represent the people of his district.
Congressman Mark Green first took the oath of office to represent the 7th District of Tennessee in Congress on January 3, 2019. It is the exact oath he first took as a cadet, on the historic Plain at West Point more than thirty years earlier. As a successful business leader, decorated combat veteran, ER physician, and former Tennessee State Senator, Green is uniquely equipped to represent the people of his district.
The son of a hardworking father and loving mother, Congressman Mark Green grew up on a dirt road in Mississippi. He came to Tennessee in his last assignment in the Army as the flight surgeon for the premier special operations aviation regiment. As a Night Stalker, Green deployed to both Iraq and Afghanistan in the War on Terror. His most memorable mission was the capture of Saddam Hussein. During the mission, he interrogated Hussein for six hours. The encounter is detailed in a book Green authored, A Night With Saddam. Congressman Green was awarded the Bronze Star, the Air Medal with V Device for Valor, among many others.
After his service in the Army, Green founded an emergency department staffing company that grew to over $200 million in annual revenue. The company provided staffing to 52 hospitals across 11 states. He also founded two medical clinics that provide free healthcare to under-served populations in Memphis and Clarksville as well as numerous medical mission trips throughout the world.
Green was elected to the Tennessee State Senate in 2012, where he distinguished himself as a conservative leader that fought for freedom and smaller government for all Tennesseans. His many legislative accomplishments include the repeal of the Hall Income Tax and the passage of the Tennessee Teacher Bill of Rights. He won the National Federation of Independent Businesses’ Guardian of Small Business award and the Latinos for Tennessee’s Legislator of the Year award, among many other recognitions.
In Congress, Green has worked tirelessly on behalf of people of Tennessee’s 7th District. He serves on the House Armed Services Committee, House Foreign Affairs Committee, and the Select Committee on the Coronavirus Crisis. In addition, Green serves as Ranking Member of the House Foreign Affairs Subcommittee on the Western Hemisphere, Civilian Security, Migration, and International Economic Policy.
Green has sponsored 24 pieces of legislation and cosponsored 168 pieces of legislation over issues facing the people of Tennessee. From strengthening rural healthcare, to holding China accountable, to supporting Gold Star families and bringing American businesses back home, Congressman Green’s well-rounded background in business, healthcare, and the military has made him distinctly qualified to address such issues.
Congressman Green’s experience building a successful healthcare company equips him to take on wasteful spending and over-regulation from Washington. He introduced the Balanced Budget Amendment to the Constitution that requires Congress to pass a balanced budget and stick to it.
His 24 years of service—between the Academy, active duty Army and Army Reserves—have impressed upon him the need for a well-cared for military family. Green made veteran families a priority during his time in the Tennessee State Senate, and has continued to do so during his time in Congress. His first bill introduced in the House was the Protecting Gold Star Spouses Act that allows for spouses to continue receiving benefits during government shutdowns. He introduced another bill for Gold Star families, the Protecting Gold Star Children Act, which places children receiving benefits in the appropriate tax bracket.
Green has also worked to improve resources for the mental and physical health of veterans. He introduced the Spiritual Readiness amendment to the NDAA to address spiking numbers of veteran suicides. In addition, he led the bipartisan fight to include provisions for veterans subjected to toxic exposure while serving at the K2 Air Base in Uzbekistan during the War on Terror. In January of 2021, the President signed an Executive Order modeled after Rep. Green’s bipartisan K2 Veterans Toxic Exposure Accountability Act that requests the Secretary of Defense recognize Uzbekistan as a combat zone for purposes of medical care. This action represents a crucial step toward recognition of K2 veterans’ severe and deadly service-connected illnesses.
His time serving in the Armed Forces also made him aware of the need for strong American leadership internationally and the threat China poses to this generation. Green has introduced 5 bills to hold China accountable: The Our Money in China Transparency Act, the Bring American Companies Home Act, the Protecting Federal Networks Act, the Secure Our Systems Against China’s Tactics Act, and the China Technology Transfer Control Act. He also introduced a resolution demanding China’s repayment of sovereign debt held by American families.
As a physician, Green recognizes life begins at conception and firmly advocates for the unborn. He introduced the Born-Alive Survivors Protection Act that requires medical attention for infants born during abortions. Green also brings the unique perspective of doctor, healthcare administrator, and cancer survivor to the issues surrounding rural healthcare in America. He introduced the bipartisan Rural Health Care Access Act and the Rural ER Access Act to cut regulation and improve emergency medical care in rural hospitals.
Congressman Green has won multiple awards for his work in Congress, including the American Freedom Fund’s Legislator of the Year Award for his work to empower veterans and the Guardian of Small Business award from the National Federation of Independent Business (NFIB). Green received a perfect A+ rating from the Susan B. Anthony List for his pro-life voting record. He also received the impressive distinction of being unanimously voted President of the Republican freshman class in the House of Representatives.
Green resides in Clarksville, Tenn., with his wife, Camilla. They are the proud parents of two grown children.
