Legislative definitions of an agency of the federal government of the United States are varied, and even contradictory. The official United States Government Manual offers no definition. While the Administrative Procedure Act definition of “agency” applies to most executive branch agencies, Congress may define an agency however it chooses in enabling legislation, and through subsequent litigation often involving the Freedom of Information Act and the Government in the Sunshine Act. These further cloud attempts to enumerate a list of agencies.
The majority of the independent agencies of the United States government are also classified as executive agencies (they are independent in that they are not subordinated under a Cabinet position). There are a small number of independent agencies that are not considered part of the executive branch, such as the Congressional Research Service and the United States Sentencing Commission, which are legislative and judicial agencies, respectively.
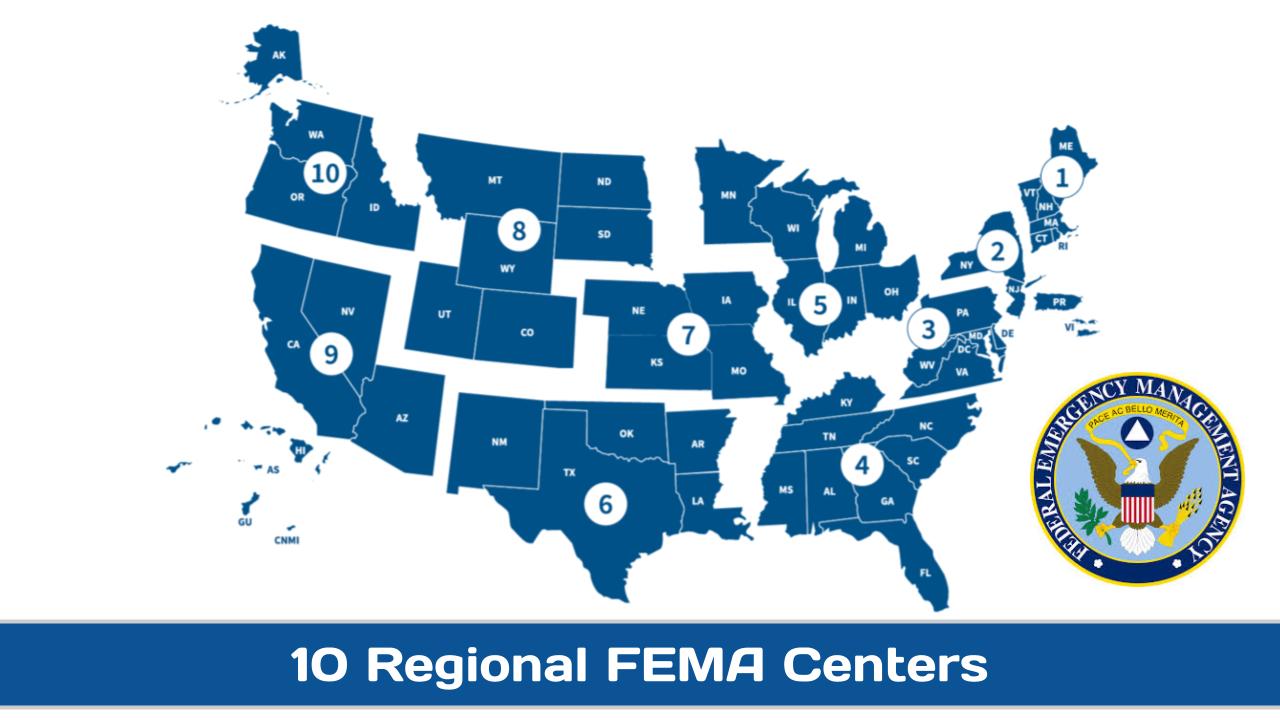
To view feature image in large screen mode (especially to see what the initials stand for), select the post then click on image to enlarge.
Source: Wikipedia
OnAir Post: Key US Agencies