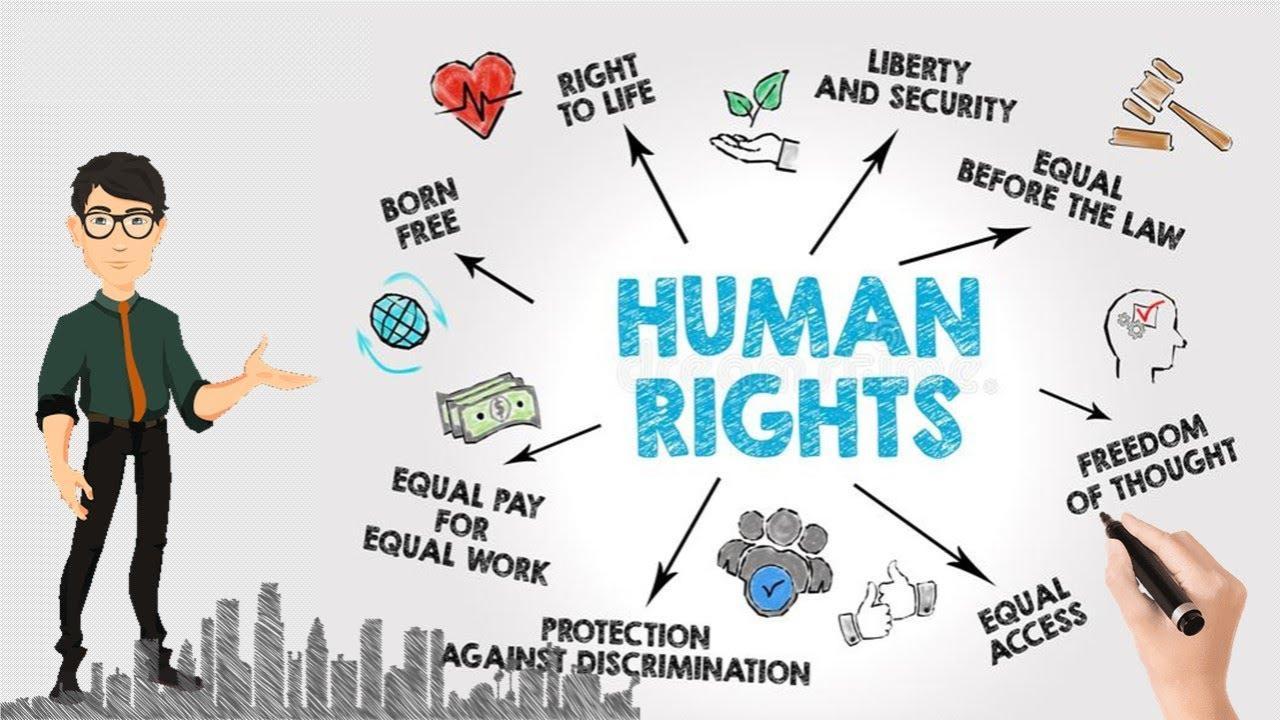
Human rights are rights inherent to all human beings, regardless of race, sex, nationality, ethnicity, language, religion, or any other status. Human rights include the right to life and liberty, freedom from slavery and torture, freedom of opinion and expression, the right to work and education, and many more.