Personal
Full Name: Mark E. Green
Gender: Male
Family: Wife: Camilla; 2 Children: Alexa, Mitchell
Birth Date: 11/08/1964
Birth Place: Jacksonville, FL
Home City: Ashland City, TN
Religion: Christian
Source: Vote Smart
Education
MD, Wright State University, Boonshoft School of Medicine, 1995-1999
MC, Systems Management, University of Southern California, 1986-1987
BS, Quantitative Business Management, United States Military Academy at West Point, 1982-1986
Political Experience
Representative, United States House of Representatives, District 7, 2019-present
Senator, Tennessee State Senate, District 22, 2013-2019
Nominated by President Donald J. Trump, Secretary of the Army, United States Department of Defense, April 7, 2017
Professional Experience
Chief Executive Officer/Chairman, Align MD, 2016-present
Chief, Department of Emergency Medicine, Gateway Medical Center
Former Vice Chief of Staff, Gateway Medical Center
Served, United States Army
Chief Executive Officer/President, Linden Risk Management, 2016-2018
President, Align MD, 2010-2016
President/Chief Executive Officer, MD-Partners Professional Limited Liability Company, 2008-2015
Emergency Department Medical Director, Bay Medical Center, 2009-2010
Author, A Night with Saddam, 2009
President, Emergency Services Network, 2004-2008
Chief of Staff Elect, Gateway Medical Center, 2007-2008
Chief, Department of Emergency Medicine, Jennie Stuart Medical Center, 2007-2008
Offices
Washington, DC Office
2446 Rayburn HOB
Washington, DC 20515
Phone: (202) 225-2811
Clarksville Office
128 N. Second St. Suite 104
Clarksville, TN 37040
Phone: (931) 266-4483
Franklin Office
305 Public Square Suite 212
Franklin, TN 37064
Phone: (629) 223-6050
Contact
Email: Government
Web Links
Politics
Source: none
Election Results
To learn more, go to this wikipedia section in this post.
Finances
Source: Open Secrets
Committees
Rep. Mark Green serves on the following committees:
- Chairman of the Committee on Homeland Security
- Member of the House Foreign Affairs Committee.
- Member of the House Foreign Affairs Subcommittee on the Western Hemisphere
- Member of the House Foreign Affairs Subcommittee on the Indo-Pacific
Rep. Green was elected by his peers to serve as the President of the Republican Freshman class during the 116th Congress.
So far, Rep. Green joined the following caucuses:
- Congressional Bipartisan Rural Health Caucus
- Co-Chair of the Colorectal Cancer Caucus
- House Freedom Caucus
- Republican Study Committee
- Special Operations Forces Caucus
- GOP Doctor’s Caucus
- Pro-Life Caucus
- Prayer Caucus
- Military Family Caucus
- Military Veterans Caucus
- Congressional Army Caucus
- House Republican Israel Caucus
- Songwriters Caucus
- Values Action Team
- Taiwan Caucus
- Congressional Recording Arts and Sciences Caucus
New Legislation
Issues
Source: Government page
More Information
Services
Source: Government page
District
Source: Wikipedia
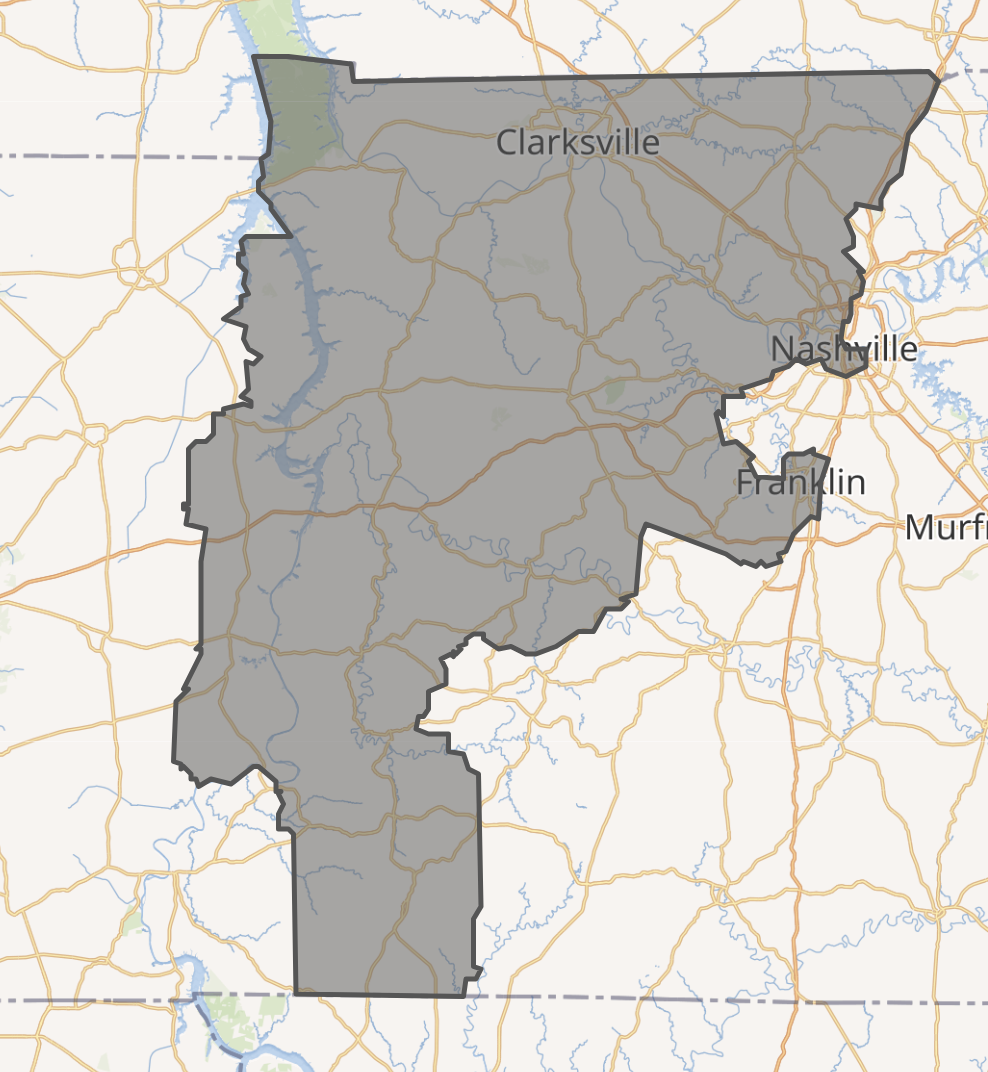 The 7th congressional district of Tennessee is a congressional district located in parts of Middle and West Tennessee. It has been represented by Republican Mark E. Green since January 2019. The seventh district has significant suburban and rural areas. Although most of the area is rural, more than half of the district’s vote is cast in either Montgomery County (Clarksville) or Williamson County (Franklin, Brentwood).
