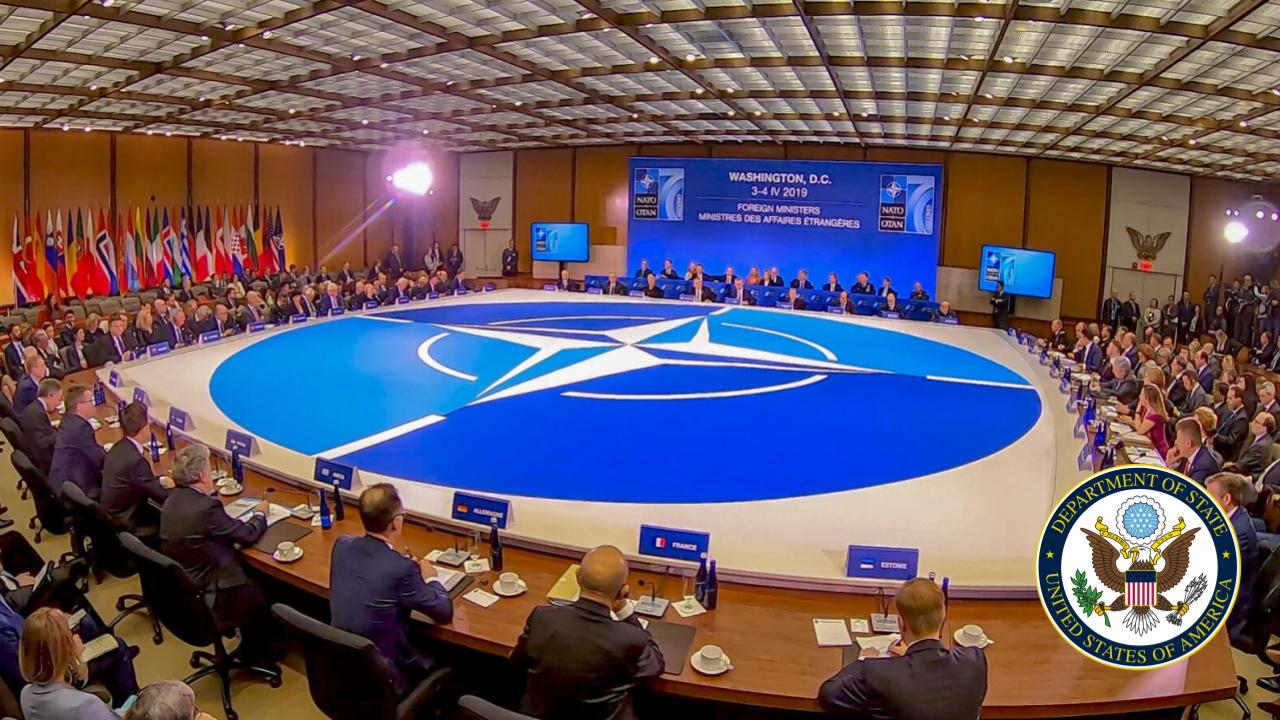
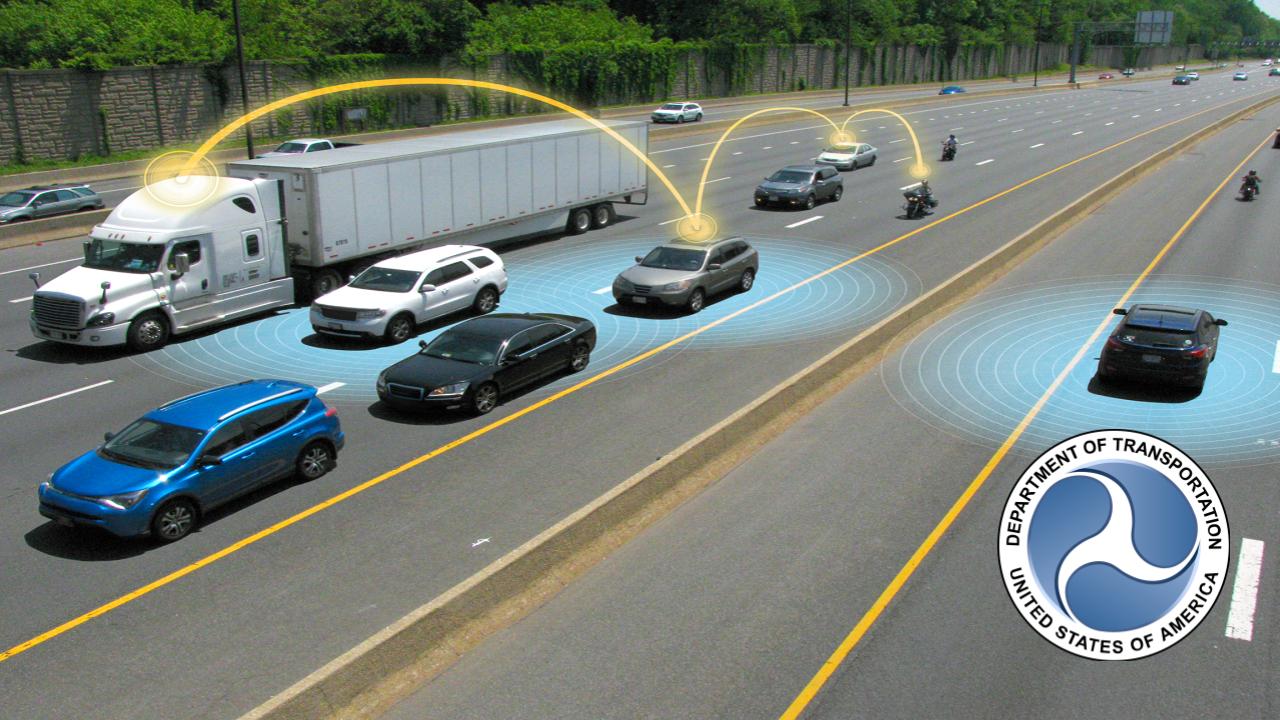
The United States federal executive departments are the principal units of the executive branch of the federal government of the United States. They are analogous to ministries common in parliamentary or semi-presidential systems but (the United States being a presidential system) they are led by a head of government who is also the head of state.
The executive departments are the administrative arms of the president of the United States. There are currently 15 executive departments.
To view feature image in large screen mode (especially to see what the initials stand for), select the post then click on image to enlarge.
OnAir Post: US Departments