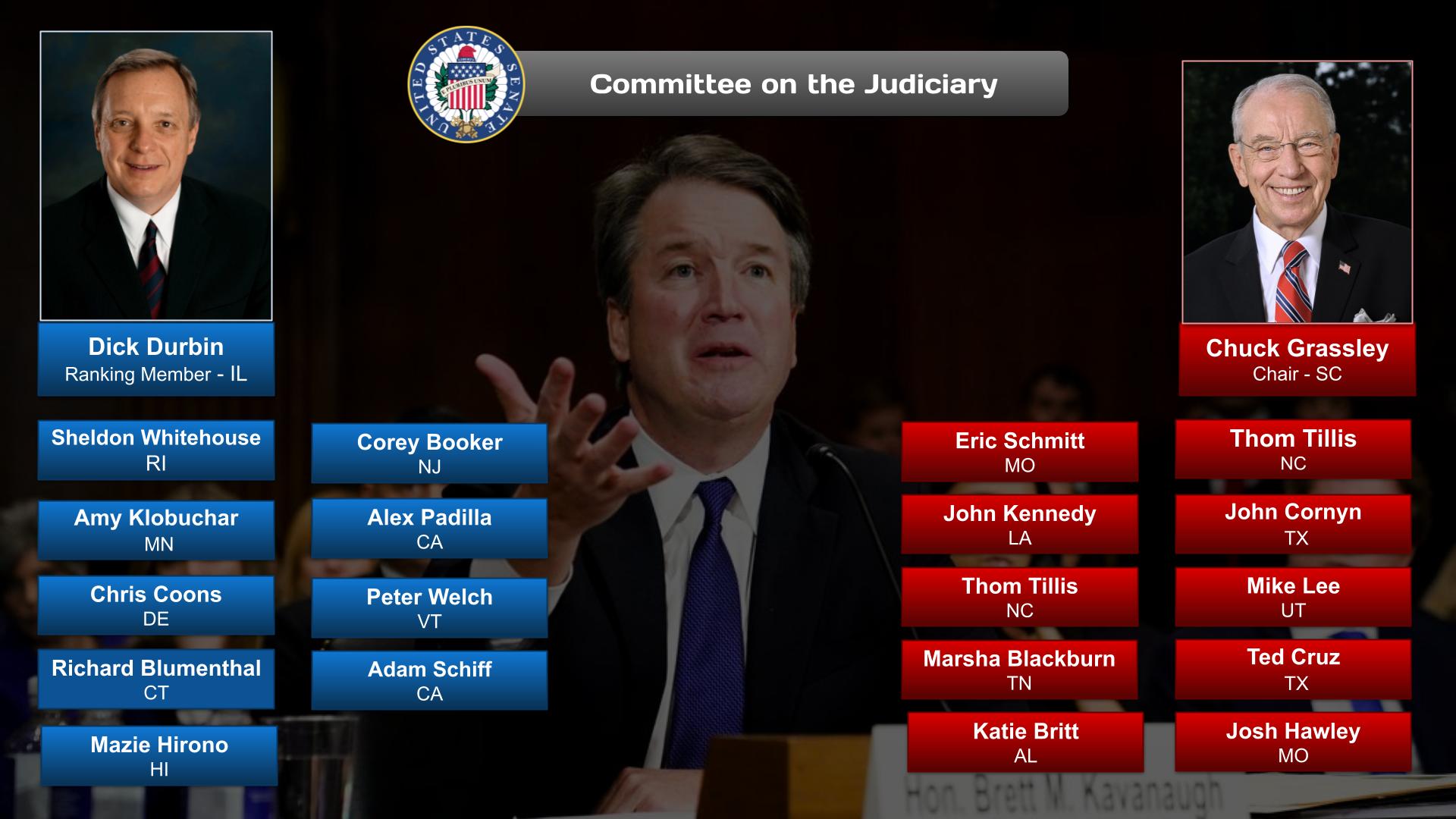
- There are many issues related to Human Rights that Congress is looking to address with legislation. In the ‘About’ section of this post is an overview of the issues and potential solutions, party positions, and web links. Other sections have information on relevant committees, chairs, & caucuses; departments & agencies; and the judiciary, nonpartisan & partisan organizations, and a wikipedia entry.
- To participate in ongoing forums, ask the post’s curators questions, and make suggestions, scroll to the ‘Discuss’ section at the bottom of each post or select the “comment” icon.
The Human Rights category has related posts and three posts on issues of particular focus: Abortion, Gun Rights, and Discrimination.
TED-Ed – 30/10/2012 (03:30)
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=yYEfLm5dLMQ
Daily, Americans exercise their rights secured by the Constitution. The most widely discussed and debated part of the Constitution is known as the Bill of Rights. Belinda Stutzman provides a refresher course on exactly what the first ten amendments grant each and every American citizen.
Lesson by Belinda Stutzman, animation by Jacques Khouri.
OnAir Post: Human Rights