The 7th congressional district of Tennessee is a congressional district located in parts of Middle and West Tennessee. It has been represented by Republican Mark E. Green since January 2019. The seventh district has significant suburban and rural areas. Although most of the area is rural, more than half of the district’s vote is cast in either Montgomery County (Clarksville) or Williamson County (Franklin, Brentwood).
By most measures, Williamson County is the wealthiest county in the state and is usually ranked near the top nationally.[4]
The district has a very strong military presence, as it includes Tennessee’s share of Fort Campbell. Politically speaking, the area was secessionist and part of the Democrats’ “Solid South” for a century after the Civil War, excluding heavily Republican Unionist Highland Rim Wayne County. However, since being carried by George Wallace in 1968 it has become and remained one of the most Republican areas in Tennessee, and has not been represented by a Democrat since the early 1970s. The presence of Nashville’s suburbs gives it a character similar to those of most affluent suburban districts in much of the South until the mid-2000s. It has a strong social conservative bent; many of the state’s most politically active churches are either located here or draw most of their congregations from here.
The rural secessionist counties are similar demographically to the 8th district and returned to the Democrats until the 2000s; three of the five Tennessee counties won by George McGovern lie within this district. However, since the mid-2000s these counties have turned overwhelmingly Republican in all elections. The only area where Democrats currently compete on anything resembling an even basis is in Clarksville, which still occasionally elects Democrats to the state legislature.
Current
Wikipedia
Mark Edward Green (born November 8, 1964) is an American politician, physician, and retired U.S. Army surgeon who served as the U.S. representative for Tennessee’s 7th congressional district from 2019 until his resignation in 2025. A member of the Republican Party, Green chaired the Committee on Homeland Security from 2023 to 2025.[1] Before his election to Congress, he served in the Tennessee Senate, representing the 22nd district from 2013 to 2018.
After graduating from West Point, Green was an infantry officer. He then graduated from Boonshoft School of Medicine at Wright State University and became a flight surgeon, serving tours of duty in the War in Afghanistan and Iraq War. He wrote a book about his experience in Operation Red Dawn, in which Saddam Hussein was captured. After retiring from the military in 2006, Green became the CEO of a hospital emergency department staffing company.
Green first entered state politics in 2012 by defeating the Democratic incumbent Tim Barnes for a seat in the Tennessee Senate. In 2017, President Donald Trump nominated Green to serve as the United States secretary of the Army, but when comments Green had made about the LGBT community were revealed, he withdrew his nomination. When U.S. representative Marsha Blackburn announced her candidacy for the United States Senate in 2018, Green announced his candidacy to succeed her, and was elected in November of that year. He was re-elected in 2020 and 2022. In October 2023, he was a candidate for Speaker of the House of Representatives, but withdrew from the race on October 24.
On June 9, 2025, Green announced that he would be resigning after the passage of the One Big Beautiful Bill Act to take a job in the private sector.[2] His last day in office was on July 20, 2025.[3]
Military career
In 1986, Green graduated from the United States Military Academy, where he earned a Bachelor of Science in quantitative business management.[4][5] In 1987 he earned a master’s degree in systems management from the University of Southern California.[6] From 1987 to 1990, Green served as an infantry officer in the United States Army. His first duty assignment after graduation from the US Army Ranger School was with the 194th Armored Brigade at Fort Knox. There he served as a rifle platoon leader, scout platoon leader, and battalion adjutant for an infantry battalion. After the Infantry Officer’s Advance Course, then-Captain Green served with the 82nd Airborne Division[7] as an airborne battalion supply officer and rifle company commander.
Following a traumatic event in which a team of surgeons and critical care doctors saved his father’s life, Green requested that the Army send him to medical school. He attended the Boonshoft School of Medicine at Wright State University, graduating with a Doctor of Medicine in 1999.[6] He did his residency in emergency medicine at Fort Hood, Texas. After his residency, Green was selected to serve as the flight surgeon for the 160th Special Operations Aviation Regiment.[8]
As a special operations flight surgeon, Green served a tour of duty in the Afghanistan War and two tours of duty in the Iraq War. He was the special operations flight surgeon during Operation Red Dawn, the military operation that captured Saddam Hussein. Green interrogated Hussein for six hours.[4][9] After his military service, he authored a book, A Night With Saddam, detailing the capture and interrogation of Hussein and his service with the Army’s elite aviation unit.[7][10] Green was honorably discharged from the Army in 2006.[9][11]
For his service, Green was awarded the Bronze Star, the Meritorious Service Medal with two oak leaf clusters, the Army Commendation Medal with two oak leaf clusters, the Achievement Medal with three oak leaf clusters, the Air Medal with the V Device for valor under heavy enemy fire while rescuing British Special Operations forces wounded near Fallujah, and the Combat Medical Badge, among other awards. He also earned the Air Assault Badge and the Flight Surgeon Badge[4][7] during his service.
Civilian career
Green founded and served as chief executive officer of Align MD, a hospital emergency department management staffing company. Align MD provides staffing to emergency departments and hospital services in 50 hospitals in 10 states.[12] Green also founded Two Rivers Medical Foundation, which provides health care to underserved populations worldwide via medical mission trips, and operates a free medical clinic in his hometown and in Memphis, Tennessee.[12]
Green served on the boards of several for-profit companies, including American Physician Partners, Align MD, and Rural Physician Partners. Green is also a board member of the Middle Tennessee Boy Scouts of America. He has served on the advisory board of the political organization Latinos for Tennessee since 2015.
In 2015, Williamson College awarded Green an honorary Doctorate of Humanities.[12][13]
Following his resignation from the Congress in 2025, Green cofounded Prosimos, a corporation focused on increasing trade and economic development between the United States and Guyana.[14]
Political career
Tennessee State Senate
Green was first elected to the Tennessee Senate in 2012, defeating Democratic incumbent Tim Barnes.[7][15][16] He was rumored to be considering a challenge to Lamar Alexander in the 2014 U.S. Senate election,[17] but declined to do so.[18]
Green is most noteworthy for his legislation ending Tennessee’s Hall Income Tax, only the second time in US history a state has repealed an income tax.[19] He also co-sponsored a bill that eliminated the statute of limitations on rape cases where the DNA profile of the suspect is known.[20] Green received awards recognizing his many laws protecting veterans and small businesses.[21][22] He led the charge in Tennessee for automated technology in auto manufacturing, speaking at national conferences on the topic.[23]
In 2015, Green proposed a pilot program to test an innovative solution to health care. The idea was to give Medicaid patients a reduced amount of health care dollars on a swipe card, giving them choice and control. The incentive is that any dollars not spent go to the patient as an addition to their earned income check. SJR 88 passed and was signed by the governor. The request for a waiver to test the program is at CMS for approval.[24]
Green won the 2016 Republican primary 84% to 16% over Lori Smith of Clarksville, Tennessee.[25] In the general election, he defeated Democratic nominee David Cutting, 67% to 33%.
Nomination as U.S. Army Secretary
In April 2017, President Donald Trump nominated Green for United States Secretary of the Army.[26] Green was Trump’s second nominee for this position after his first nominee, Vincent Viola, withdrew from consideration.[27]
Green drew some opposition based on public comments about transgender people.[28] At a September 2016 Tea Party gathering in Chattanooga, Tennessee, Green said, “If you polled the psychiatrists, they’re going to tell you that transgender is a disease.”[29] He also supported a state law that limited access to public restrooms for transgender people to those matching their legal sex, not their gender identity, and told internet radio talk show host CJ Porter that he viewed his support of that law as part of his duty as a state senator to “crush evil”.[29][30]
Green also said that if school districts “want to have a bathroom that’s separate for all of the, you know, guys or gals with question marks” but were concerned the “AFL-CIO is going to sue you, well, I got your back.” It is assumed Green meant the American Civil Liberties Union (ACLU), not the American Federation of Labor and Congress of Industrial Organizations (AFL–CIO).[31] Green also said that he would “not tolerate” students learning about Muslim beliefs and practices.[32] Green added later that he doesn’t “think we should teach the Lord’s Prayer” in schools either. In a call for separation of church and state, he said, “Leave that to the churches, the synagogues, and the mosques.”[33]
Green withdrew his nomination on May 5, 2017.[34]
2018 Tennessee gubernatorial election
On January 4, 2017, Green filed paperwork to run for governor in the 2018 gubernatorial election.[35] But in late 2017, when 7th District Representative Marsha Blackburn announced her candidacy for the United States Senate, Green announced he was running for the open congressional seat.[36] His state senate district included almost all of the northeastern part of the congressional district.
U.S. House of Representatives
Elections
2018
Green became the Republican nominee for the 2018 U.S. House of Representatives election in Tennessee’s 7th congressional district after running unopposed for the nomination.[37] His State Senate district included much of the northern part of the congressional district. Green won the general election in November and took office in January 2019.
2020
In the 2020 Republican primary, Green was unopposed. On November 3, he defeated Democratic nominee Kiran Sreepada and two independents with 69.9% of the vote.
2022
In the 2022 Republican primary, Green was unopposed. On November 8, he defeated Democratic nominee Odessa Kelly with 60.0% of the vote.
2024
In the 2024 Republican primary, Green was unopposed. On election day, he defeated Democratic nominee Megan Barry with 59.5% of the vote.
Tenure
After incumbent U.S. Senator Lamar Alexander announced he would not seek reelection in 2020, Green was considered a likely candidate for the seat. But on July 11, 2019, he announced that he would not be a candidate.[38]
In late February 2021, Green and a dozen other Republican House members skipped votes and enlisted others to vote for them, citing the ongoing COVID-19 pandemic. But he and the other members were actually attending the Conservative Political Action Conference, which was held at the same time as their slated absences.[39] In response, the Campaign for Accountability, an ethics watchdog group, filed a complaint with the House Committee on Ethics and requested an investigation into Green and the other lawmakers.[40]
In August 2022, Business Insider reported that Green had violated the Stop Trading on Congressional Knowledge (STOCK) Act of 2012, a federal transparency and conflict-of-interest law, by failing to properly disclose a purchase of stock in NGL Energy Partners worth between $100,000 and $250,000.[41] In a closed-door GOP meeting in 2024, Green called Secretary of Homeland Security Alejandro Mayorkas “a reptile with no balls.”[42]
On February 14, 2024, Green announced that he would not run for re-election, but he reversed this decision on February 29.[43] On July 29, 2024, Green was announced as one of seven Republican members of a bipartisan task force investigating the attempted assassination of Donald Trump.[44]
On June 9, 2025, Green announced his intent to resign from Congress following the passage of the One Big Beautiful Bill Act due to a private sector employment opportunity “too exciting to pass up”. However, he said he will remain in Congress until “the House votes once again on the reconciliation package”, setting a potentially unprecedented case of conflict of interest of being employed by a private entity while voting in Congress.[45] On July 4, 2025 it was announced that he would resign on July 20.[3] The 7th district special election to elect his replacement, on December 2, 2025, was won by Republican Matt Van Epps.
Committee assignments
Caucus memberships
- Freedom Caucus[50]
- Republican Study Committee[51]
- Special Operations Forces Caucus
- GOP Doctor’s Caucus
- Pro-Life Caucus
- Prayer Caucus
- Military Family Caucus
- Military Veterans Caucus
- Congressional Army Caucus
- Congressional Taiwan Caucus[52]
- House Republican Israel Caucus
- Songwriters Caucus
- Values Action Team
- Congressional Recording Arts and Sciences Caucus
Political positions

Abortion
Green opposes abortion. In a 2019 op-ed, he wrote, “modern science has revealed that mother and baby are, in fact, two separate persons—long before the baby is born” and argued that “a child becomes a child at conception”.[53]
Climate change
Green has expressed skepticism about the scientific consensus on climate change. During a town hall meeting, he acknowledged that carbon dioxide levels are increasing but questioned whether they are causing global warming. He stated, “I’m not yet convinced that the science is proving that we’re warming, but I am very convinced that we have aerial fertilization going on, and if we continue to cut trees in Brazil and other places, we’re going to hurt ourselves, and then we will have warming.” He also highlighted concerns about deforestation’s role in climate change.[54]
Creationism
Green rejects the theory of evolution, which is consensus in biology; in a 2015 lecture he used creationist reasoning such as “irreducible complexity“.[55]
2020 election
In December 2019, Green voted against the articles of impeachment in the first impeachment of Donald Trump.[56]
In December 2020, Green was one of 126 Republican members of the House of Representatives to sign an amicus brief in support of Texas v. Pennsylvania, a lawsuit filed at the United States Supreme Court contesting the results of the 2020 presidential election, in which Joe Biden prevailed over incumbent Donald Trump.[57] The Supreme Court declined to hear the case on the basis that Texas lacked standing under Article III of the Constitution to challenge the results of an election held by another state.[58][59][60]
Vaccines
In 2018, as a congressman-elect, Green said at a constituent meeting, “there is some concern that the rise in autism is the result of the preservatives that are in our vaccines”, a claim that has been repeatedly debunked by scientific studies and rejected by medical organizations such as the American Academy of Pediatrics.[61]
Transgender People
Green suggested military should not allow transgender troops due to “immorality”, and claimed without evidence that physicians agree that “transgenderism” is a “disease”.[45]
Welfare
Green has suggested that welfare interrupts “the opportunity for people to come to a saving knowledge of who God is”, and Americans should rely on God instead of governmental assistance.[62]
2024 Republican primary
Green was named as part of the Trump campaign’s Tennessee leadership team.[63]
Israel-Palestine conflict
Green voted to support Israel following the October 7 attacks.[64][65]
Personal life
Green and his wife, Camie, have two children. For most of his tenure in the state senate, he lived in Ashland City, Cheatham County, south of Clarksville and west of Nashville.[8][66] He has since moved to Clarksville.
In August 2024, Green filed for a divorce from his wife of nearly 36 years, citing irreconcilable differences.[67] In a text message circulated among House Republicans, his wife later accused him of having an affair with a younger woman working as a political reporter for Axios. However, she later admitted to misidentifying the woman after receiving a cease and desist letter from the company.[68] The actual woman involved anonymously confirmed the affair to Politico in an effort to clear the reporter’s name.[69]
Electoral history
Tennessee State Senate
| Primary election | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Party | Candidate | Votes | % | |||
| Republican | Mark Green | 4,849 | 100.00% | |||
| Total votes | 4,849 | 100.00% | ||||
| General election | ||||||
| Republican | Mark Green | 31,963 | 53.08% | |||
| Democratic | Tim Barnes (incumbent) | 28,257 | 46.92% | |||
| Total votes | 60,220 | 100.00% | ||||
| Republican gain from Democratic | ||||||
| Primary election | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Party | Candidate | Votes | % | |
| Republican | Mark Green (incumbent) | 6,183 | 84.17% | |
| Republican | Lori L. Smith | 1,163 | 15.83% | |
| Total votes | 7,346 | 100.00% | ||
| General election | ||||
| Republican | Mark Green (incumbent) | 41,497 | 67.04% | |
| Democratic | David L. Cutting | 20,406 | 32.96% | |
| Total votes | 61,903 | 100.00% | ||
| Republican hold | ||||
U.S. House
| Primary election | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Party | Candidate | Votes | % | |
| Republican | Mark Green | 83,314 | 100.00% | |
| Total votes | 83,314 | 100.00% | ||
| General election | ||||
| Republican | Mark Green | 170,071 | 66.86% | |
| Democratic | Justin Kanew | 81,661 | 32.10% | |
| Independent | Lenny Ladner | 1,582 | 0.62% | |
| Independent | Brent Legendre | 1,070 | 0.42% | |
| Total votes | 254,384 | 100.00% | ||
| Republican hold | ||||
| Primary election | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Party | Candidate | Votes | % | |
| Republican | Mark Green (incumbent) | 73,540 | 100.00% | |
| Total votes | 73,540 | 100.00% | ||
| General election | ||||
| Republican | Mark Green (incumbent) | 245,188 | 69.93% | |
| Democratic | Kiran Sreepada | 95,839 | 27.33% | |
| Independent | Ronald Brown | 7,603 | 2.17% | |
| Independent | Scott Vieira | 2,005 | 0.57% | |
| Total votes | 350,635 | 100.00% | ||
| Republican hold | ||||
| Primary election | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Party | Candidate | Votes | % | |
| Republican | Mark Green (incumbent) | 48,968 | 100.00% | |
| Total votes | 48,968 | 100.00% | ||
| General election | ||||
| Republican | Mark Green (incumbent) | 108,421 | 59.96% | |
| Democratic | Odessa Kelly | 68,973 | 38.14% | |
| Independent | Steven J. Hooper | 3,428 | 1.90% | |
| Total votes | 180,822 | 100.0% | ||
| Republican hold | ||||
| Primary election | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Party | Candidate | Votes | % | |
| Republican | Mark Green (incumbent) | 31,871 | 100.00% | |
| Total votes | 31,871 | 100.00% | ||
| General election | ||||
| Republican | Mark Green (incumbent) | 191,992 | 59.50% | |
| Democratic | Megan Barry | 122,764 | 38.05% | |
| Independent | Shaun Greene | 7,900 | 2.45% | |
| Total votes | 322,656 | 100.00% | ||
| Republican hold | ||||
References
- ^ “Freedom Caucus Republican to Lead Homeland Security Committee”. Bloomberg Government. January 9, 2023. Retrieved January 9, 2023.
- ^ “Rep. Mark Green Retires from the U.S. House of Representatives”. June 9, 2025. Retrieved June 9, 2025.
- ^ a b Doherty, Erin (July 5, 2025). “Rep. Mark Green resigns from Congress, leaving Speaker Johnson with an even narrower Republican majority in the House”. CNBC. Retrieved July 6, 2025.
- ^ a b c “Senator Green to speak to Wilson County Conservative Republicans”. Thechronicleofmtjuliet.com. July 23, 2013. Archived from the original on October 29, 2013. Retrieved August 13, 2013.
- ^ “PN1038 – Army”. U.S. Congress. May 2, 1986. Retrieved April 8, 2017.
- ^ a b “Mark Green’s Biography”. Vote Smart. Retrieved January 6, 2019.
- ^ a b c d Bonecutter, Hank (November 22, 2011). “Mark Green to run for State Senate » Clarksville, TN Online”. Clarksvilleonline.com. Retrieved August 13, 2013.
- ^ a b “Tennessee State Senator Mark Green Launches new website”. Clarksvilleonline.com. February 2, 2013. Retrieved August 13, 2013.
- ^ a b Everett, Laurie (July 26, 2013). “State senator talks about his role in Saddam Hussein’s capture”. Lebanon Democrat. Archived from the original on October 23, 2013. Retrieved August 13, 2013.
- ^ Jordan, Elise (December 13, 2009). “A Sleepover With Saddam”. Daily Beast.
- ^ “Congressman Mark Green”. Combat Veterans for Congress.
- ^ a b c “Dr. Mark Green for Tennessee”. Retrieved April 26, 2017.
- ^ “Keynote Speaker Also Proud Military Veteran”. Williamson College. Archived from the original on July 31, 2016. Retrieved March 5, 2016.
- ^ Taylor, Sarah Grace (September 18, 2025). “Ex-Congressman Mark Green discusses his new business, Prosimos”. Nashville Banner. Retrieved December 2, 2025.
- ^ Hicks, Mark (November 7, 2012). “Republican Mark Green victorious over incumbent Sen. Barnes”. The Tennessean. Retrieved August 13, 2013.
- ^ Bonecutter, Hank (December 21, 2012). “Tennessee State Senator Elect Mark Green Introduces First Bill » Clarksville, TN Online”. Clarksvilleonline.com. Retrieved August 13, 2013.
- ^ Garrison, Joey (July 8, 2013). “Political Notebook: Lawmaker sparks buzz he may challenge Alexander”. The Tennessean. Retrieved August 13, 2013.
- ^ Humphrey, Tom (July 14, 2013). “Political notebook: Ramsey, Campfield reject entreaties to oppose Sen. Alexander”. Knoxville News Sentinel. Retrieved July 13, 2015.
- ^ Harvath, Joe (May 15, 2016). “Hall Tax repeal will benefit Tennessee’s economy”. The Tennessean. Retrieved November 10, 2010.
- ^ “Under New Legislation, Tennessee Prosecutors Can Stop Statute of Limitations When Suspect’s DNA Profile is Known”. Tennessee Senate Republicans, via Wayback Machine. Archived from the original on November 10, 2017. Retrieved January 6, 2019.
- ^ Erwin (November 2016). “Senator Mark Green receives NFIB award”. Clarksville Now. Retrieved November 10, 2017.
- ^ “A First for Tennessee Veterans Courts”. Tennessee Senate Republicans. April 23, 2015. Retrieved November 10, 2017.
- ^ “Senator Mark Green speaks in national forum on autonomous cars, job creation”. The Leaf-Chronicle. May 20, 2016. Retrieved November 10, 2017.
- ^ Rech, Marcus (April 6, 2016). “Tennessee Senate Unanimously Approves Medicaid opt-out Program”. The Heartland Institute. Retrieved November 17, 2017.
- ^ Ingersoll, Stephanie (August 4, 2016). “Green wins GOP nomination for Senate race”. The Leaf-Chronicle. Retrieved November 17, 2017.
- ^ Collins, Michael (April 7, 2017). “President Trump nominates Tennessee state Sen. Mark Green for Army secretary”. USA Today. Retrieved January 23, 2019.
- ^ Palmeri, Tara; O’Brien, Connor (March 17, 2017). “Sources: Trump to nominate former flight surgeon Mark Green as Army secretary”. Politico. Retrieved May 3, 2017.
- ^ “LGBT advocates ‘deeply concerned’ with Mark Green nomination as Army secretary”. The Tennessean. Retrieved December 14, 2018.
- ^ a b Collins, Michael (May 2, 2017). “Sen. John McCain: Army Secretary Nominee’s past comments ‘very concerning’“. USA Today. Retrieved May 3, 2017.
- ^ Terkel, Amanda (April 20, 2017). “Trump Pick For Army Secretary Says He Opposes Transgender Equality Because He Must ‘Crush Evil’“. Huffington Post. Retrieved December 26, 2017.
- ^ “Trump derelict in filling key military defense roles”. MSNBC. Retrieved May 6, 2017.
- ^ Collins, Michael (April 16, 2017). “Muslims, LGBT Advocates prepare to fight Mark Green’s nomination as Army Secretary”. The Tennessean. Retrieved May 3, 2017.
- ^ “Sen. Mark Green discusses Sec. Of Army nomination, opioid crisis, illegal immigration and more – Franklin Home Page”. Archived from the original on September 5, 2019. Retrieved December 4, 2019.
- ^ “NBC Twitter”. NBC News. May 5, 2017. Retrieved May 5, 2017.
- ^ “Sen. Mark Green launches bid for governor, hires Trump’s state director”. The Tennessean. Retrieved January 5, 2017.
- ^ “Blackburn for Senate, Green for House”. Nashville Post. October 5, 2017. Retrieved October 17, 2017.
- ^ Almukhtar, Sarah (August 2, 2018). “Tennessee Primary Election Results”. The New York Times. Retrieved August 3, 2018.
- ^ Allison, Natalie; Ebert, Joel (July 11, 2019). “US Rep. Mark Green says he won’t run for US Senate in 2020”. The Tennessean. Retrieved January 23, 2020.
- ^ Bash, Dana; Raju, Manu; Diaz, Daniella; Fox, Lauren; Warren, Michael (February 26, 2021). “More than a dozen Republicans tell House they can’t attend votes due to ‘public health emergency.’ They’re slated to be at CPAC”. CNN. Retrieved March 10, 2021.
- ^ Grayer, Annie; Diaz, Daniella (March 10, 2021). “First on CNN: Watchdog group requests investigation into 13 GOP lawmakers for misusing proxy voting”. CNN. Retrieved March 10, 2021.
- ^ Hall, Madison (August 2, 2022). “Republican Rep. Mark Green of Tennessee violated a federal conflict-of-interest law with a late disclosure of a stock purchase worth up to $250,000”. Business Insider. Archived from the original on February 5, 2024. Retrieved July 17, 2024.
- ^ Carney, Jordain; Beavers, Olivia (February 6, 2024). “House GOP’s Mayorkas impeachment effort on life support”. Politico.
- ^ Lesniewski, Niels (February 29, 2024). “Homeland Chairman Green reverses course, will seek reelection”. Roll Call. Retrieved February 29, 2024.
- ^ “House leaders announce members of bipartisan task force investigating Trump assassination attempt”. CBS News. July 29, 2024. Retrieved July 31, 2024.
- ^ a b Legum, Judd. “Congressman accepts private-sector job, says he will remain in Congress indefinitely”. popular.info. Retrieved October 12, 2025.
- ^ “Rep. Green Selected Chairman of House Homeland Security Committee”. Congressman Mark Green. January 9, 2023. Retrieved March 14, 2023.
- ^ “Full Committee”. Committee on Foreign Affairs. Retrieved March 14, 2023.
- ^ “Subcommittee on Indo-Pacific”. Committee on Foreign Affairs. Retrieved March 14, 2023.
- ^ “Subcommittee on Western Hemisphere”. Committee on Foreign Affairs. Retrieved March 14, 2023.
- ^ McPherson, Lindsey (October 31, 2018). “As House Republicans Brace for Losses, Freedom Caucus Prepares for Growth”. rollcall.com. Archived from the original on October 18, 2019. Retrieved November 17, 2018.
Potential recruits receiving Freedom Fund money this cycle include Chip Roy in Texas’ 21st District, Yvette Herrell in New Mexico’s 2nd District, Mark Harris in North Carolina’s 9th District, Greg Steube in Florida’s 17th District, Denver Riggleman in Virginia’s 5th District, Mark Green in Tennessee’s 7th District, Russ Fulcher in Idaho’s 1st District, Ron Wright in Texas’ 6th District and Ben Cline in Virginia’s 6th District.
- ^ “Member List”. Republican Study Committee. Retrieved December 21, 2017.
- ^ “Congressional Taiwan Caucus”. Congressman Brad Sherman. Retrieved August 12, 2025.
- ^ Mark Green, Scientific findings have the potential to change the way abortion is viewed, The Hill (January 17, 2019).
- ^ “Mark Green talks climate change, medical marijuana and student loan debt during town hall meeting – Brentwood Home Page”. Archived from the original on April 28, 2019. Retrieved February 11, 2019.
- ^ “Trump Army secretary pick gave a lecture arguing against the theory of evolution”. CNN. May 1, 2017.
- ^ Ebert, Joel (December 18, 2019). “Tennessee’s House members split along party lines on impeaching President Donald Trump”. The Tennessean. Retrieved January 23, 2020.
- ^ Blood, Michael R.; Riccardi, Nicholas (December 5, 2020). “Biden officially secures enough electors to become president”. AP News. Archived from the original on December 8, 2020. Retrieved December 12, 2020.
- ^ Liptak, Adam (December 11, 2020). “Supreme Court Rejects Texas Suit Seeking to Subvert Election”. The New York Times. ISSN 0362-4331. Archived from the original on December 11, 2020. Retrieved December 12, 2020.
- ^ “Order in Pending Case” (PDF). Supreme Court of the United States. December 11, 2020. Archived (PDF) from the original on December 11, 2020. Retrieved December 11, 2020.
- ^ Diaz, Daniella. “Brief from 126 Republicans supporting Texas lawsuit in Supreme Court”. CNN. Archived from the original on December 12, 2020. Retrieved December 11, 2020.
- ^ Allison, Natalie. “Tennessee U.S. Rep.-elect Mark Green alleges vaccines may cause autism, questions CDC data”. The Tennessean. Retrieved January 22, 2021.
- ^ West, Emily R. “Group criticizes Sen. Mark Green over remarks about government programs and God”. The Tennessean. Retrieved October 12, 2025.
- ^ Metzger, Bryan; Saddiq, Omar (February 13, 2023). “Most Republicans are on the fence about Trump’s 2024 re-election bid. Here are the few elected officials backing him so far”. Business Insider. Retrieved February 13, 2023.
- ^ Demirjian, Karoun (October 25, 2023). “House Declares Solidarity With Israel in First Legislation Under New Speaker”. The New York Times. ISSN 0362-4331. Retrieved October 30, 2023.
- ^ Washington, U. S. Capitol Room H154; p:225-7000, DC 20515-6601 (October 25, 2023). “Roll Call 528 Roll Call 528, Bill Number: H. Res. 771, 118th Congress, 1st Session”. Office of the Clerk, U.S. House of Representatives. Retrieved October 30, 2023.
{{cite web}}: CS1 maint: numeric names: authors list (link) - ^ Green’s listing at Tennessee State Senate page
- ^ “Tennessee US Rep. Mark Green files for divorce after 35 years”. State Affairs. Retrieved August 27, 2024.
- ^ Taylor, Sarah Grace (September 13, 2024). “Rep. Mark Green Accused by Wife of Affair with Younger Woman”. Nashville Banner. Retrieved September 13, 2024.
- ^ Bade, Rachael (September 13, 2024). “GOP lawmaker’s wife accuses him of an affair — and points the finger at the wrong woman”. Politico. Retrieved September 13, 2024.
- ^ “State of Tennessee – August 2, 2012 – Republican Primary” (PDF). Secretary of State of Tennessee. August 29, 2012. Retrieved June 19, 2025.
- ^ “State of Tennessee – November 6, 2012 – General Election” (PDF). Secretary of State of Tennessee. December 5, 2012. Retrieved June 19, 2025.
- ^ “State of Tennessee – August 4, 2016 – Republican Primary” (PDF). Secretary of State of Tennessee. September 1, 2016. Retrieved June 19, 2025.
- ^ “State of Tennessee – November 8, 2016 – State General” (PDF). Secretary of State of Tennessee. December 13, 2016. Retrieved June 19, 2025.
- ^ “State of Tennessee – Totals – August 2, 2018 – Republican Primary” (PDF). Secretary of State of Tennessee. August 30, 2018. Retrieved June 19, 2025.
- ^ “State of Tennessee – Totals – November 6, 2018 – State General” (PDF). Secretary of State of Tennessee. Retrieved June 19, 2025.
- ^ “State of Tennessee – August 6, 2020 Republican Primary” (PDF). Secretary of State of Tennessee.
- ^ “State of Tennessee – November 3, 2020 – State General” (PDF). Secretary of State of Tennessee. December 2, 2020. Retrieved June 19, 2025.
- ^ “State of Tennessee Republican Primary” (PDF). Secretary of State of Tennessee. September 1, 2022. Retrieved November 10, 2022.
- ^ State of Tennessee General Election Results, November 8, 2022, Results By Office (PDF). Secretary of State of Tennessee (Report). December 13, 2022. Retrieved December 24, 2022.
- ^ “State of Tennessee – August 1, 2024 – Republican Primary” (PDF). Secretary of State of Tennessee. August 29, 2024. Retrieved June 19, 2025.
- ^ “State of Tennessee – Totals – November 5, 2024 – State General” (PDF). Secretary of State of Tennessee. December 2, 2024. p. 2. Archived (PDF) from the original on December 4, 2024. Retrieved February 4, 2025.
External links
- Congressman Mark E. Green official U.S. House website
- Mark E. Green for Congress Archived December 17, 2018, at the Wayback Machine
- Biography at the Biographical Directory of the United States Congress
- Financial information (federal office) at the Federal Election Commission
- Legislation sponsored at the Library of Congress
- Profile at Vote Smart
- Appearances on C-SPAN




